Page 2548 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2548
Chapter 157 Hematologic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS 2271
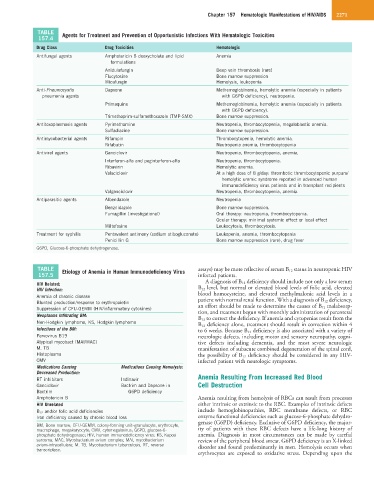
TABLE Agents for Treatment and Prevention of Opportunistic Infections With Hematologic Toxicities
157.4
Drug Class Drug Toxicities Hematologic
Antifungal agents Amphotericin B deoxycholate and lipid Anemia
formulations
Anidulafungin Deep vein thrombosis (rare)
Flucytosine Bone marrow suppression
Micafungin Hemolysis, leukopenia
Anti-Pneumocystis Dapsone Methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia (especially in patients
pneumonia agents with G6PD deficiency), neutropenia.
Primaquine Methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia (especially in patients
with G6PD deficiency).
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) Bone marrow suppression.
Antitoxoplasmosis agents Pyrimethamine Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, megaloblastic anemia.
Sulfadiazine Bone marrow suppression.
Antimycobacterial agents Rifampin Thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia.
Rifabutin Neutropenia anemia, thrombocytopenia
Antiviral agents Ganciclovir Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia,
Interferon-alfa and peginterferon-alfa Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Ribavirin Hemolytic anemia.
Valaciclovir At a high dose of 8 g/day: thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/
hemolytic uremic syndrome reported in advanced human
immunodeficiency virus patients and in transplant recipients
Valganciclovir Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia.
Antiparasitic agents Albendazole Neutropenia
Benznidazole Bone marrow suppression.
Fumagillin (investigational) Oral therapy: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Ocular therapy: minimal systemic effect or local effect
Miltefosine Leukocytosis, thrombocytosis.
Treatment for syphilis Pentavalent antimony (sodium stibogluconate) Leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia
Penicillin G Bone marrow suppression (rare), drug fever
G6PD, Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
TABLE Etiology of Anemia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus assays) may be more reflective of serum B 12 status in neutropenic HIV
157.5 infected patients.
A diagnosis of B 12 deficiency should include not only a low serum
HIV Related:
HIV Infection: B 12 level, but normal or elevated blood levels of folic acid, elevated
Anemia of chronic disease blood homocysteine, and elevated methylmalonic acid levels in a
patient with normal renal function. With a diagnosis of B 12 deficiency,
Blunted production/response to erythropoietin an effort should be made to determine the causes of B 12 malabsorp-
Suppression of CFU-GEMM (HIV/inflammatory cytokines) tion, and treatment begun with monthly administration of parenteral
Neoplasms Infiltrating BM: B 12 to correct the deficiency. If anemia and cytopenias result from the
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, KS, Hodgkin lymphoma B 12 deficiency alone, treatment should result in correction within 4
Infections of the BM: to 6 weeks. Because B 12 deficiency is also associated with a variety of
Parvovirus B19 neurologic defects, including motor and sensory neuropathy, cogni-
Atypical mycobact (MAI/MAC) tive defects including dementia, and the most severe neurologic
M. TB manifestation of subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord,
Histoplasma the possibility of B 12 deficiency should be considered in any HIV-
CMV infected patient with neurologic symptoms.
Medications Causing Medications Causing Hemolysis:
Decreased Production:
RT inhibitors Indinavir Anemia Resulting From Increased Red Blood
Ganciclovir Bactrim and Dapsone in Cell Destruction
Bactrim G6PD deficiency
Amphotericin B Anemia resulting from hemolysis of RBCs can result from processes
HIV Unrelated either intrinsic or extrinsic to the RBC. Examples of intrinsic defects
B 12 and/or folic acid deficiencies include hemoglobinopathies, RBC membrane defects, or RBC
Iron deficiency caused by chronic blood loss enzyme functional deficiencies such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydro-
genase (G6PD) deficiency. Exclusive of G6PD deficiency, the major-
BM, Bone marrow; CFU-GEMM, colony-forming unit–granulocyte, erythrocyte,
macrophage, megakaryocyte; CMV, cytomegalovirus; G6PD, glucose-6- ity of patients with these RBC defects have a life-long history of
phosphate dehydrogenase; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; KS, Kaposi anemia. Diagnosis in most circumstances can be made by careful
sarcoma; MAC, Mycobacterium avium complex; MAI, mycobacterium review of the peripheral blood smear. G6PD deficiency is an X-linked
avium-intracellulare; M. TB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, RT, reverse disorder and found predominantly in men. Hemolysis occurs when
transcriptase.
erythrocytes are exposed to oxidative stress. Depending upon the