Page 1226 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1226
1200 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 79: Lymphocytosis and Lymphocytopenia 1201
TABLE 79–2. Characteristics of Clinical and Screening Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis
Clinical MBL Screening MBL
Risk of transformation to CLL-requiring therapy 1–2% per year Extremely rare
Hematologic followup interval 6–12 months 12–18 months
Risk of infections Yes No
Eligible for blood donation No Yes
Eligible for stem-cell donation No No
CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MBL, monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis.
Adapted with permission from Molica S, Mauro FR, Molica M, et al: Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis: a reappraisal of its clinical implications.
Leuk Lymphoma 53(9):1660–1665, 2012.
genes used by the B cells most commonly have evidence of somatic selection, suggesting that inappropriate clearance of B cells expressing
mutations, implying that the expanded B cells have undergone germinal low-affinity immunoglobulin receptors plays a role in this disorder. 35
center maturation in an immune response(s) to antigen(s). 33,34 Analyses The cause(s) of this type of lymphocytosis is unknown. Gender
of the immunoglobulin variable-region genes expressed by memory- and genotype may be important in the pathogenesis, as the patients
type B cells of patients failed to reveal evidence of positive antigenic most commonly are young to middle-age women who often are human
A B
C D
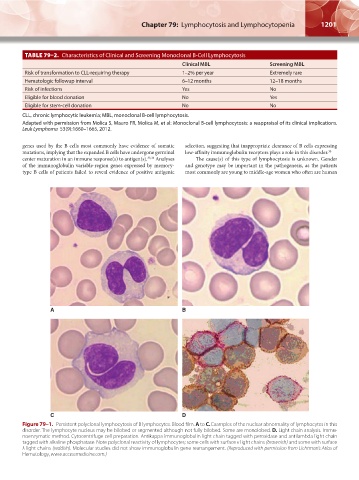
Figure 79–1. Persistent polyclonal lymphocytosis of B lymphocytes. Blood film. A to C. Examples of the nuclear abnormality of lymphocytes in this
disorder. The lymphocyte nucleus may be bilobed or segmented although not fully bilobed. Some are monolobed. D. Light chain analysis. Immu-
noenzymatic method. Cytocentrifuge cell preparation. Antikappa immunoglobulin light chain tagged with peroxidase and antilambda light chain
tagged with alkaline phosphatase. Note polyclonal reactivity of lymphocytes; some cells with surface κ light chains (brownish) and some with surface
λ light chains (reddish). Molecular studies did not show immunoglobulin gene rearrangement. (Reproduced with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of
Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
Kaushansky_chapter 79_p1199-1210.indd 1201 9/17/15 4:06 PM