Page 1323 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1323
1298 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 84: Polycythemia Vera 1299
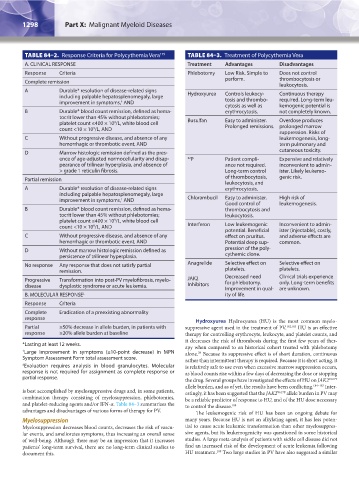
TABLE 84–2. Response Criteria for Polycythemia Vera 179 TABLE 84–3. Treatment of Polycythemia Vera
A. CLINICAL RESPONSE Treatment Advantages Disadvantages
Response Criteria Phlebotomy Low Risk. Simple to Does not control
perform. thrombocytosis or
Complete remission
leukocytosis.
A Durable* resolution of disease-related signs Hydroxyurea Controls leukocy- Continuous therapy
including palpable hepatosplenomegaly, large tosis and thrombo- required. Long-term leu-
improvement in symptoms, AND
†
cytosis as well as kemogenic potential is
B Durable* blood count remission, defined as hema- erythrocytosis. not completely known.
tocrit lower than 45% without phlebotomies; Busulfan Easy to administer. Overdose produces
platelet count ≤400 × 10 /L, white blood cell Prolonged remissions. prolonged marrow
9
9
count <10 × 10 /L, AND
suppression. Risks of
C Without progressive disease, and absence of any leukemogenesis, long-
hemorrhagic or thrombotic event, AND term pulmonary and
D Marrow histologic remission defined as the pres- cutaneous toxicity.
ence of age-adjusted normocellularity and disap- 32 P Patient compli- Expensive and relatively
pearance of trilinear hyperplasia, and absence of ance not required. inconvenient to admin-
> grade 1 reticulin fibrosis. Long-term control ister. Likely leukemo-
Partial remission of thrombocytosis, genic risk.
leukocytosis, and
A Durable* resolution of disease-related signs erythrocytosis.
including palpable hepatosplenomegaly, large Chlorambucil Easy to administer. High risk of
improvement in symptoms, AND
†
Good control of leukemogenesis.
B Durable* blood count remission, defined as hema- thrombocytosis and
tocrit lower than 45% without phlebotomies; leukocytosis.
platelet count ≤400 × 10 /L, white blood cell
9
count <10 × 10 /L, AND Interferon Low leukemogenic Inconvenient to admin-
9
potential. Beneficial ister (injectable), costly,
C Without progressive disease, and absence of any effect on pruritus. and adverse effects are
hemorrhagic or thrombotic event, AND Potential deep sup- common.
D Without marrow histologic remission defined as pression of the poly-
persistence of trilinear hyperplasia. cythemic clone.
No response Any response that does not satisfy partial Anagrelide Selective effect on Selective effect on
remission. platelets. platelets.
Progressive Transformation into post-PV myelofibrosis, myelo- JAK2 Decreased need Clinical trials experience
for phlebotomy.
only. Long-term benefits
disease dysplastic syndrome or acute leukemia. Inhibitors Improvement in qual- are unknown.
B. MOLECULAR RESPONSE ‡ ity of life.
Response Criteria
Complete Eradication of a preexisting abnormality
response
Hydroxyurea Hydroxyurea (HU) is the most common myelo-
Partial ≥50% decrease in allele burden, in patients with suppressive agent used in the treatment of PV. 182,183 HU is an effective
response ≥20% allele burden at baseline therapy for controlling erythrocyte, leukocyte, and platelet counts, and
it decreases the risk of thrombosis during the first few years of ther-
*Lasting at least 12 weeks. apy when compared to an historical cohort treated with phlebotomy
† Large improvement in symptoms (≥10-point decrease) in MPN alone. Because its suppressive effect is of short duration, continuous
78
Symptom Assessment Form total assessment score. rather than intermittent therapy is required. Because it is short acting, it
‡ Evaluation requires analysis in blood granulocytes. Molecular is relatively safe to use even when excessive marrow suppression occurs,
response is not required for assignment as complete response or as blood counts rise within a few days of decreasing the dose or stopping
partial response. the drug. Several groups have investigated the effects of HU on JAK2 V617F
allele burden, and as of yet, the results have been conflicting. 184–187 Inter-
is best accomplished by myelosuppressive drugs and, in some patients, estingly, it has been suggested that the JAK2 V617F allele burden in PV may
combination therapy consisting of myelosuppression, phlebotomies, be a reliable predictor of response to HU, and of the HU dose necessary
and platelet-reducing agents and/or IFN-α. Table 84–3 summarizes the to control the disease. 188
advantages and disadvantages of various forms of therapy for PV. The leukemogenic risk of HU has been an ongoing debate for
Myelosuppression many years. Because HU is not an alkylating agent, it has less poten-
Myelosuppression decreases blood counts, decreases the risk of vascu- tial to cause acute leukemic transformation than other myelosuppres-
lar events, and ameliorates symptoms, thus increasing an overall sense sive agents, but its leukemogenicity was questioned in some historical
of well-being. Although there may be an impression that it increases studies. A large meta-analysis of patients with sickle cell disease did not
patients’ long-term survival, there are no long-term clinical studies to find an increased risk of the development of acute leukemia following
189
document this. HU treatment. Two large studies in PV have also suggested a similar
Kaushansky_chapter 84_p1291-1306.indd 1298 9/21/15 11:11 AM