Page 1912 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1912
1692 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
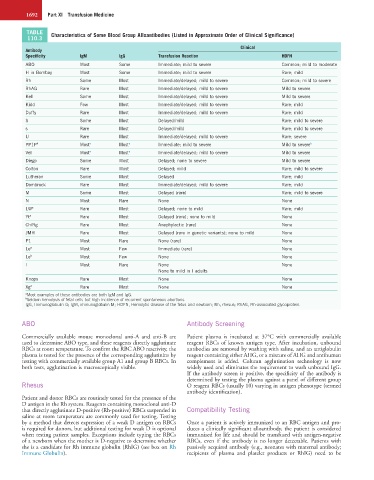
TABLE Characteristics of Some Blood Group Alloantibodies (Listed in Approximate Order of Clinical Significance)
110.3
Clinical
Antibody
Specificity IgM IgG Transfusion Reaction HDFN
ABO Most Some Immediate; mild to severe Common; mild to moderate
H in Bombay Most Some Immediate; mild to severe Rare; mild
Rh Some Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Common; mild to severe
RhAG Rare Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Mild to severe
Kell Some Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Mild to severe
Kidd Few Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Rare; mild
Duffy Rare Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Rare; mild
S Some Most Delayed/mild Rare; mild to severe
s Rare Most Delayed/mild Rare; mild to severe
U Rare Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Rare; severe
PP1P k Most a Most a Immediate; mild to severe Mild to severe b
Vel Most a Most a Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Mild to severe
Diego Some Most Delayed; none to severe Mild to severe
Colton Rare Most Delayed; mild Rare; mild to severe
Lutheran Some Most Delayed Rare; mild
Dombrock Rare Most Immediate/delayed; mild to severe Rare; mild
M Some Most Delayed (rare) Rare; mild to severe
N Most Rare None None
LW a Rare Most Delayed; none to mild Rare; mild
Yt a Rare Most Delayed (rare); none to mild None
Ch/Rg Rare Most Anaphylactic (rare) None
JMH Rare Most Delayed (rare in genetic variants); none to mild None
P1 Most Rare None (rare) None
Le a Most Few Immediate (rare) None
Le b Most Few None None
I Most Rare None None
None to mild in I adults
Knops Rare Most None None
Xg a Rare Most None None
a Most examples of these antibodies are both IgM and IgG.
b Seldom hemolysis of fetal cells but high incidence of recurrent spontaneous abortions.
IgG, Immunoglobulin G; IgM, immunoglobulin M; HDFN, Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn; Rh, rhesus; RhAG, Rh-associated glycoprotein.
ABO Antibody Screening
Commercially available mouse monoclonal anti-A and anti-B are Patient plasma is incubated at 37°C with commercially available
used to determine ABO type, and these reagents directly agglutinate reagent RBCs of known antigen type. After incubation, unbound
RBCs at room temperature. To confirm the RBC ABO reactivity, the antibodies are removed by washing with saline, and an antiglobulin
plasma is tested for the presence of the corresponding agglutinins by reagent containing either AHG, or a mixture of AHG and antihuman
testing with commercially available group A1 and group B RBCs. In complement is added. Column agglutination technology is now
both tests, agglutination is macroscopically visible. widely used and eliminates the requirement to wash unbound IgG.
If the antibody screen is positive, the specificity of the antibody is
determined by testing the plasma against a panel of different group
Rhesus O reagent RBCs (usually 10) varying in antigen phenotype (termed
antibody identification).
Patient and donor RBCs are routinely tested for the presence of the
D antigen in the Rh system. Reagents containing monoclonal anti-D
that directly agglutinate D-positive (Rh-positive) RBCs suspended in Compatibility Testing
saline at room temperature are commonly used for testing. Testing
by a method that detects expression of a weak D antigen on RBCs Once a patient is actively immunized to an RBC antigen and pro-
is required for donors, but additional testing for weak D is optional duces a clinically significant alloantibody, the patient is considered
when testing patient samples. Exceptions include typing the RBCs immunized for life and should be transfused with antigen-negative
of a newborn when the mother is D-negative to determine whether RBCs, even if the antibody is no longer detectable. Patients with
she is a candidate for Rh immune globulin (RhIG) (see box on Rh passively acquired antibody (e.g., neonates with maternal antibody;
Immune Globulin). recipients of plasma and platelet products or RhIG) need to be