Page 409 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 409
Chapter 27 Granulocytopoiesis and Monocytopoiesis 331
A B C D E
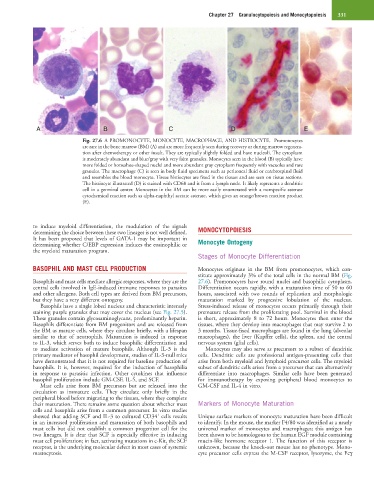
Fig. 27.6 A PROMONOCYTE, MONOCYTE, MACROPHAGE, AND HISTIOCYTE. Promonocytes
are rare in the bone marrow (BM) (A) and are more frequently seen during recovery or during marrow regenera-
tion after chemotherapy or other insult. They are typically slightly folded and have nucleoli. The cytoplasm
is moderately abundant and blue/gray with very faint granules. Monocytes seen in the blood (B) typically have
more folded or horseshoe-shaped nuclei and more abundant gray cytoplasm frequently with vacuoles and rare
granules. The macrophage (C) is seen in body fluid specimens such as peritoneal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid
and resembles the blood monocyte. Tissue histiocytes are fixed in the tissues and are seen on tissue sections.
The histiocyte illustrated (D) is stained with CD68 and is from a lymph node. It likely represents a dendritic
cell in a germinal center. Monocytes in the BM can be more easily enumerated with a nonspecific esterase
cytochemical reaction such as alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase, which gives an orange/brown reaction product
(E).
to induce myeloid differentiation, the modulation of the signals
determining the choice between these two lineages is not well defined. MONOCYTOPOIESIS
It has been proposed that levels of GATA-1 may be important in
determining whether C/EBP expression induces the eosinophilic or Monocyte Ontogeny
the myeloid maturation program.
Stages of Monocyte Differentiation
BASOPHIL AND MAST CELL PRODUCTION Monocytes originate in the BM from promonocytes, which con-
stitute approximately 3% of the total cells in the normal BM (Fig.
Basophils and mast cells mediate allergic responses, where they are the 27.6). Promonocytes have round nuclei and basophilic cytoplasm.
central cells involved in IgE-induced immune responses to parasites Differentiation occurs rapidly, with a maturation time of 50 to 60
and other allergens. Both cell types are derived from BM precursors, hours, associated with two rounds of replication and morphologic
but they have a very different ontogeny. maturation marked by progressive lobulation of the nucleus.
Basophils have a single lobed nucleus and characteristic intensely Stress-induced release of monocytes occurs primarily through their
staining purple granules that may cover the nucleus (see Fig. 27.5). premature release from the proliferating pool. Survival in the blood
These granules contain glycosaminoglycans, predominantly heparin. is short, approximately 8 to 72 hours. Monocytes then enter the
Basophils differentiate from BM progenitors and are released from tissues, where they develop into macrophages that may survive 2 to
the BM as mature cells, where they circulate briefly, with a lifespan 3 months. Tissue-fixed macrophages are found in the lung (alveolar
similar to that of neutrophils. Maturation is induced in response macrophages), the liver (Kupffer cells), the spleen, and the central
to IL-3, which serves both to induce basophilic differentiation and nervous system (glial cells).
to mediate activation of mature basophils. Although IL-3 is the Monocytes may also serve as precursors to a subset of dendritic
primary mediator of basophil development, studies of IL-3-null mice cells. Dendritic cells are professional antigen-presenting cells that
have demonstrated that it is not required for baseline production of arise from both myeloid and lymphoid precursor cells. The myeloid
basophils. It is, however, required for the induction of basophilia subset of dendritic cells arises from a precursor that can alternatively
in response to parasitic infection. Other cytokines that influence differentiate into macrophages. Similar cells have been generated
basophil proliferation include GM-CSF, IL-5, and SCF. for immunotherapy by exposing peripheral blood monocytes to
Mast cells arise from BM precursors but are released into the GM-CSF and IL-4 in vitro.
circulation as immature cells. They circulate only briefly in the
peripheral blood before migrating to the tissues, where they complete
their maturation. There remains some question about whether mast Markers of Monocyte Maturation
cells and basophils arise from a common precursor. In vitro studies
+
showed that adding SCF and IL-3 to cultured CD34 cells results Unique surface markers of monocyte maturation have been difficult
in an increased proliferation and maturation of both basophils and to identify. In the mouse, the marker F4/80 was identified as a nearly
mast cells but did not establish a common progenitor cell for the universal marker of monocytes and macrophages; this antigen has
two lineages. It is clear that SCF is especially effective in inducing been shown to be homologous to the human EGF module containing
mast cell proliferation; in fact, activating mutations in c-Kit, the SCF mucin-like hormone receptor 1. The function of this receptor is
receptor, is the underlying molecular defect in most cases of systemic unknown, because the knock-out mouse has no phenotype. Mono-
mastocytosis. cyte precursor cells express the M-CSF receptor, lysozyme, the Fcγ