Page 1467 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1467
1442 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1443
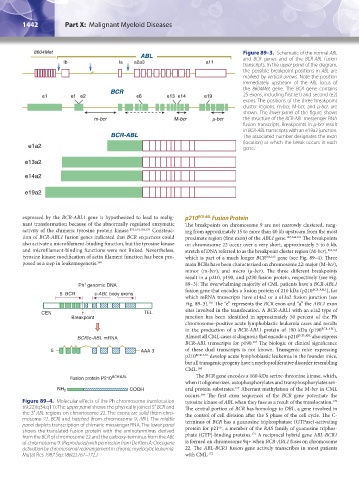
Figure 89–3. Schematic of the normal ABL
and BCR genes and of the BCR-ABL fusion
transcripts. In the upper panel of the diagram,
the possible breakpoint positions in ABL are
marked by vertical arrows. Note the position
immediately upstream of the ABL locus of
the 8604Met gene. The BCR gene contains
25 exons, including first (e1) and second (e2)
exons. The positions of the three breakpoint
cluster regions, m-bcr, M-bcr, and μ-bcr, are
shown. The lower panel of the figure shows
the structure of the BCR-ABL messenger RNA
fusion transcripts. Breakpoints in μ-bcr result
in BCR-ABL transcripts with an e19a2 junction.
The associated number designates the exon
(location) at which the break occurs in each
gene.
expressed by the BCR-ABL1 gene is hypothesized to lead to malig- p210 BCR-ABL Fusion Protein
nant transformation because of the abnormally regulated enzymatic The breakpoints on chromosome 9 are not narrowly clustered, rang-
activity of the chimeric tyrosine protein kinase. 153,154,158,159 Construc- ing from approximately 15 to more than 40 kb upstream from the most
tion of BCR-ABL1 fusion genes indicated that BCR sequences could proximate region (first exon) of the ABL1 gene. 143,144,161 The breakpoints
also activate a microfilament-binding function, but the tyrosine kinase on chromosome 22 occur over a very short, approximately 5 to 6 kb,
and microfilament-binding functions were not linked. Nevertheless, stretch of DNA referred to as the breakpoint cluster region (M-bcr), 162,163
tyrosine kinase modification of actin filament function has been pro- which is part of a much longer BCR 164,165 gene (see Fig. 89–4). Three
posed as a step in leukemogenesis. 160 main BCRs have been characterized on chromosome 22: major (M-bcr),
minor (m-bcr), and micro (μ-bcr). The three different breakpoints
result in a p210, p190, and p230 fusion protein, respectively (see Fig.
1
Ph genomic DNA 89–3). The overwhelming majority of CML patients have a BCR-ABL1
fusion gene that encodes a fusion protein of 210 kDa (p210 BCR-ABL1 ), for
5 BCR c-ABL body exons
which mRNA transcripts have e14a2 or a e13a2 fusion junction (see
Fig. 89–3). The “e” represents the BCR exon and “a” the ABL1 exon
166
sites involved in the translocation. A BCR-ABL1 with an e1a2 type of
CEN TEL
Breakpoint junction has been identified in approximately 50 percent of the Ph
chromosome–positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases and results
in the production of a BCR-ABL1 protein of 190 kDa (p190 BCR-ABL ).
BCR/c-ABL mRNA Almost all CML cases at diagnosis that encode a p210 BCR-ABL also express
BCR-ABL transcripts for p190. The biologic or clinical significance
167
5 AAA 3 of these dual transcripts is not known. Transgenic mice expressing
p210 BCR-ABL develop acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the founder mice,
but all transgenic progeny have a myeloproliferative disorder resembling
CML. 168
Fusion protein P210 BCR/ABL The BCR gene encodes a 160-kDa serine-threonine kinase, which,
when it oligomerizes, autophosphorylates and transphosphorylates sev-
169
NH 2 COOH eral protein substrates. Aberrant methylation of the M-bcr in CML
occurs. The first exon sequences of the BCR gene potentiate the
166
Figure 89–4. Molecular effects of the Ph chromosome translocation tyrosine kinase of ABL when they fuse as a result of the translocation.
170
t(9;22)(q34;q11). The upper panel shows the physically joined 5′ BCR and The central portion of BCR has homology to DBL, a gene involved in
the 3′ ABL regions on chromosome 22. The exons are solid (from chro- the control of cell division after the S phase of the cell cycle. The C-
mosome 22, BCR) and hatched (from chromosome 9, ABL). The middle terminus of BCR has a guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase)-activating
panel depicts transcription of chimeric messenger RNA. The lower panel protein for p21 , a member of the RAS family of guanosine triphos-
rac
shows the translated fusion protein with the aminoterminus derived 171
from the BCR of chromosome 22 and the carboxy-terminus from the ABL phate (GTP)-binding proteins. A reciprocal hybrid gene ABL-BCR1
of chromosome 9. (Reproduced with permission from De Klein A: Oncogene is formed on chromosome 9q+ when BCR-ABL1 fuses on chromosome
activation by chromosomal rearrangement in chronic myelocytic leukemia. 22. The ABL-BCR1 fusion gene actively transcribes in most patients
Mutat Res 1987 Sep;186(2):161–172.) with CML. 172
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1442 9/18/15 3:41 PM