Page 1228 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1228
1202 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 79: Lymphocytosis and Lymphocytopenia 1203
A B C
D E F
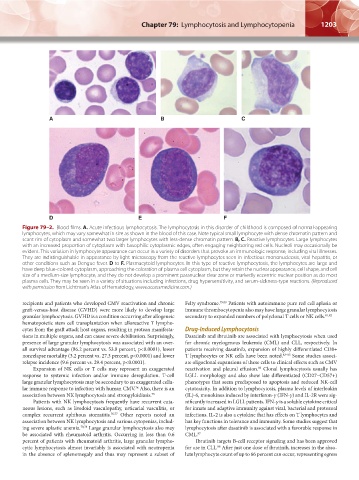
Figure 79–2. Blood films. A. Acute infectious lymphocytosis. The lymphocytosis in this disorder of childhood is composed of normal-appearing
lymphocytes, which may vary somewhat in size as shown in the blood of this case. Note typical small lymphocyte with dense chromatin pattern and
scant rim of cytoplasm and somewhat two larger lymphocytes with less-dense chromatin pattern. B, C. Reactive lymphocytes. Large lymphocytes
with an increased proportion of cytoplasm with basophilic cytoplasmic edges, often engaging neighboring red cells. Nucleoli may occasionally be
evident. This variation in lymphocyte appearance can occur in a variety of disorders that provoke an immunologic response, including viral illnesses.
They are indistinguishable in appearance by light microscopy from the reactive lymphocytes seen in infectious mononucleosis, viral hepatitis, or
other conditions such as Dengue fever. D to F. Plasmacytoid lymphocytes. In this type of reactive lymphocytosis, the lymphocytes are large and
have deep blue-colored cytoplasm, approaching the coloration of plasma cell cytoplasm, but they retain the nuclear appearance, cell shape, and cell
size of a medium-size lymphocyte, and they do not develop a prominent paranuclear clear zone or markedly eccentric nuclear position as do most
plasma cells. They may be seen in a variety of situations including infections, drug hypersensitivity, and serum-sickness-type reactions. (Reproduced
with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
recipients and patients who developed CMV reactivation and chronic Felty syndrome. 79,80 Patients with autoimmune pure red cell aplasia or
graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) were more likely to develop large immune thrombocytopenia also may have large granular lymphocytosis
granular lymphocytosis. GVHD is a condition occurring after allogeneic secondary to expanded numbers of polyclonal T cells or NK cells. 81,82
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation when alloreactive T lympho-
cytes from the graft attack host organs, resulting in protean manifesta- Drug-Induced Lymphocytosis
tions in multiple organs, and can cause severe debilitation. Surprisingly, Dasatinib and ibrutinib are associated with lymphocytosis when used
presence of large granular lymphocytosis was associated with an over- for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and CLL, respectively. In
all survival advantage (86.2 percent vs. 53.8 percent, p<0.0001), lower patients receiving dasatinib, expansion of highly differentiated CD8+
nonrelapse mortality (3.2 percent vs. 27.3 percent, p<0.0001) and lower T lymphocytes or NK cells have been noted. 83–85 Some studies associ-
relapse incidence (9.6 percent vs. 29.4 percent, p<0.0001). ate oligoclonal expansions of these cells to clinical effects such as CMV
Expansion of NK cells or T cells may represent an exaggerated reactivation and pleural effusion. Clonal lymphocytosis usually has
86
response to systemic infection and/or immune deregulation. T-cell LGLL morphology and also show late differentiated (CD27–CD57+)
large granular lymphocytosis may be secondary to an exaggerated cellu- phenotypes that seem predisposed to apoptosis and reduced NK-cell
lar immune response to infection with human CMV. Also, there is an cytotoxicity. In addition to lymphocytosis, plasma levels of interleukin
74
association between NK lymphocytosis and strongyloidiasis. 75 (IL)-6, monokines induced by interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and IL-2R were sig-
Patients with NK lymphocytosis frequently have recurrent cuta- nificantly increased in LGLL patients. IFN-γ is a soluble cytokine critical
neous lesions, such as livedoid vasculopathy, urticarial vasculitis, or for innate and adaptive immunity against viral, bacterial and protozoal
complex recurrent aphthous stomatitis. 76,77 Other reports noted an infections. IL-2 is also a cytokine that has effects on T lymphocytes and
association between NK lymphocytosis and various cytopenias, includ- has key functions in tolerance and immunity. Some studies suggest that
ing severe aplastic anemia. 70,78 Large granular lymphocytosis also may lymphocytosis after dasatinib is associated with a favorable response in
be associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Occurring in less than 0.6 CML. 87
percent of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, large granular lympho- Ibrutinib targets B-cell receptor signaling and has been approved
cytic lymphocytosis almost invariably is associated with neutropenia for use in CLL. After just one dose of ibrutinib, increases in the abso-
88
in the absence of splenomegaly and thus may represent a subset of lute lymphocyte count of up to 66 percent can occur, representing egress
Kaushansky_chapter 79_p1199-1210.indd 1203 9/17/15 4:07 PM