Page 290 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 290
Chapter 22 Natural Killer Cell Immunity 241
CD56
CD16 CD16 CD56
IL-2R αβγ
IL-2R αβγ
c-kit CD56 bright CD56 dim NK cell NK cell
NK cell NK cell
L-selectin
Activating Inhibitory Activating Inhibitory
CD94/NKG2A KIR receptor receptor receptor receptor
ADCC
natural cytotoxicity HLA class I
IFN-γ, TNF-α, Activating ligand Activating
GM-CSF, IL-10 ligand ligand
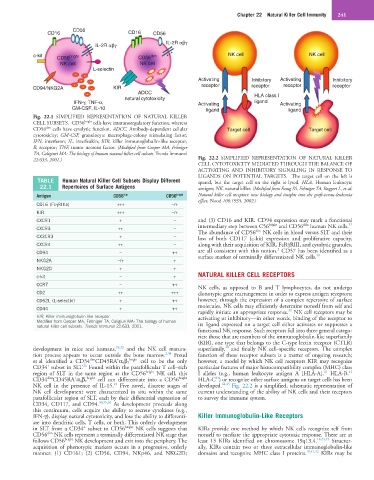
Fig. 22.1 SIMPLIFIED REPRESENTATION OF NATURAL KILLER
CELL SUBSETS. CD56 bright cells have immunoregulatory function, whereas
dim
CD56 cells have cytolytic function. ADCC, Antibody-dependent cellular Target cell Target cell
cytotoxicity; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor;
IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; KIR, killer immunoglobulin-like receptor;
R, receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. (Modified from Cooper MA, Fehniger
TA, Caligiuri MA: The biology of human natural killer cell subsets. Trends Immunol
22:633, 2001.) Fig. 22.2 SIMPLIFIED REPRESENTATION OF NATURAL KILLER
CELL CYTOTOXICITY MEDIATED THROUGH THE BALANCE OF
ACTIVATING AND INHIBITORY SIGNALING IN RESPONSE TO
LIGANDS ON POTENTIAL TARGETS. The target cell on the left is
TABLE Human Natural Killer Cell Subsets Display Different spared, but the target cell on the right is lysed. HLA, Human leukocyte
22.1 Repertoires of Surface Antigens antigen; NK, natural killer. (Modified from Farag SS, Fehniger TA, Ruggeri L, et al:
Antigen CD56 dim CD56 bright Natural killer cell receptors: new biology and insights into the graft-versus-leukemia
effect. Blood 100:1935, 2002.)
CD16 (FcγRIIIa) +++ −/+
KIR +++ −/+
CXCR1 + − and (3) CD16 and KIR. CD94 expression may mark a functional
bright
dim
37
CXCR3 ++ − intermediary step between C56 and CD56 human NK cells.
dim
The abundance of CD56 NK cells in blood versus SLT and their
CX3CR3 + − loss of both CD117 (c-kit) expression and proliferative capacity,
CXCR4 ++ − along with their acquisition of KIR, FcRγRIII, and cytolytic granules,
2
CD94 − ++ are all consistent with this notion. CD57 has been identified as a
38
NKG2A −/+ + surface marker of terminally differentiated NK cells.
NKG2D + +
c-kit − + NATURAL KILLER CELL RECEPTORS
CCR7 − ++ NK cells, as opposed to B and T lymphocytes, do not undergo
CD2 ++ +++ clonotypic gene rearrangement in order to express antigen receptors;
CD62L (L-selectin) + ++ however, through the expression of a complex repertoire of surface
CD44 + ++ molecules, NK cells may efficiently determine nonself from self and
39
rapidly initiate an appropriate response. NK cell receptors may be
KIR, Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor. activating or inhibitory—in other words, binding of the receptor to
Modified from Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA: The biology of human its ligand expressed on a target cell either activates or suppresses a
natural killer cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22:633, 2001.
functional NK response. Such receptors fall into three general catego-
ries: those that are members of the immunoglobulin-like superfamily
(KIR), one type that belongs to the C-type lectin receptor (CTLR)
40
development in mice and humans, 32,33 and the NK cell matura- superfamily, and finally NK cell–specific receptors. The complex
tion process appears to occur outside the bone marrow. 2,34 Freud function of these receptor subsets is a matter of ongoing research;
dim + bright
et al identified a CD34 CD45RA α 4 β 7 cell to be the only however, a model by which NK cell receptors KIR may recognize
+
26
CD34 subset in SLT. Found within the parafollicular T cell–rich particular features of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class
41
42
region of SLT in the same region as the CD56 bright NK cell, this I alleles (e.g., human leukocyte antigen A [HLA-A], HLA-B,
dim + bright bright 43
CD34 CD45RA α 4 β 7 cell can differentiate into a CD56 HLA-C ) or recognize other surface antigens on target cells has been
22
NK cell in the presence of IL-15. Five novel, discrete stages of developed. 44,45 Fig. 22.2 is a simplified, schematic representation of
NK cell development were characterized in situ within the same current understanding of the ability of NK cells and their receptors
parafollicular region of SLT, each by their differential expression of to survey the immune system.
CD34, CD117, and CD94. 30,35,36 As development proceeds along
this continuum, cells acquire the ability to secrete cytokines (e.g.,
IFN-γ), display natural cytotoxicity, and lose the ability to differenti- Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors
ate into dendritic cells, T cells, or both. This orderly development
+
in SLT from a CD34 subset to CD56 bright NK cells suggests that KIRs provide one method by which NK cells recognize self from
dim
CD56 NK cells represent a terminally differentiated NK stage that nonself to mediate the appropriate cytotoxic response. There are at
follows CD56 bright NK development and exit into the periphery. The least 15 KIRs identified on chromosome 19q13.4. 18,44,45 Structur-
acquisition of phenotypic markers occurs in a progressive, orderly ally, KIRs contain two or three extracellular immunoglobulin-like
manner: (1) CD161; (2) CD56, CD94, NKp46, and NKG2D; domains and recognize MHC class I proteins. 18,41,42 KIRs may be