Page 2316 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2316
2290 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 134: Atherothrombosis: Disease Initiation, Progression, and Treatment 2291
Old thrombus
Critically stenotic vulnerable plaque
G
Extensive calcification Calcium nodule
F Vulnerable plaque with calcified nodule
Leaking vasa vasorum/ angiogenesis
E Vulnerable plaque with intraplaque hemorrhage
ypes of Vulnerable Plaque
Nonocclusive mural thrombin/ fibrin Intact cap
Eroded vulnerable plaque
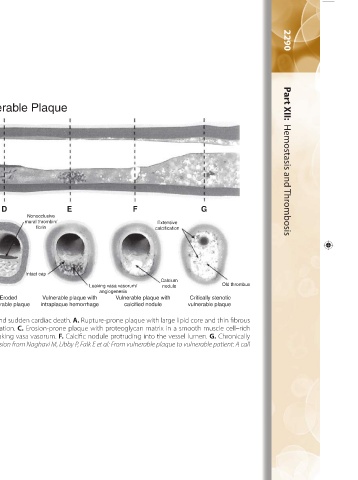
D Different types of vulnerable plaque as underlying cause of acute coronary events and sudden cardiac death. A. Rupture-prone plaque with large lipid core and thin fibrous
Platelets Proteoglycans cap infiltrated by macrophages. B. Ruptured plaque with subocclusive thrombus and early organization. C. Erosion-prone plaque with proteoglycan matrix in a smooth muscle cell–rich plaque. D. Eroded plaque with subocclusive thrombus. E. Intraplaque hemorrhage secondary to leaking vasa vasorum. F. Calcific nodule protruding into the vessel lumen. G. Chronically stenotic plaque with severe calcification, old thrombus, and eccentric lumen. (Reproduced with permission from Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E et al: From vulnerable plaque
Erosion-prone vulnerable plaque
C
Different T Dysfunctional endothelium Smooth muscle cells
B Ruptured/healing vulnerable plaque
Ruptured cap
Nonocclusive clot Collagen Large lipid cone for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: Part I. Circulation 108(14):1664–1672, 2003.)
A Rupture-prone vulnerable plaque
Macrophage Thin cap
Figure 134–6.
Normal
Kaushansky_chapter 134_p2281-2302.indd 2290 17/09/15 3:49 pm