Page 1464 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1464
1438 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1439
100
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Incidence rate (cases/100,000 population) 10 1 Male
Female
0.1
<1 1–4 5–9 10–1415–19 20–24 25–29 30–34 35–39 40–44 45–49 50–54 55–59 60–64 65–69 70–74 75–79 80–84 85+
Age
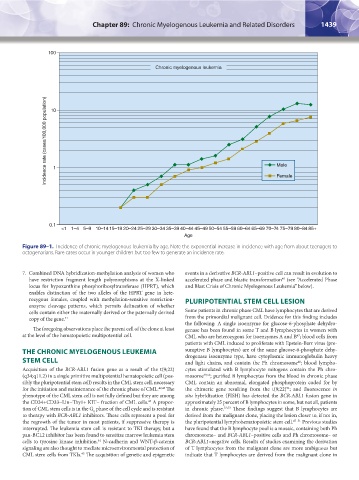
Figure 89–1. Incidence of chronic myelogenous leukemia by age. Note the exponential increase in incidence with age from about teenagers to
octogenarians. Rare cases occur in younger children but too few to generate an incidence rate.
7. Combined DNA hybridization-methylation analysis of women who events in a derivative BCR-ABL1–positive cell can result in evolution to
have restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the X-linked accelerated phase and blastic transformation (see “Accelerated Phase
46
locus for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT), which and Blast Crisis of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia” below).
enables distinction of the two alleles of the HPRT gene in hete-
rozygous females, coupled with methylation-sensitive restriction- PLURIPOTENTIAL STEM CELL LESION
enzyme cleavage patterns, which permits delineation of whether
cells contain either the maternally derived or the paternally derived Some patients in chronic phase CML have lymphocytes that are derived
copy of the gene. 41 from the primordial malignant cell. Evidence for this finding includes
the following: A single isoenzyme for glucose-6-phosphate dehydro-
The foregoing observations place the parent cell of the clone at least genase has been found in some T and B lymphocytes in women with
at the level of the hematopoietic multipotential cell. CML who are heterozygous for isoenzymes A and B ; blood cells from
47
patients with CML induced to proliferate with Epstein-Barr virus (pre-
THE CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA sumptive B lymphocytes) are of the same glucose-6-phosphate dehy-
drogenase isoenzyme type, have cytoplasmic immunoglobulin heavy
STEM CELL and light chains, and contain the Ph chromosome ; blood lympho-
48
Acquisition of the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene as a result of the t(9;22) cytes stimulated with B lymphocyte mitogens contain the Ph chro-
(q34;q11.2) in a single primitive multipotential hematopoietic cell (pos- mosome 49,50 ; purified B lymphocytes from the blood in chronic phase
sibly the pluripotential stem cell) results in the CML stem cell, necessary CML contain an abnormal, elongated phosphoprotein coded for by
for the initiation and maintenance of the chronic phase of CML. 42,43 The the chimeric gene resulting from the t(9;22) ; and fluorescence in
51
phenotype of the CML stem cell is not fully defined but they are among situ hybridization (FISH) has detected the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene in
the CD34+CD33−Lin−Thy1+ KIT− fraction of CML cells. A propor- approximately 25 percent of B lymphocytes in some, but not all, patients
43
tion of CML stem cells is in the G phase of the cell cycle and is resistant in chronic phase. 52,53 These findings suggest that B lymphocytes are
0
to therapy with BCR-ABL1 inhibitors. These cells represent a pool for derived from the malignant clone, placing the lesion closer to, if not in,
the regrowth of the tumor in most patients, if suppressive therapy is the pluripotential lymphohematopoietic stem cell. 47–51 Previous studies
interrupted. The leukemia stem cell is resistant to TKI therapy, but a have found that the B lymphocyte pool is a mosaic, containing both Ph
pan-BCL2 inhibitor has been found to sensitize marrow leukemia stem chromosome– and BCR-ABL1–positive cells and Ph chromosome– or
cells to tyrosine kinase inhibition. N-cadherin and WNT-β-catenin BCR-ABL1–negative cells. Results of studies examining the derivation
44
signaling are also thought to mediate microenvironmental protection of of T lymphocytes from the malignant clone are more ambiguous but
CML stem cells from TKIs. The acquisition of genetic and epigenetic indicate that T lymphocytes are derived from the malignant clone in
45
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1439 9/18/15 3:41 PM