Page 183 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 183
158 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 11: Genomics 159
dNTP-containing buffer solution across the Ion Chip surface. The flow Biosciences approach is in the read length obtained, which ranges
of the four nucleotides occurs in a stepwise fashion, with a detection according to the template type but can exceed 50,000 bases with the
step and an intervening wash. When a specific dNTP is incorporated input of very long molecules to the library construction.
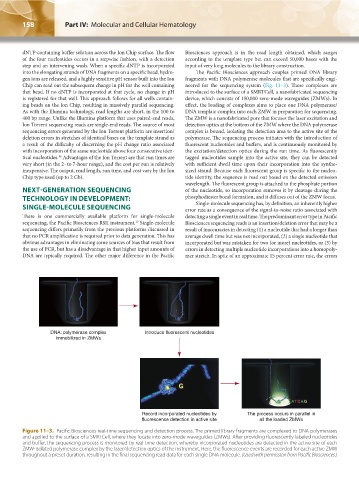
into the elongating strands of DNA fragments on a specific bead, hydro- The Pacific Biosciences approach couples primed DNA library
gen ions are released, and a highly sensitive pH sensor built into the Ion fragments with DNA polymerase molecules that are specifically engi-
Chip can read out the subsequent change in pH for the well containing neered for the sequencing system (Fig. 11–3). These complexes are
that bead. If no dNTP is incorporated at that cycle, no change in pH introduced to the surface of a SMRTCell, a nanofabricated sequencing
is registered for that well. This approach follows for all wells contain- device, which consists of 150,000 zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs). In
ing beads on the Ion Chip, resulting in massively parallel sequencing. effect, the loading of complexes aims to place one DNA polymerase/
As with the Illumina technology, read lengths are short, in the 100 to DNA template complex into each ZMW in preparation for sequencing.
400 bp range. Unlike the Illumina platform that uses paired-end reads, The ZMW is a nanofabricated pore that focuses the laser excitation and
Ion Torrent sequencing reads are single-end reads. The source of most detection optics at the bottom of the ZMW where the DNA polymerase
sequencing errors generated by the Ion Torrent platform are insertion/ complex is bound, isolating the detection area to the active site of the
deletion errors in stretches of identical bases on the template strand as polymerase. The sequencing process initiates with the introduction of
a result of the difficulty of discerning the pH change ratio associated fluorescent nucleotides and buffers, and is continuously monitored by
with incorporation of the same nucleotide above four consecutive iden- the excitation/detection optics during the run time. As fluorescently
tical nucleotides. Advantages of the Ion Torrent are that run times are tagged nucleotides sample into the active site, they can be detected
16
very short (in the 2- to 7-hour range), and the cost per run is relatively with sufficient dwell time upon their incorporation into the synthe-
inexpensive. The output, read length, run time, and cost vary by the Ion sized strand. Because each fluorescent group is specific to the nucleo-
Chip type used (up to 2 Gb). tide identity, the sequence is read out based on the detected emission
wavelength. The fluorescent group is attached to the phosphate portion
NEXT-GENERATION SEQUENCING of the nucleotide, so incorporation removes it by cleavage during the
TECHNOLOGY IN DEVELOPMENT: phosphodiester bond formation, and it diffuses out of the ZMW focus.
Single-molecule sequencing has, by definition, an inherently higher
SINGLE-MOLECULE SEQUENCING error rate as a consequence of the signal-to-noise ratio associated with
There is one commercially available platform for single-molecule detecting a single event in real time. The predominant error type in Pacific
sequencing, the Pacific Biosciences RSII instrument. Single-molecule Biosciences sequencing reads is an insertion/deletion error that may be a
17
sequencing differs primarily from the previous platforms discussed in result of inaccuracies in detecting (1) a nucleotide that had a longer than
that no PCR amplification is required prior to data generation. This has average dwell time but was not incorporated, (2) a single nucleotide that
obvious advantages in eliminating some sources of bias that result from incorporated but was mistaken for two (or more) nucleotides, or (3) by
the use of PCR, but has a disadvantage in that higher input amounts of errors in detecting multiple nucleotide incorporations into a homopoly-
DNA are typically required. The other major difference in the Pacific mer stretch. In spite of an approximate 15 percent error rate, the errors
DNA: polymerase complex Introduce fluorescent nucleotides
immobilized in ZMWs
Record incorporated nucleotides by The process occurs in parallel in
fluorescence detection in active site all the loaded ZMWs
Figure 11–3. Pacific Biosciences real-time sequencing and detection process. The primed library fragments are complexed to DNA polymerases
and applied to the surface of a SMRTCell, where they locate into zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs). After providing fluorescently labeled nucleotides
and buffer, the sequencing process is monitored by real time detection, whereby incorporated nucleotides are detected in the active site of each
ZMW-isolated polymerase complex by the laser/detection optics of the instrument. Here, the fluorescence events are recorded for each active ZMW
throughout a preset duration, resulting in the final sequencing read data for each single DNA molecule. (Used with permission from Pacific Biosciences.)
Kaushansky_chapter 11_p0155-0164.indd 158 9/18/15 11:48 PM