Page 1407 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1407
1382 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 88: Acute Myelogenous Leukemia 1383
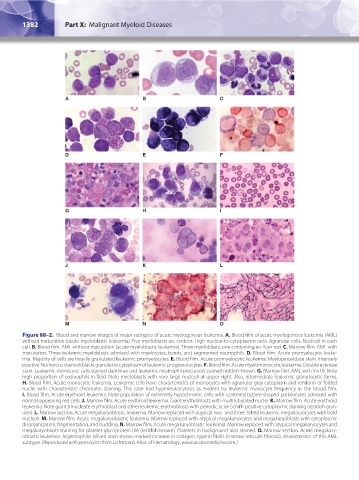
A B C
D E F
G H I
J K L
M N O
Figure 88–2. Blood and marrow images of major subtypes of acute myelogenous leukemia. A. Blood film of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
without maturation (acute myeloblastic leukemia). Five myeloblasts are evident. High nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio. Agranular cells. Nucleoli in each
cell. B. Blood film. AML without maturation (acute myeloblastic leukemia). Three myeloblasts, one containing an Auer rod. C. Marrow film. AML with
maturation. Three leukemic myeloblasts admixed with myelocytes, bands, and segmented neutrophils. D. Blood film. Acute promyelocytic leuke-
mia. Majority of cells are heavily granulated leukemic promyelocytes. E. Blood film. Acute promyelocytic leukemia. Myeloperoxidase stain. Intensely
positive. Numerous stained (black) granules in cytoplasm of leukemic progranulocytes. F. Blood film. Acute myelomonocytic leukemia. Double esterase
stain. Leukemic monocytic cells stained dark blue and leukemic neutrophil precursors stained reddish-brown. G. Marrow film. AML with inv16. Note
high proportion of eosinophils in field. Note myeloblasts with very large nucleoli at upper right. Also, intermediate leukemic granulocytic forms.
H. Blood film. Acute monocytic leukemia. Leukemic cells have characteristics of monocytes with agranular gray cytoplasm and reniform or folded
nuclei with characteristic chromatin staining. This case had hyperleukocytosis as evident by leukemic monocyte frequency in the blood film.
I. Blood film. Acute erythroid leukemia. Note population of extremely hypochromic cells with scattered bizarre-shaped poikilocytes admixed with
normal-appearing red cells. J. Marrow film. Acute erythroid leukemia. Giant erythroblasts with multilobulated nuclei. K. Marrow film. Acute erythroid
leukemia. Note giant trinucleate erythroblast and other leukemic erythroblasts with periodic acid–Schiff–positive cytoplasmic staining (reddish gran-
ules). L. Marrow section. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Marrow replaced with atypical two- and three-lobed leukemic megakaryocytes with bold
nucleoli. M. Marrow film. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Marrow replaced with atypical megakaryocytes and megakaryoblasts with cytoplasmic
disorganization, fragmentation, and budding. N. Marrow film. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Marrow replaced with atypical megakaryocytes and
megakaryoblasts staining for platelet glycoprotein IIIA (reddish-brown). Platelets in background also stained. O. Marrow section. Acute megakary-
oblastic leukemia. Argentophilic (silver) stain shows marked increase in collagen, type III fibrils (marrow reticulin fibrosis), characteristic of this AML
subtype. (Reproduced with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
Kaushansky_chapter 88_p1373-1436.indd 1382 9/21/15 11:01 AM