Page 1053 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1053
1028 Part VII: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils, and Mast Cells Chapter 66: Disorders of Neutrophil Function 1029
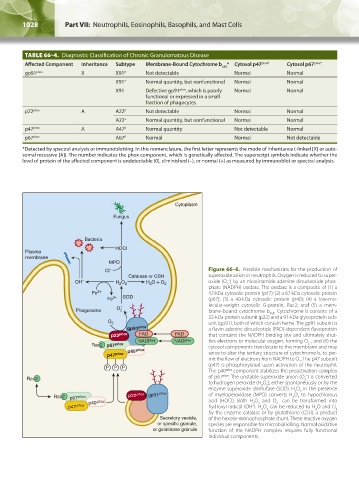
TABLE 66–4. Diagnostic Classification of Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Affected Component Inheritance Subtype Membrane-Bound Cytochrome b * Cytosol p47 phox* Cytosol p67 phox*
558
gp91 phox X X91 0 Not detectable Normal Normal
X91 + Normal quantity, but nonfunctional Normal Normal
X91 – Defective gp91 phox , which is poorly Normal Normal
functional or expressed in a small
fraction of phagocytes
p22 phox A A22 0 Not detectable Normal Normal
A22 + Normal quantity, but nonfunctional Normal Normal
p47 phox A A47 0 Normal quantity Not detectable Normal
p67 phox A67 0 Normal Normal Not detectable
*Detected by spectral analysis or immunoblotting. In this nomenclature, the first letter represents the mode of inheritance (-linked [X] or auto-
somal recessive [A]). The number indicates the phox component, which is genetically affected. The superscript symbols indicate whether the
level of protein of the affected component is undetectable (0), diminished (–), or normal (+) as measured by immunoblot or spectral analysis.
Cytoplasm
Fungus
Bacteria
HOCl
Plasma
membrane
MPO
Cl – Figure 66–6. Possible mechanisms for the production of
Catalase or GSH superoxide anion in neutrophils. Oxygen is reduced to super-
–
OH – H 2 O 2 H O + O oxide (O ) by an nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phos-
2
2
2
phate (NADPH) oxidase. The oxidase is a composite of (1) a
Fe 2+ 47-kDa cytosolic protein (p47); (2) a 67-kDa cytosolic protein
Fe 3+ SOD (p67); (3) a 40-kDa cytosolic protein (p40); (4) a low-mo-
Phagosome O 2 – lecular-weight cytosolic G-protein, Rac2; and (5) a mem-
brane-bound cytochrome b . Cytochrome b consists of a
558
22-kDa protein subunit (p22) and a 91-kDa glycoprotein sub-
O 2 unit (gp91), both of which contain heme. The gp91 subunit is
gp91 phox a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-dependent flavoprotein
p22 phox FAD FAD that contains the NADPH binding site and ultimately shut-
–
NADPH NADPH tles electrons to molecular oxygen, forming O , and (6) the
2
Rac2 p67 phox cytosol components translocate to the membrane and may
p40 phox serve to alter the tertiary structure of cytochrome b, to per-
p47 phox
mit the flow of electrons from NADPH to O . The p47 subunit
2
(p47) is phosphorylated upon activation of the neutrophil.
P P P
The p40 phox component stabilizes the preactivation complex
–
Rac2 of p67 phox . The unstable superoxide anion (O ) is converted
2
to hydrogen peroxide (H O ), either spontaneously or by the
2
2
enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD). H O in the presence
2
2
Rac2 p67 phox p22 phox gp91 phox of myeloperoxidase (MPO) converts H O to hypochlorous
2
2
–
p40 phox acid (HOCl). Both H O and O can be transformed into
2
2
2
p47 phox hydroxyl radical (OH ). H O can be reduced to H O and O
–
2
2
2
2
by the enzyme catalase or by glutathione (GSH), a product
Secretory vesicle, of the hexose-monophosphate shunt. These reactive oxygen
or specific granule, species are responsible for microbial killing. Normal oxidative
or gelatinase granule function of the NADPH complex requires fully functional
individual components.
Kaushansky_chapter 66_p1005-1042.indd 1028 9/21/15 10:48 AM