Page 1469 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1469
1444 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1445
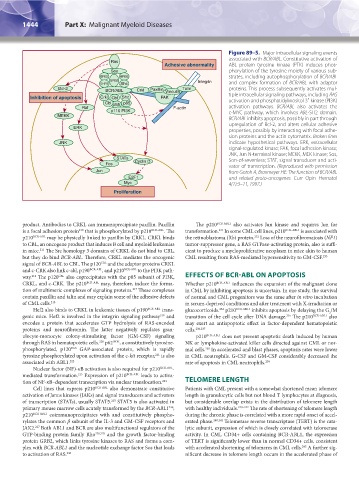
Figure 89–5. Major intracellular signaling events
associated with BCR/ABL. Constitutive activation of
Ras
Adhesive abnormality ABL protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) induces phos-
Sos phorylation of the tyrosine moiety of various sub-
GRB2 GRB2 strates, including autophosphorylation of BCR/ABL
GRB2 Integrin
SHP2 Shc and complex formation of BCR/ABL with adaptor
Bcl-2 BCR/ABL Crkl Paxillin Vinculin Talin proteins. This process subsequently activates mul-
Inhibition of apoptosis Crkl Cbl Shc FAK tiple intracellular signaling pathways, including RAS
activation and phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K)
Cbl p85 p85
Raf F-actin activation pathways. BCR/ABL also activates the
p110 PI3K c-MYC pathway, which involves ABL-SH2 domain.
MEKK
BCR/ABL inhibits apoptosis, possibly in part through
upregulation of Bcl-2, and alters cellular adhesive
ERK
properties, possibly by interacting with focal adhe-
sion proteins and the actin cytomatrix. Broken lines
JNK indicate hypothetical pathways. ERK, extracellular
signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase;
JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; MEKK, MEK kinase; Sos,
STATs Son-of-sevenless; STAT, signal transducer and acti-
Fos Cyclin D vator of transcription. (Reproduced with permission
Jun from Gotoh A, Broxmeyer HE: The function of BCR/ABL
E2F1 and related proto-oncogenes. Curr Opin Hematol
Myc 4(1):3–11, 1997.)
Proliferation
product. Antibodies to CRKL can immunoprecipitate paxillin. Paxillin The p210 BCR-ABL1 also activates Jun kinase and requires Jun for
is a focal adhesion protein that is phosphorylated by p210 BCR-ABL . The transformation. In some CML cell lines, p210 BCR-ABL1 is associated with
210
231
p210 BCR-ABL may be physically linked to paxillin by CRKL. CRKL binds the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein. Loss of the neurofibromatosis (NF1)
232
to CBL, an oncogene product that induces B cell and myeloid leukemias tumor-suppressor gene, a RAS GTPase-activating protein, also is suffi-
in mice. The Src homology 3 domains of CRKL do not bind to CBL, cient to produce a myeloproliferative neoplasm in mice akin to human
211
but they do bind BCR-ABL. Therefore, CRKL mediates the oncogenic CML resulting from RAS-mediated hypersensitivity to GM-CSF. 233
signal of BCR-ABL to CBL. The p120 CBL and the adaptor proteins CRKL
and c-CRK also link c-abl, p190 BCR-ABL , and p210 BCR-ABL to the PI3K path-
way. The p120 CBL also coprecipitates with the p85 subunit of PI3K, EFFECTS OF BCR-ABL ON APOPTOSIS
212
CRKL, and c-CRK. The p210 BCR-ABL may, therefore, induce the forma- Whether p210 BCR-ABL1 influences the expansion of the malignant clone
tion of multimeric complexes of signaling proteins. These complexes in CML by inhibiting apoptosis is uncertain. In one study, the survival
217
contain paxillin and talin and may explain some of the adhesive defects of normal and CML progenitors was the same after in vitro incubation
of CML cells. 218 in serum-deprived conditions and after treatment with X-irradiation or
Hef2 also binds to CRKL in leukemic tissues of p190 BCR-ABL trans- glucocorticoids. p210 BCR-ABL1 inhibits apoptosis by delaying the G /M
234
2
genic mice. Hef2 is involved in the integrin signaling pathway and transition of the cell cycle after DNA damage. The p210 BCR-ABL1 also
235
219
encodes a protein that accelerates GTP hydrolysis of RAS-encoded may exert an antiapoptotic effect in factor-dependent hematopoietic
proteins and neurofibromin. The latter negatively regulates gran- cells. 236,237
ulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) signaling p210 BCR-ABL1 does not prevent apoptotic death induced by human
through RAS in hematopoietic cells. p62 DOK , a constitutively tyrosine- NK or lymphokine-activated killer cells directed against CML or nor-
220
phosphorylated, p120 RAS GAP-associated protein, which is rapidly mal cells. In accelerated and blast phases, apoptosis rates were lower
238
tyrosine phosphorylated upon activation of the c-kit receptor, is also in CML neutrophils. G-CSF and GM-CSF considerably decreased the
221
associated with ABL1. 222 rate of apoptosis in CML neutrophils. 239
Nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation is also required for p210 BCR-ABL -
mediated transformation. Expression of p210 BCR-ABL leads to activa-
223
tion of NF-κB–dependent transcription via nuclear translocation. 224 TELOMERE LENGTH
Cell lines that express p210 BCR-ABL also demonstrate constitutive Patients with CML present with a somewhat shortened mean telomere
activation of Janus kinases (JAKs) and signal transducers and activators length in granulocytic cells but not blood T lymphocytes at diagnosis,
of transcription (STATs), usually STAT5. STAT5 is also activated in but considerable overlap exists in the distribution of telomere length
225
primary mouse marrow cells acutely transformed by the BCR-ABL1 ; with healthy individuals. 240–242 The rate of shortening of telomere length
226
p210 BCR-ABL1 coimmunoprecipitates with and constitutively phospho- during the chronic phase is correlated with a more rapid onset of accel-
rylates the common β subunit of the IL-3 and GM-CSF receptors and erated phase. 240,242 Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) is the cata-
JAK2. Both ABL1 and BCR are also multifunctional regulators of the lytic subunit, expression of which is closely correlated with telomerase
227
GTP-binding protein family Rho 228,229 and the growth factor-binding activity. In CML CD34+ cells containing BCR-ABL1, the expression
protein GRB2, which links tyrosine kinases to RAS and forms a com- of TERT is significantly lower than in normal CD34+ cells, consistent
plex with BCR-ABL1 and the nucleotide exchange factor Sos that leads with accelerated shortening of telomeres in CML cells. A further sig-
243
to activation of RAS. 230 nificant decrease in telomere length occurs in the accelerated phase of
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1444 9/18/15 3:41 PM