Page 1558 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1558
1532 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 92: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia 1533
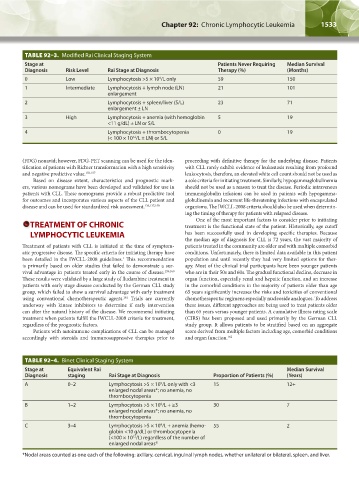
TABLE 92–3. Modified Rai Clinical Staging System
Stage at Patients Never Requiring Median Survival
Diagnosis Risk Level Rai Stage at Diagnosis Therapy (%) (Months)
0 Low Lymphocytosis >5 × 10 /L only 59 150
9
1 Intermediate Lymphocytosis + lymph node (LN) 21 101
enlargement
2 Lymphocytosis + spleen/liver (S/L) 23 71
enlargement ± LN
3 High Lymphocytosis + anemia (with hemoglobin 5 19
<11 g/dL) ± LN or S/L
4 Lymphocytosis + thrombocytopenia 0 19
(< 100 × 10 /L ± LN) or S/L
12
(FDG) nonavid; however, FDG-PET scanning can be used for the iden- proceeding with definitive therapy for the underlying disease. Patients
tification of patients with Richter transformation with a high sensitivity with CLL rarely exhibit evidence of leukostasis resulting from profound
and negative predictive value. 156,157 leukocytosis, therefore, an elevated white cell count should not be used as
Based on disease extent, characteristics and prognostic mark- a sole criteria for initiating treatment. Similarly, hypogammaglobulinemia
ers, various nomograms have been developed and validated for use in should not be used as a reason to treat the disease. Periodic intravenous
patients with CLL. These nomograms provide a robust predictive tool immunoglobulin infusions can be used in patients with hypogamma-
for outcomes and incorporates various aspects of the CLL patient and globulinemia and recurrent life-threatening infections with encapsulated
disease and can be used for standardized risk assessment. 136,137,158 organisms. The IWCLL-2008 criteria should also be used when determin-
ing the timing of therapy for patients with relapsed disease.
One of the most important factors to consider prior to initiating
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC treatment is the functional state of the patient. Historically, age cutoff
LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA has been successfully used in developing specific therapies. Because
the median age of diagnosis for CLL is 72 years, the vast majority of
Treatment of patients with CLL is initiated at the time of symptom- patients treated in the community are older and with multiple comorbid
atic progressive disease. The specific criteria for initiating therapy have conditions. Unfortunately, there is limited data available in this patient
been detailed in the IWCLL-2008 guidelines. This recommendation population and until recently they had very limited options for ther-
1
is primarily based on older studies that failed to demonstrate a sur- apy. Most of the clinical trial participants have been younger patients
vival advantage in patients treated early in the course of disease. 159,160 who are in their 50s and 60s. The gradual functional decline, decrease in
These results were validated by a large study of fludarabine treatment in organ function, especially renal and hepatic function, and an increase
patients with early stage disease conducted by the German CLL study in the comorbid conditions in the majority of patients older than age
group, which failed to show a survival advantage with early treatment 65 years significantly increases the risks and toxicities of conventional
using conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Trials are currently chemotherapeutic regimens especially nucleoside analogues. To address
161
underway with kinase inhibitors to determine if early intervention these issues, different approaches are being used to treat patients older
can alter the natural history of the disease. We recommend initiating than 65 years versus younger patients. A cumulative illness rating scale
treatment when patients fulfill the IWCLL-2008 criteria for treatment, (CIRS) has been proposed and used primarily by the German CLL
regardless of the prognostic factors. study group. It allows patients to be stratified based on an aggregate
Patients with autoimmune complications of CLL can be managed score derived from multiple factors including age, comorbid conditions
accordingly with steroids and immunosuppressive therapies prior to and organ function. 162
TABLE 92–4. Binet Clinical Staging System
Stage at Equivalent Rai Median Survival
Diagnosis staging Rai Stage at Diagnosis Proportion of Patients (%) (Years)
A 0–2 Lymphocytosis >5 × 10 /L only with <3 15 12+
9
enlarged nodal areas*; no anemia, no
thrombocytopenia
B 1–2 Lymphocytosis >5 × 10 /L + ≥3 30 7
9
enlarged nodal areas*; no anemia, no
thrombocytopenia
C 3–4 Lymphocytosis >5 × 10 /L + anemia (hemo- 55 2
9
globin <10 g/dL) or thrombocytopenia
(<100 × 10 /L) regardless of the number of
12
enlarged nodal areas*
*Nodal areas counted as one each of the following: axillary, cervical, inguinal lymph nodes, whether unilateral or bilateral, spleen, and liver.
Kaushansky_chapter 92_p1527-1552.indd 1533 9/18/15 10:47 AM