Page 2545 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2545
2268 Part XIII Consultative Hematology
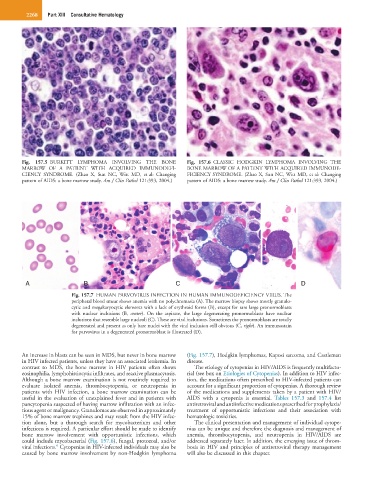
Fig. 157.5 BURKITT LYMPHOMA INVOLVING THE BONE Fig. 157.6 CLASSIC HODGKIN LYMPHOMA INVOLVING THE
MARROW OF A PATIENT WITH ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFI- BONE MARROW OF A PATIENT WITH ACQUIRED IMMUNODE-
CIENCY SYNDROME. (Zhao X, Sun NC, Witt MD, et al: Changing FICIENCY SYNDROME. (Zhao X, Sun NC, Witt MD, et al: Changing
pattern of AIDS: a bone marrow study. Am J Clin Pathol 121:393, 2004.) pattern of AIDS: a bone marrow study. Am J Clin Pathol 121:393, 2004.)
A B C D
Fig. 157.7 HUMAN PARVOVIRUS INFECTION IN HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS. The
peripheral blood smear shows anemia with no polychromasia (A). The marrow biopsy shows mostly granulo-
cytic and megakaryocytic elements with a lack of erythroid forms (B), except for rare large pronormoblasts
with nuclear inclusions (B, center). On the aspirate, the large degenerating pronormoblasts have nuclear
inclusions that resemble large nucleoli (C). These are viral inclusions. Sometimes the pronormoblasts are totally
degenerated and present as only bare nuclei with the viral inclusion still obvious (C, right). An immunostain
for parvovirus in a degenerated pronormoblast is illustrated (D).
An increase in blasts can be seen in MDS, but never in bone marrow (Fig. 157.7), Hodgkin lymphomas, Kaposi sarcoma, and Castleman
in HIV infected patients, unless they have an associated leukemia. In disease.
contrast to MDS, the bone marrow in HIV patients often shows The etiology of cytopenias in HIV/AIDS is frequently multifacto-
eosinophilia, lymphohistiocytic infiltrates, and reactive plasmacytosis. rial (see box on Etiologies of Cytopenias). In addition to HIV infec-
Although a bone marrow examination is not routinely required to tion, the medications often prescribed to HIV-infected patients can
evaluate isolated anemia, thrombocytopenia, or neutropenia in account for a significant proportion of cytopenias. A thorough review
patients with HIV infection, a bone marrow examination can be of the medications and supplements taken by a patient with HIV/
useful in the evaluation of unexplained fever and in patients with AIDS with a cytopenia is essential. Tables 157.3 and 157.4 list
pancytopenia suspected of having marrow infiltration with an infec- antiretroviral and antiinfective medications prescribed for prophylaxis/
tious agent or malignancy. Granulomas are observed in approximately treatment of opportunistic infections and their association with
15% of bone marrow trephines and may result from the HIV infec- hematologic toxicities.
tion alone, but a thorough search for mycobacterium and other The clinical presentation and management of individual cytope-
infections is required. A particular effort should be made to identify nias can be unique and therefore the diagnosis and management of
bone marrow involvement with opportunistic infections, which anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia in HIV/AIDS are
could include mycobacterial (Fig. 157.6), fungal, protozoal, and/or addressed separately later. In addition, the emerging issue of throm-
6
viral infections. Cytopenias in HIV-infected individuals may also be bosis in HIV and principles of antiretroviral therapy management
caused by bone marrow involvement by non-Hodgkin lymphoma will also be discussed in this chapter.