Page 184 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 184
158 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 11: Genomics 159
are essentially random, which means that oversampling (or “coverage”) outside of the known genes, inspired the development of methods to
of the sequence of interest can correct most errors, resulting in a cumu- focus sequencing onto these loci. In particular, hybrid capture tech-
lative error rate of around 0.1 percent following read assembly. The very niques were developed that provided either a subset of known genes
18
long read lengths possible on this platform enable read assembly, rather (all kinases, for example), or all the known genes (the “exome”) by a
than read alignment needed in short read platform data analysis. Assem- series of selective steps that led directly to NGS data generation (Fig.
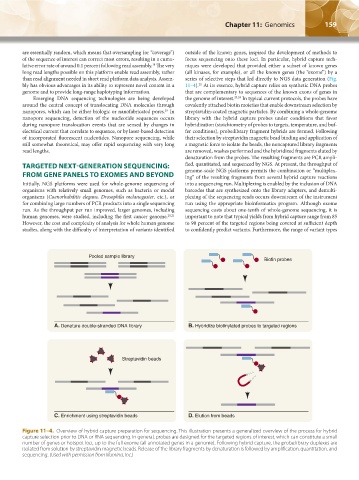
bly has obvious advantages in its ability to represent novel content in a 11–4). At its essence, hybrid capture relies on synthetic DNA probes
22
genome and to provide long-range haplotyping information. that are complementary to sequences of the known exons of genes in
Emerging DNA sequencing technologies are being developed the genome of interest. 23,24 In typical current protocols, the probes have
around the central concept of translocating DNA molecules through covalently attached biotin moieties that enable downstream selection by
nanopores, which can be either biologic or nanofabricated pores. In streptavidin-coated magnetic particles. By combining a whole-genome
19
nanopore sequencing, detection of the nucleotide sequences occurs library with the hybrid capture probes under conditions that favor
during nanopore translocation events that are sensed by changes in hybridization (stoichiometry of probes to targets, temperature, and buf-
electrical current that correlate to sequence, or by laser-based detection fer conditions), probe:library fragment hybrids are formed. Following
of incorporated fluorescent nucleotides. Nanopore sequencing, while their selection by streptavidin magnetic bead binding and application of
still somewhat theoretical, may offer rapid sequencing with very long a magnetic force to isolate the beads, the noncaptured library fragments
read lengths. are removed, washes performed and the hybridized fragments eluted by
denaturation from the probes. The resulting fragments are PCR ampli-
TARGETED NEXT-GENERATION SEQUENCING: fied, quantitated, and sequenced by NGS. At present, the throughput of
FROM GENE PANELS TO EXOMES AND BEYOND genome-scale NGS platforms permits the combination or “multiplex-
ing” of the resulting fragments from several hybrid capture reactions
Initially, NGS platforms were used for whole-genome sequencing of into a sequencing run. Multiplexing is enabled by the inclusion of DNA
organisms with relatively small genomes, such as bacteria or model barcodes that are synthesized onto the library adapters, and demulti-
organisms (Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, etc.), or plexing of the sequencing reads occurs downstream of the instrument
for combining large numbers of PCR products into a single sequencing run using the appropriate bioinformatics program. Although exome
run. As the throughput per run improved, larger genomes, including sequencing costs about one-tenth of whole-genome sequencing, it is
human genomes, were studied, including the first cancer genome. 20,21 important to note that typical yields from hybrid capture range from 85
However, the cost and complexity of analysis for whole human genome to 90 percent of the targeted regions being covered at sufficient depth
studies, along with the difficulty of interpretation of variants identified to confidently predict variants. Furthermore, the range of variant types
Pooled sample library
Biotin probes
A. Denature double-stranded DNA library B. Hybridize biotinylated probes to targeted regions
Streptavidin beads
C. Enrichment using streptavidin beads D. Elution from beads
Figure 11–4. Overview of hybrid capture preparation for sequencing. This illustration presents a generalized overview of the process for hybrid
capture selection prior to DNA or RNA sequencing. In general, probes are designed for the targeted regions of interest, which can constitute a small
number of genes or hotspot loci, up to the full exome (all annotated genes in a genome). Following hybrid capture, the probe:library duplexes are
isolated from solution by streptavidin magnetic beads. Release of the library fragments by denaturation is followed by amplification, quantitation, and
sequencing. (Used with permission from Illumina, Inc.)
Kaushansky_chapter 11_p0155-0164.indd 159 9/18/15 11:48 PM