Page 1266 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1266
1240 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 81: Hematologic Manifestations of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome 1241
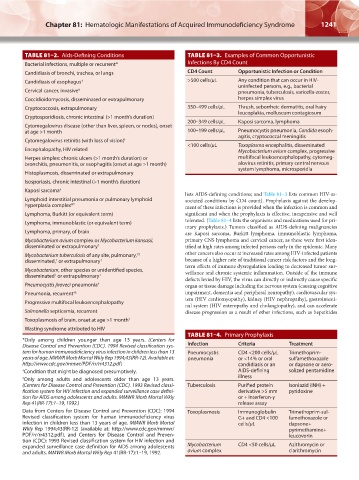
TABLE 81–2. Aids-Defining Conditions TABLE 81–3. Examples of Common Opportunistic
Bacterial infections, multiple or recurrent* Infections By CD4 Count
Candidiasis of bronchi, trachea, or lungs CD4 Count Opportunistic Infection or Condition
Candidiasis of esophagus † >500 cells/μL Any condition that can occur in HIV-
uninfected persons, e.g., bacterial
Cervical cancer, invasive § pneumonia, tuberculosis, varicella-zoster,
Coccidioidomycosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary herpes simplex virus
Cryptococcosis, extrapulmonary 350–499 cells/μL Thrush, seborrheic dermatitis, oral hairy
leucoplakia, molluscum contagiosum
Cryptosporidiosis, chronic intestinal (>1 month’s duration)
200–349 cells/μL Kaposi sarcoma, lymphoma
Cytomegalovirus disease (other than liver, spleen, or nodes), onset
at age >1 month 100–199 cells/μL Pneumocystis pneumonia, Candida esoph-
agitis, cryptococcal meningitis
Cytomegalovirus retinitis (with loss of vision) †
<100 cells/μL Toxoplasma encephalitis, disseminated
Encephalopathy, HIV related Mycobacterium avium complex, progressive
Herpes simplex: chronic ulcers (>1 month’s duration) or multifocal leukoencephalopathy, cytomeg-
bronchitis, pneumonitis, or esophagitis (onset at age >1 month) alovirus retinitis, primary central nervous
system lymphoma, microsporidia
Histoplasmosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary
Isosporiasis, chronic intestinal (>1 month’s duration)
Kaposi sarcoma †
lists AIDS-defining conditions; and Table 81–3 lists common HIV-as-
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia or pulmonary lymphoid sociated conditions by CD4 count). Prophylaxis against the develop-
hyperplasia complex* † ment of these infections is provided when the infection is common and
Lymphoma, Burkitt (or equivalent term) significant and when the prophylaxis is effective, inexpensive and well
tolerated. (Table 81–4 lists the organisms and medications used for pri-
Lymphoma, immunoblastic (or equivalent term)
mary prophylaxis.) Tumors classified as AIDS-defining malignancies
Lymphoma, primary, of brain are Kaposi sarcoma, Burkitt lymphoma, immunoblastic lymphoma,
Mycobacterium avium complex or Mycobacterium kansasii, primary CNS lymphoma and cervical cancer, as these were first iden-
disseminated or extrapulmonary † tified at high rates among infected persons early in the epidemic. Many
Mycobacterium tuberculosis of any site, pulmonary, other cancers also occur at increased rates among HIV-infected patients
†§
disseminated, or extrapulmonary † because of a higher rate of traditional cancer risk factors and the long-
†
term effects of immune dysregulation leading to decreased tumor sur-
Mycobacterium, other species or unidentified species, veillance and chronic systemic inflammation. Outside of the immune
†
disseminated or extrapulmonary †
defects levied by HIV, the virus can directly or indirectly cause specific
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia † organ or tissue damage including the nervous system (causing cognitive
Pneumonia, recurrent †§ impairment, dementia and peripheral neuropathy), cardiovascular sys-
tem (HIV cardiomyopathy), kidney (HIV nephropathy), gastrointesti-
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
nal system (HIV enteropathy and cholangiopathy), and can accelerate
Salmonella septicemia, recurrent disease progression as a result of other infections, such as hepatitides
Toxoplasmosis of brain, onset at age >1 month †
Wasting syndrome attributed to HIV
TABLE 81–4. Primary Prophylaxis
*Only among children younger than age 13 years. (Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 1994 Revised classification sys- Infection Criteria Treatment
tem for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 13 Pneumocystis CD4 <200 cells/μL Trimethoprim-
years of age. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1994;43(RR-12). Available at: pneumonia or <14% or oral sulfamethoxazole
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/PDF/rr/rr4312.pdf) candidiasis or an or dapsone or aero-
† Condition that might be diagnosed presumptively. AIDS-defining solized pentamidine
§ Only among adults and adolescents older than age 13 years. illness
(Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 1993 Revised classi- Tuberculosis Purified protein Isoniazid (INH) +
fication system for HIV infection and expanded surveillance case defini- derivative >5 mm pyridoxine
tion for AIDS among adolescents and adults. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly or + Interferon-γ
Rep 41(RR-17):1–19, 1992.) release assay
Data from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): 1994 Toxoplasmosis Immunoglobulin Trimethoprim-sul-
Revised classification system for human immunodeficiency virus G+ and CD4 <100 famethoxazole or
infection in children less than 13 years of age. MMWR Morb Mortal cells/μL dapsone+
Wkly Rep 1994;43(RR-12) (available at: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/ pyrimethamine+
PDF/rr/rr4312.pdf), and Centers for Disease Control and Preven- leucovorin
tion (CDC): 1993 Revised classification system for HIV infection and
expanded surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents Mycobacterium CD4 <50 cells/μL Azithromycin or
and adults. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 41(RR-17):1–19, 1992. avium complex clarithromycin
Kaushansky_chapter 81_p1239-1260.indd 1241 9/21/15 11:18 AM