Page 1966 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1966
1740 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
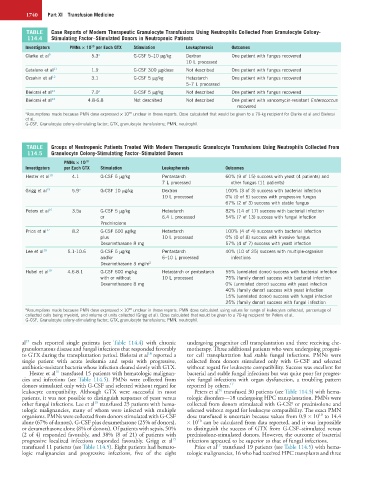
TABLE Case Reports of Modern Therapeutic Granulocyte Transfusions Using Neutrophils Collected From Granulocyte Colony-
114.4 Stimulating Factor–Stimulated Donors in Neutropenic Patients
Investigators PMNs × 10 per Each GTX Stimulation Leukapheresis Outcomes
10
Clarke et al 9 5.3 a G-CSF 5–10 µg/kg Dextran One patient with fungus recovered
10 L processed
Catalano et al 11 1.9 G-CSF 300 µg/dose Not described One patient with fungus recovered
Ozsahin et al 12 3.1 G-CSF 5 µg/kg Hetastarch One patient with fungus recovered
5–7 L processed
Bielorai et al 13 7.0 a G-CSF 5 µg/kg Not described One patient with fungus recovered
Bielorai et al 14 4.8-6.8 Not described Not described One patient with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
recovered
10
a Assumptions made because PMN dose expressed × 10 unclear in these reports. Dose calculated that would be given to a 70-kg recipient for Clarke et al and Bielorai
et al.
G-CSF, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GTX, granulocyte transfusions; PMN, neutrophil.
TABLE Groups of Neutropenic Patients Treated With Modern Therapeutic Granulocyte Transfusions Using Neutrophils Collected From
114.5 Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor–Stimulated Donors
PMNs × 10
10
Investigators per Each GTX Stimulation Leukapheresis Outcomes
Hester et al 10 4.1 G-CSF 5 µg/kg Pentastarch 60% (9 of 15) success with yeast (4 patients) and
7 L processed other fungus (11 patients)
Grigg et al 15 5.9 a G-CSF 10 µg/kg Dextran 100% (3 of 3) success with bacterial infection
10 L processed 0% (0 of 5) success with progressive fungus
67% (2 of 3) success with stable fungus
Peters et al 16 3.5a G-CSF 5 µg/kg Hetastarch 82% (14 of 17) success with bacterial infection
or 6.4 L processed 54% (7 of 13) success with fungal infection
Prednisolone
Price et al 17 8.2 G-CSF 600 µg/kg Hetastarch 100% (4 of 4) success with bacterial infection
plus 10 L processed 0% (0 of 8) success with invasive fungus
Dexamethasone 8 mg 57% (4 of 7) success with yeast infection
Lee et al 18 5.1-10.6 G-CSF 5 µg/kg Pentastarch 40% (10 of 25) success with multiple-organism
and/or 6–10 L processed infections
Dexamethasone 3 mg/m 2
Hubel et al 19 4.6-8.1 G-CSF 600 mg/kg Hetastarch or pentastarch 55% (unrelated donor) success with bacterial infection
with or without 10 L processed 75% (family donor) success with bacterial infection
Dexamethasone 8 mg 0% (unrelated donor) success with yeast infection
40% (family donor) success with yeast infection
15% (unrelated donor) success with fungal infection
25% (family donor) success with fungal infection
10
a Assumptions made because PMN dose expressed × 10 unclear in these reports. PMN dose calculated using values for range of leukocytes collected, percentage of
collected cells being myeloid, and volume of units collected (Grigg et al). Dose calculated that would be given to a 70-kg recipient for Peters et al.
G-CSF, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GTX, granulocyte transfusions; PMN, neutrophil.
13
al each reported single patients (see Table 114.4) with chronic undergoing progenitor cell transplantation and three receiving che-
granulomatous disease and fungal infections that responded favorably motherapy. Three additional patients who were undergoing progeni-
14
to GTX during the transplantation period. Bielorai et al reported a tor cell transplantation had stable fungal infections. PMNs were
single patient with acute leukemia and sepsis with progressive, collected from donors stimulated only with G-CSF and selected
antibiotic-resistant bacteria whose infection cleared slowly with GTX. without regard for leukocyte compatibility. Success was excellent for
10
Hester et al transfused 15 patients with hematologic malignan- bacterial and stable fungal infections but was quite poor for progres-
cies and infections (see Table 114.5). PMNs were collected from sive fungal infections with organ dysfunction, a troubling pattern
donors stimulated only with G-CSF and selected without regard for reported by others. 17
16
leukocyte compatibility. Although GTX were successful in most Peters et al transfused 30 patients (see Table 114.5) with hema-
patients, it was not possible to distinguish responses of yeast versus tologic disorders—18 undergoing HPC transplantation. PMNs were
18
other fungal infections. Lee et al transfused 25 patients with hema- collected from donors stimulated with G-CSF or prednisolone and
tologic malignancies, many of whom were infected with multiple selected without regard for leukocyte compatibility. The exact PMN
10
organisms. PMNs were collected from donors stimulated with G-CSF dose transfused is uncertain because values from 0.9 × 10 to 14.4
10
alone (67% of donors), G-CSF plus dexamethasone (25% of donors), × 10 can be calculated from data reported, and it was impossible
or dexamethasone alone (8% of donors). Of patients with sepsis, 50% to distinguish the success of GTX from G-CSF–stimulated versus
(2 of 4) responded favorably, and 38% (8 of 21) of patients with prednisolone-stimulated donors. However, the outcome of bacterial
15
progressive localized infections responded favorably. Grigg et al infections appeared to be superior to that of fungal infections.
17
transfused 11 patients (see Table 114.5). Eight patients had hemato- Price et al transfused 19 patients (see Table 114.5) with hema-
logic malignancies and progressive infections, five of the eight tologic malignancies, 16 who had received HPC transplants and three