Page 712 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 712
604 Part V Red Blood Cells
Fig. 42.14 FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY DEMONSTRATING A “SEA FAN” APPEARANCE OF
SICKLE PROLIFERATIVE RETINOPATHY. (Courtesy W.C. Mentzer.)
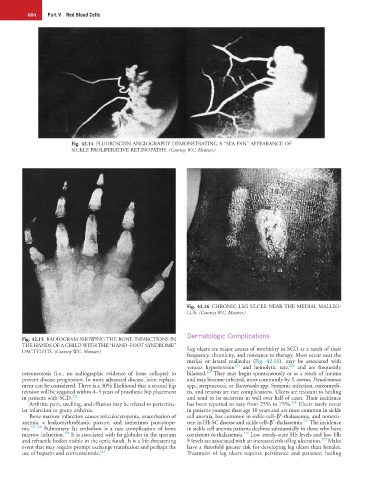
Fig. 42.16 CHRONIC LEG ULCER NEAR THE MEDIAL MALLEO-
LUS. (Courtesy W.C. Mentzer.)
Dermatologic Complications
Fig. 42.15 RADIOGRAM SHOWING THE BONE INFARCTIONS IN
THE HANDS OF A CHILD WITH THE “HAND–FOOT SYNDROME” Leg ulcers are major causes of morbidity in SCD as a result of their
DACTYLITIS. (Courtesy W.C. Mentzer.)
frequency, chronicity, and resistance to therapy. Most occur near the
medial or lateral malleolus (Fig. 42.16), may be associated with
225
226
venous hypertension and hemolytic rate, and are frequently
227
osteonecrosis (i.e., no radiographic evidence of bone collapse) to bilateral. They may begin spontaneously or as a result of trauma
prevent disease progression. In more advanced disease, joint replace- and may become infected, most commonly by S. aureus, Pseudomonas
ment can be considered. There is a 30% likelihood that a second hip spp., streptococci, or Bacteroides spp. Systemic infection, osteomyeli-
revision will be required within 4–5 years of prosthetic hip placement tis, and tetanus are rare complications. Ulcers are resistant to healing
in patients with SCD. 223 and tend to be recurrent in well over half of cases. Their incidence
228
Arthritic pain, swelling, and effusion may be related to periarticu- has been reported to vary from 25% to 75%. Ulcers rarely occur
lar infarction or gouty arthritis. in patients younger than age 10 years and are most common in sickle
Bone marrow infarction causes reticulocytopenia, exacerbation of cell anemia, less common in sickle cell–β°-thalassemia, and nonexis-
+
227
anemia, a leukoerythroblastic picture, and sometimes pancytope- tent in Hb SC disease and sickle cell–β -thalassemia. The incidence
nia. 137,138 Pulmonary fat embolism is a rare complication of bone in sickle cell anemia patients declines substantially in those who have
227
224
marrow infarction. It is associated with fat globules in the sputum coexistent α-thalassemia. Low steady-state Hb levels and low Hb
229
and refractile bodies visible in the optic fundi. It is a life-threatening F levels are associated with an increased risk of leg ulceration. Males
event that may require prompt exchange transfusion and perhaps the have a threefold greater risk for developing leg ulcers than females.
use of heparin and corticosteroids. 224 Treatment of leg ulcers requires persistence and patience; healing