Page 182 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 182
156 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 11: Genomics 157
Unlike Sanger sequencing, Illumina’s sequencing-by-synthesis SEQUENCING BY PH CHANGE SENSING: THE
method generates relatively short read lengths, typically 100 to 300 bp. ION TORRENT PLATFORM
The limitations on read length are primarily a signal-to-noise issue,
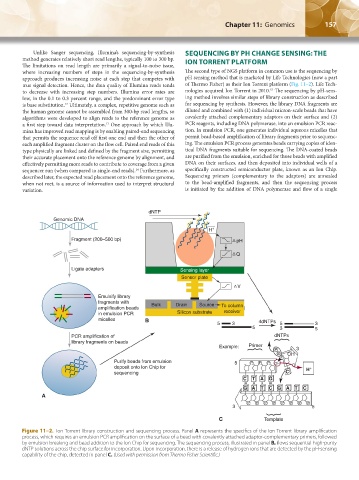
where increasing numbers of steps in the sequencing-by-synthesis The second type of NGS platform in common use is the sequencing by
approach produces increasing noise at each step that competes with pH sensing method that is marketed by Life Technologies (now a part
true signal detection. Hence, the data quality of Illumina reads tends of Thermo Fisher) as their Ion Torrent platform (Fig. 11–2). Life Tech-
15
to decrease with increasing step numbers. Illumina error rates are nologies acquired Ion Torrent in 2010. The sequencing by pH-sens-
low, in the 0.1 to 0.3 percent range, and the predominant error type ing method involves similar steps of library construction as described
12
is base substitution. Ultimately, a complex, repetitive genome such as for sequencing by synthesis. However, the library DNA fragments are
the human genome cannot be assembled from 300-bp read lengths, so diluted and combined with (1) individual micron-scale beads that have
algorithms were developed to align reads to the reference genome as covalently attached complementary adaptors on their surface and (2)
a first step toward data interpretation. One approach by which Illu- PCR reagents, including DNA polymerase, into an emulsion PCR reac-
13
mina has improved read mapping is by enabling paired-end sequencing tion. In emulsion PCR, one generates individual aqueous micelles that
that permits the sequence read off first one end and then the other of permit bead-based amplification of library fragments prior to sequenc-
each amplified fragment cluster on the flow cell. Paired end reads of this ing. The emulsion PCR process generates beads carrying copies of iden-
type physically are linked and defined by the fragment size, permitting tical DNA fragments suitable for sequencing. The DNA-coated beads
their accurate placement onto the reference genome by alignment, and are purified from the emulsion, enriched for those beads with amplified
effectively permitting more reads to contribute to coverage from a given DNA on their surfaces, and then deposited into individual wells of a
14
sequencer run (when compared to single-end reads). Furthermore, as specifically constructed semiconductor plate, known as an Ion Chip.
described later, the expected read placement onto the reference genome, Sequencing primers (complementary to the adaptors) are annealed
when not met, is a source of information used to interpret structural to the bead-amplified fragments, and then the sequencing process
variation. is initiated by the addition of DNA polymerase and flow of a single
dNTP
Genomic DNA
H +
Fragment (200–500 bp) pH
Q
Ligate adapters Sensing layer
Sensor plate
V
Emulsify library
fragments with Bulk Drain Source
amplification beads To column
in emulsion PCR Silicon substrate receiver
micelles B
5 3 4dNTPs 5 3
5 3 5
PCR amplification of dNTPs
library fragments on beads
Example: Primer
P 3
P OH
P
Purify beads from emulsion 5 P P P OH
deposit onto lon Chip for H +
sequencing C
C T A G
G A T C G A T C
A
P P P P P P P P
3 5
C Template
Figure 11–2. Ion Torrent library construction and sequencing process. Panel A represents the specifics of the Ion Torrent library amplification
process, which requires an emulsion PCR amplification on the surface of a bead with covalently attached adaptor-complementary primers, followed
by emulsion breaking and bead addition to the Ion Chip for sequencing. The sequencing process, illustrated in panel B, flows sequential high-purity
dNTP solutions across the chip surface for incorporation. Upon incorporation, there is a release of hydrogen ions that are detected by the pH-sensing
capability of the chip, detected in panel C. (Used with permission from Thermo Fisher Scientific.)
Kaushansky_chapter 11_p0155-0164.indd 157 9/18/15 11:48 PM