Page 337 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 337
Chapter 24 Complement and Immunoglobulin Biology Leading to Clinical Translation 279
Extract RNA PCR to amplify Generation of
Phage
V H Linker V L coat
cDNA synthesis V H , V K and λ protein phage library
L
Introduce into phage DNA
Pooled human
lymphocytes
Elute
bound
phage
Retain bound phage Add phage to immobilized antigen
Amplify eluted
phage in bacteria Elute and
reamplify
phage
Add phage to immobilized antigen Retain bound phage Phage displaying
under increased binding stringency scFV with high
B conditions affinity for antigen
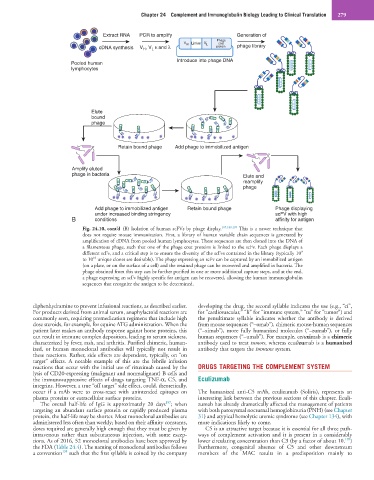
Fig. 24.10, cont’d (B) Isolation of human scFVs by phage display. 185,188,189 This is a newer technique that
does not require mouse immunization. First, a library of human variable chain sequences is generated by
amplification of cDNA from pooled human lymphocytes. These sequences are then cloned into the DNA of
a filamentous phage, such that one of the phage coat proteins is linked to the scFv. Each phage displays a
9
different scFv, and a critical step is to ensure the diversity of the scFvs contained in the library (typically 10
10
to 10 unique clones are desirable). The phage expressing an scFv can be captured by an immobilized antigen
(on a plate, or on the surface of a cell) and the retained phage can be recovered and amplified in bacteria. The
phage obtained from this step can be further purified in one or more additional capture steps, and at the end,
a phage expressing an scFv highly specific for antigen can be recovered, allowing the human immunoglobulin
sequences that recognize the antigen to be determined.
diphenhydramine to prevent infusional reactions, as described earlier. developing the drug, the second syllable indicates the use (e.g., “ci”,
For products derived from animal serum, anaphylactoid reactions are for “cardiovascular,” “li” for “immune system,” “tu” for “tumor”) and
commonly seen, requiring premedication regimens that include high the penultimate syllable indicates whether the antibody is derived
dose steroids, for example, for equine ATG administration. When the from mouse sequences (“–omab”), chimeric mouse-human sequences
patient later makes an antibody response against horse proteins, this (“–ximab”), more fully humanized molecules (“–zumab”), or fully
can result in immune complex deposition, leading to serum sickness, human sequences (“–umab”). For example, cetuximab is a chimeric
characterized by fever, rash, and arthritis. Purified chimeric, human- antibody used to treat tumors, whereas eculizumab is a humanized
ized, or human monoclonal antibodies will typically not result in antibody that targets the immune system.
these reactions. Rather, side effects are dependent, typically, on “on
target” effects. A notable example of this are the febrile infusion
reactions that occur with the initial use of rituximab caused by the DRUGS TARGETING THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
lysis of CD20-expressing (malignant and nonmalignant) B cells and
the immunosuppressive effects of drugs targeting TNF-α, C5, and Eculizumab
integrins. However, a true “off target” side effect, could, theoretically,
occur if a mAb were to cross-react with unintended epitopes on The humanized anti-C5 mAb, eculizumab (Soliris), represents an
plasma proteins or extracellular surface proteins. interesting link between the previous sections of this chapter. Eculi-
197
The overall half-life of IgG is approximately 20 days ; when zumab has already dramatically affected the management of patients
targeting an abundant surface protein or rapidly produced plasma with both paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) (see Chapter
protein, the half-life may be shorter. Most monoclonal antibodies are 31) and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (see Chapter 134), with
administered less often than weekly; based on their affinity constants, more indications likely to come.
doses required are generally high enough that they must be given by C5 is an attractive target because it is essential for all three path-
intravenous rather than subcutaneous injection, with some excep- ways of complement activation and it is present in a considerably
199
tions. As of 2016, 52 monoclonal antibodies have been approved by lower circulating concentration than C3 (by a factor of about 10. )
the FDA (Table 24.4). The naming of monoclonal antibodies follows Furthermore, congenital absence of C5 and other downstream
198
a convention such that the first syllable is coined by the company members of the MAC results in a predisposition mainly to