Page 2281 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2281
2028 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Patient With Factor VIII Deficiency and an Inhibitor). Typically, the
HTC and its physicians serve as a community resource to help guide
Patient Normal Imidazole the care of complex inhibitor patients at other institutions when
plasma plasma buffer timely transport is not feasible because of active bleeding and hemo-
(pH 7.3) dynamic instability.
In general, there are two main aspects that should be considered:
first that bleeds may be more frequent and are more difficult to treat
50/50 mix and, second, that any available treatment is not as efficacious as FVIII
Incubate in hemophilia with no inhibitors.
2 hr @ 37˚ C
FVIII assay Minor Bleeding Episodes
In established low-titer alloantibody FVIII inhibitor patients (consis-
tently less than 5 BU after repeated challenges) or in patients with
low-titer transient inhibitors, larger doses of FVIII concentrate
Buffered FVIII replacement can be given to overcome the neutralizing properties of
Patient normal deficient
plasma plasma plasma the inhibitor. Such treatment may provide therapeutic levels of FVIII
activity. The following equation approximates the dose necessary to
pH 7.4 overcome the neutralization effects of a low-titer FVIII inhibitor:
50/50 mix FVIII Replacement Loading Dose
= 2 ( Body Weight in kg 80 100 − Hematocrit) 100]) BU
(
0
)
[
(
Incubate
2 hr @ 37˚ C
FVIII activity levels should be determined after the infusion to ensure
FVIII assay that adequate therapeutic levels are achieved and sustained. For
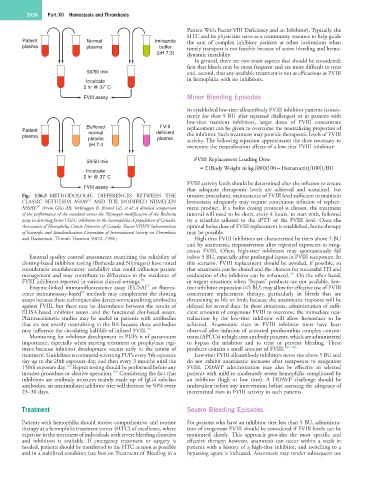
Fig. 136.3 METHODOLOGIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE invasive procedures, maintenance of FVIII level sufficient to maintain
94
CLASSIC BETHESDA ASSAY AND THE MODIFIED NIJMEGEN hemostasis adequately may require continuous infusion of replace-
96
ASSAY. (From Giles AR, Verbruggen B, Rivard GE, et al: A detailed comparison ment product. If a bolus dosing protocol is chosen, the treatment
of the performance of the standard versus the Nijmegen modification of the Bethesda interval will need to be short, every 4 hours, to start with, followed
assay in detecting factor VIII:C inhibitors in the haemophilia A population of Canada. by a schedule tailored to the aPTT or the FVIII level. Once the
Association of Hemophilia Centre Directors of Canada. Factor VIII/IX Subcommittee optimal bolus dose of FVIII replacement is established, home therapy
of Scientific and Standardization Committee of International Society on Thrombosis may be possible.
and Haemostasis, Thromb Haemost 9:872, 1998.) High-titer FVIII inhibitors are characterized by titers above 5 BU
and by anamnestic responsiveness after repeated exposures to exog-
enous FVIII. Often, high-titer inhibitors may spontaneously fall
External quality control assessments examining the reliability of below 5 BU, especially after prolonged lapses in FVIII reexposure. In
clotting-based inhibitor testing (Bethesda and Nijmegen) have noted this scenario, FVIII replacement should be avoided, if possible, so
considerable interlaboratory variability that could influence patient that anamnesis can be abated and the chances for successful ITI and
101
management and may contribute to differences in the incidence of eradication of the inhibitor can be enhanced. On the other hand,
FVIII inhibitors reported in various clinical settings. 96 in urgent situations when “bypass” products are not available, low-
97
Enzyme-linked immunofluorescence assay (ELISA) or fluores- titer inhibitor expression (<5 BU) may allow for effective use of FVIII
98
cence immunoassay-based methods may complement the clotting concentrate replacement therapy, particularly in bleeds that are
assays because these techniques also detect nonneutralizing antibodies threatening to life or limb, because the anamnestic response will be
against FVIII, but there may be discordance between the results of delayed for several days. In these situations, administration of suffi-
ELISA-based inhibitor assays, and the functional clot-based assays. cient amounts of exogenous FVIII to overcome the immediate neu-
Pharmacokinetic studies may be useful in patients with antibodies tralization by the low-titer inhibitor will allow hemostasis to be
that are not overtly neutralizing in the BA because these antibodies achieved. Anamnestic rises in FVIII inhibitor titers have been
may influence the circulating half-life of infused FVIII. 99 observed after infusion of activated prothrombin complex concen-
Monitoring for inhibitor development in PUPs is of paramount trates (APCCs) to high-titer antibody patients, which are administered
importance, especially when starting treatment or prophylaxis regi- to bypass the inhibitor and to treat or prevent bleeding. These
mens because inhibitor development occurs early in the course of products contain a small amount of FVIII. 101–104
treatment. Guidelines recommend screening PUPs every 5th exposure Low-titer FVIII alloantibody inhibitors never rise above 5 BU and
day up to the 20th exposure day, and then every 3 months until the do not exhibit anamnestic increases after reexposure to exogenous
100
150th exposure day. Repeat testing should be performed before any FVIII. DDAVP administration may also be effective in selected
100
invasive procedure or elective operation. Considering the fact that patients with mild to moderately severe hemophilia complicated by
inhibitors are antibody mixtures mainly made up of IgG4 subclass an inhibitor (high or low titer). A DDAVP challenge should be
antibodies, an unstimulated inhibitor titer will decrease by 50% every undertaken before any intervention before assessing the adequacy of
25–30 days. incremental rises in FVIII activity in such patients.
Treatment Severe Bleeding Episodes
Patients with hemophilia should receive comprehensive and routine For patients who have an inhibitor titer less than 5 BU, administra-
therapy at a hemophilia treatment center (HTC) of excellence, where tion of exogenous FVIII should be considered if FVIII levels can be
expertise in the treatment of individuals with severe bleeding disorders monitored closely. This approach provides the most specific and
and inhibitors is available. If emergency treatment or surgery is effective therapy; however, anamnesis can occur within a week in
needed, patients should be transferred to the HTC as soon as possible patients with a history of a high-titer inhibitor, and switching to a
and in a stabilized condition (see box on Treatment of Bleeding in a bypassing agent is indicated. Anamnesis may render subsequent use