Page 1466 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1466
1440 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1441
p210 BCR-ABL interacts with actin filaments through an actin-binding chromosome and its normal counterpart, 22. Using quinacrine (Q)
138
12
domain. BCR-ABL1 transfection is associated with increased spon- and Giemsa (G) banding, Rowley reported in 1973 that the material
taneous motility, membrane ruffling, formation of long actin exten- missing from chromosome 22 was not lost (deleted) from the cell, but
sions (filopodia), and accelerated rate of protrusion and retraction of was translocated to the distal portion of the long arm of chromosome 9.
pseudopodia on fibronectin-coated surfaces. IFN-α treatment slowly The amount of material translocated to chromosome 9 was approxi-
converts the abnormal motility phenotype of BCR-ABL1–transformed mately equivalent to that lost from chromosome 22, and the transloca-
132
12
cells toward normal. Integrins regulate the c-ABL–encoded tyrosine tion was predicted to be balanced. Moreover, the breaks were localized
kinase activity and its cytoplasmic nuclear transport. The p210 BCR-ABL1 to band 34 on the long arm of chromosome 9 and band 11 on the long
133
abrogates the anchorage requirement but not the growth factor require- arm of chromosome 22. Therefore, the classic Ph chromosome is t(9;22)
ment for proliferation. 134 (q34;q11), abbreviated t(Ph) (Fig. 89–2). The Ph chromosome can
In normal cells exposed to IL-3, paxillin tyrosine residues are develop on either the maternal or the paternal member of the pair. 139
phosphorylated. In cells transformed by p210 BCR-ABL1 , the tyrosines of
paxillin, vinculin, p125 FAK , talin, and tensin are constitutively phospho- Mutation of ABL1 and BCR Genes
rylated. Pseudopodia enriched in focal adhesion proteins 134,135 are pres- Mutations of the ABL1 gene on chromosome 9 and of the BCR gene on
ent in cells expressing p210 BCR-ABL1 . chromosome 22 are central to the development of CML (Fig. 89–3). 140–142
The sum of evidence suggests that defects in adhesion (contact In 1982, the human cellular homologue ABL1 of the transforming
and anchoring) of CML primitive cells remove them from their con- sequence of the Abelson murine leukemia virus was localized to human
143
trolling signals normally received from microenvironmental cells via chromosome 9. In 1983, ABL1 was shown to be on the segment of
144
cytokine messages. These signals retain the balance among cell sur- chromosome 9 that is translocated to chromosome 22 by demon-
vival, cell death, cell proliferation, and cell differentiation. Inappropriate strating reaction to hybridization probes for ABL1 only in somatic cell
phosphorylation of cytoskeletal proteins, possibly independent of the hybrids of human CML cells containing 22q− but not those containing
mutant tyrosine kinase, is thought to be the key factor in disturbed inte- 9q+. v-abl is the viral oncogenic homologue of the normal cellular ABL1
grin function of CML cells. gene. This gene (v-abl) can induce malignant transformation of cells in
culture and can induce leukemia in susceptible mice. 145
The ABL1 gene is rearranged and amplified in cell lines from
MOLECULAR PATHOLOGY patients with CML. Cell lines and fresh isolates of CML cells contain
146
Ph Chromosome an abnormal, elongated 8-kb RNA transcript, 147–150 which is transcribed
The genetic disturbance became evident with the knowledge that CML from the new chimeric gene produced by the fusion of the 5′ portion of
was derived from a primitive cell containing a 22q− abnormality. the BCR gene left on chromosome 22 with the 3′ portion of the ABL1
6,11
The abnormal chromosome contained only 60 percent of the DNA gene translocated from chromosome 9 (Fig. 89–4). The fusion mRNA
144
136
in other G-group chromosomes. Cytogenetic analysis indicated the leads to the translation of a unique tyrosine phosphoprotein kinase of
G-group chromosome involved was different from the extra G-group 210 kDa (p210 BCR-ABL ), which can phosphorylate tyrosine residues on
chromosome in Down syndrome, which had been assigned number cellular proteins similar to the action of the v-abl protein product. 151–155
21. Thus, the former was assigned number 22—even though it proved The ABL1 locus contains at least two alleles, one having a 500-bp dele-
to be slightly longer than the chromosome involved in Down syn- tion. In normal cells, the ABL1 protooncogene codes for a tyrosine
157
drome. 11,137 The Paris Conference on Nomenclature decided not to undo kinase of molecular weight 145,000, which is translated only in trace
152
the concept that Down syndrome is trisomy 21 and assigned the Ph quantities and lacks any in vitro kinase activity. The fusion product
5 5
IGL IGL
q11 BCR 5 BCR
c-ABL
c-SiS 3 3
5
q34 c-ABL 3 BCR
3 c-SiS
1
(Ph )
9 22 9q + 22q –
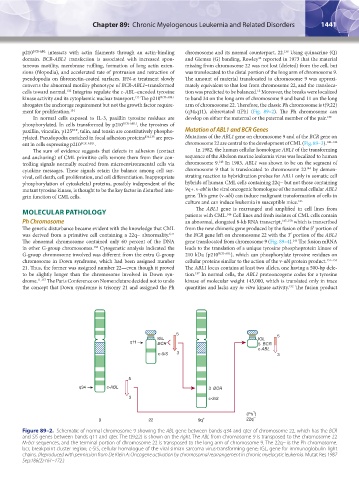
Figure 89–2. Schematic of normal chromosome 9 showing the ABL gene between bands q34 and qter of chromosome 22, which has the BCR
and SIS genes between bands q11 and qter. The t(9;22) is shown on the right. The ABL from chromosome 9 is transposed to the chromosome 22
M-bcr sequences, and the terminal portion of chromosome 22 is transposed to the long arm of chromosome 9. The 22q− is the Ph chromosome.
bcr, breakpoint cluster region; c-SiS, cellular homologue of the viral simian sarcoma virus-transforming gene; IGL, gene for immunoglobulin light
chains. (Reproduced with permission from De Klein A: Oncogene activation by chromosomal rearrangement in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Mutat Res 1987
Sep;186(2):161–172.)
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1441 9/18/15 3:41 PM