Page 2153 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2153
2128 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 123: Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B 2129
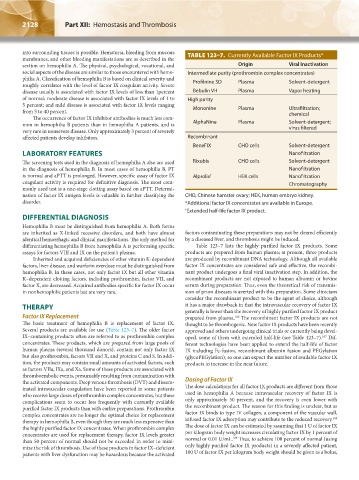
into surrounding tissues is possible. Hematuria, bleeding from mucous TABLE 123–7. Currently Available Factor IX Products*
membranes, and other bleeding manifestations are as described in the
section on hemophilia A. The physical, psychological, vocational, and Origin Viral Inactivation
social aspects of the disease are similar to those encountered with hemo- Intermediate purity (prothrombin complex concentrates)
philia A. Classification of hemophilia B is based on clinical severity and Profilnine SD Plasma Solvent-detergent
roughly correlates with the level of factor IX coagulant activity. Severe
disease usually is associated with factor IX levels of less than 1percent Bebulin VH Plasma Vapor heating
of normal; moderate disease is associated with factor IX levels of 1 to High purity
5 percent; and mild disease is associated with factor IX levels ranging Mononine Plasma Ultrafiltration;
from 5 to 40 percent. chemical
The occurrence of factor IX inhibitor antibodies is much less com-
mon in hemophilia B patients than in hemophilia A patients, and is AlphaNine Plasma Solvent-detergent;
virus filtered
very rare in nonsevere disease. Only approximately 3 percent of severely
affected patients develop inhibitors. Recombinant
BeneFIX CHO cells Solvent-detergent
LABORATORY FEATURES Nanofiltration
The screening tests used in the diagnosis of hemophilia A also are used Rixubis CHO cells Solvent-detergent
in the diagnosis of hemophilia B. In most cases of hemophilia B, PT Nanofiltration
is normal and aPTT is prolonged. However, specific assay of factor IX Alprolix † HEK cells Nanofiltration
coagulant activity is required for definitive diagnosis. The most com- Chromatography
monly used test is a one-stage clotting assay based on aPTT. Determi-
nation of factor IX antigen levels is valuable in further classifying the CHO, Chinese hamster ovary; HEK, human embryo kidney.
disorder. *Additional factor IX concentrates are available in Europe.
† Extended half-life factor IX product.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Hemophilia B must be distinguished from hemophilia A. Both forms
are inherited as X-linked recessive disorders, and both have almost factors contaminating these preparations may not be cleared efficiently
identical hemorrhagic and clinical manifestations. The only method for by a diseased liver, and thrombosis might be induced.
differentiating hemophilia B from hemophilia A is performing specific Table 123–7 lists the highly purified factor IX products. Some
assays for factors VIII and IX on the patient’s plasma. products are prepared from human plasma; at present, three products
Inherited and acquired deficiencies of other vitamin K-dependent are produced by recombinant DNA technology. Although all available
factors, liver disease, and warfarin overdose must be distinguished from factor IX concentrates are considered safe and effective, the recombi-
hemophilia B. In these cases, not only factor IX but all other vitamin nant product undergoes a final viral inactivation step. In addition, the
K–dependent clotting factors, including prothrombin, factor VII, and recombinant products are not exposed to human albumin or bovine
factor X, are decreased. Acquired antibodies specific for factor IX occur serum during preparation. Thus, even the theoretical risk of transmis-
in nonhemophilic patients but are very rare. sion of prion diseases is averted with this preparation. Some clinicians
consider the recombinant product to be the agent of choice, although
THERAPY it has a major drawback in that the intravascular recovery of factor IX
generally is lower than the recovery of highly purified factor IX product
Factor IX Replacement prepared from plasma. The recombinant factor IX products are not
106
The basic treatment of hemophilia B is replacement of factor IX. thought to be thrombogenic. New factor IX products have been recently
Several products are available for use (Table 123–7). The older factor approved and others undergoing clinical trials or currently being devel-
IX– containing products often are referred to as prothrombin complex oped, some of them with extended half-life (see Table 123–7). Dif-
107
concentrates. These products, which are prepared from large pools of ferent technologies have been applied to extend the half-life of factor
human plasma (several thousand donors), contain not only factor IX IX including Fc-fusion, recombinant albumin fusion and PEGylation
but also prothrombin, factors VII and X, and proteins C and S. In addi- (glycoPEGylation), so one can expect the number of available factor IX
tion, the products may contain small amounts of activated factors, such products to increase in the near future.
as factors VIIa, IXa, and Xa. Some of these products are associated with
thromboembolic events, presumably resulting from contamination with
the activated components. Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and dissem- Dosing of Factor IX
inated intravascular coagulation have been reported in some patients The dose calculations for all factor IX products are different from those
who receive large doses of prothrombin complex concentrates, but these used in hemophilia A because intravascular recovery of factor IX is
complications seem to occur less frequently with currently available only approximately 50 percent, and the recovery is even lower with
purified factor IX products than with earlier preparations. Prothrombin the recombinant product. The reason for this finding is unclear, but as
complex concentrates are no longer the optimal choice for replacement factor IX binds to type IV collagen, a component of the vascular wall,
108
therapy in hemophilia B, even though they are much less expensive than infused factor IX adsorption may contribute to the reduced recovery.
the highly purified factor IX concentrates. When prothrombin complex The dose of factor IX can be estimated by assuming that 1 U of factor IX
concentrates are used for replacement therapy, factor IX levels greater per kilogram body weight increases circulating factor IX by 1 percent of
109
than 50 percent of normal should not be exceeded in order to mini- normal or 0.01 U/mL. Thus, to achieve 100 percent of normal (using
mize the risk of thrombosis. Use of these products in factor IX–deficient only highly purified factor IX products) in a severely affected patient,
patients with liver dysfunction may be hazardous because the activated 100 U of factor IX per kilogram body weight should be given as a bolus,
Kaushansky_chapter 123_p2113-2132.indd 2128 9/21/15 4:36 PM