Page 341 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 341
Chapter 24 Complement and Immunoglobulin Biology Leading to Clinical Translation 283
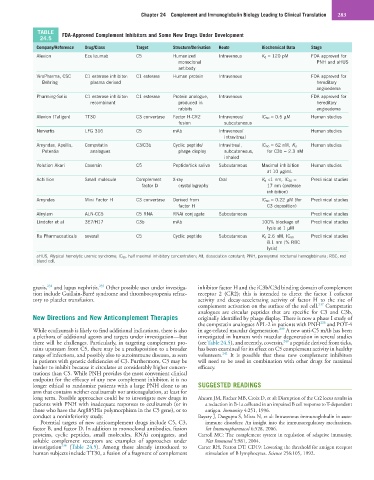
TABLE FDA-Approved Complement Inhibitors and Some New Drugs Under Development
24.5
Company/Reference Drug/Class Target Structure/Derivation Route Biochemical Data Stage
Alexion Eculizumab C5 Humanized Intravenous K d = 120 pM FDA approved for
monoclonal PNH and aHUS
antibody
ViroPharma, CSC C1 esterase inhibitor: C1 esterase Human protein Intravenous FDA approved for
Behring plasma derived hereditary
angioedema
Pharming-Salix C1 esterase inhibitor: C1 esterase Protein analogue, Intravenous FDA approved for
recombinant produced in hereditary
rabbits angioedema
Alexion (Taligen) TT30 C3 convertase Factor H-CR2 Intravenous/ IC 50 = 0.5 µM Human studies
fusion subcutaneous
Norvartis LFG 316 C5 mAb Intravenous/ Human studies
intravitreal
Amyndas, Apellis, Compstatin C3/C3b Cyclic peptide/ Intravitreal, IC 50 = 62 nM, K d Human studies
Potentia analogues phage display subcutaneous, for C3b = 2.3 nM
inhaled
Volution Akari Coversin C5 Peptide/tick saliva Subcutaneous Maximal inhibition Human studies
at 10 µg/mL
Achillion Small molecule Complement X-ray Oral K d <1 nm, IC 50 = Preclinical studies
factor D crystallography 17 nm (protease
inhibition)
Amyndas Mini Factor H C3 convertase Derived from IC 50 = 0.22 µM (for Preclinical studies
factor H C3 deposition)
Alnylam ALN-CC5 C5 RNA RNAi conjugate Subcutaneous Preclinical studies
Lindofer et al 3E7/H17 C3b mAb 100% blockage of Preclinical studies
lysis at 1 µM
Ra Pharmaceuticals several C5 Cyclic peptide Subcutaneous K d 2.6 nM, IC 50 Preclinical studies
8.1 nm (% RBC
lysis)
aHUS, Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome; IC 50 , half maximal inhibitory concentration; Kd, dissociation constant; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; RBC, red
blood cell.
235
234
gravis, and lupus nephritis. Other possible uses under investiga- inhibitor factor H and the iC3b/C3d binding domain of complement
tion include Guillain-Barré syndrome and thrombocytopenia refrac- receptor 2 (CR2); this is intended to direct the factor I cofactor
tory to platelet transfusion. activity and decay-accelerating activity of factor H to the site of
237
complement activation on the surface of the red cell. Compstatin
analogues are circular peptides that are specific for C3 and C3b,
New Directions and New Anticomplement Therapies originally identified by phage display. There is now a phase I study of
238
the compstatin analogues APL-2 in patients with PNH and POT-4
239
While eculizumab is likely to find additional indications, there is also in age-related macular degeneration. A new anti-C5 mAb has been
a plethora of additional agents and targets under investigation—but investigated in humans with macular degeneration in several studies
240
there will be challenges. Particularly, in targeting complement pro- (see Table 24.5), and recently, coversin, a peptide derived from ticks,
teins upstream from C5, there may be a predisposition to a broader has been examined for its effect on C5 complement activity in healthy
241
range of infections, and possibly also to autoimmune diseases, as seen volunteers. It is possible that these new complement inhibitors
in patients with genetic deficiencies of C3. Furthermore, C3 may be will need to be used in combination with other drugs for maximal
harder to inhibit because it circulates at considerably higher concen- efficacy.
trations than C5. While PNH provides the most convenient clinical
endpoint for the efficacy of any new complement inhibitor, it is no
longer ethical to randomize patients with a large PNH clone to an SUGGESTED READINGS
arm that contains neither eculizumab nor anticoagulation, at least for
long term. Possible approaches could be to investigate new drugs in Ahearn JM, Fischer MB, Croix D, et al: Disruption of the Cr2 locus results in
patients with PNH with inadequate responses to eculizumab (or in a reduction in B-1a cells and in an impaired B cell response to T-dependent
those who have the Arg885His polymorphism in the C5 gene), or to antigen. Immunity 4:251, 1996.
conduct a noninferiority study. Bayary J, Dasgupta S, Misra N, et al: Intravenous immunoglobulin in auto-
Potential targets of new anticomplement drugs include C5, C3, immune disorders: An insight into the immunoregulatory mechanisms.
factor B, and factor D. In addition to monoclonal antibodies, fusion Int Immunopharmacol 6:528, 2006.
proteins, cyclic peptides, small molecules, RNAi conjugates, and Carroll MC: The complement system in regulation of adaptive immunity.
soluble complement receptors are examples of approaches under Nat Immunol 5:981, 2004.
236
investigation (Table 24.5). Among those already introduced to Carter RH, Fearon DT: CD19: Lowering the threshold for antigen receptor
human subjects include TT30, a fusion of a fragment of complement stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science 256:105, 1992.