Page 233 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 233
208 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 15: Apoptosis Mechanisms: Relevance to the Hematopoietic System 209
which are several genes that suppress apoptosis. As a result, this NF-κB most relevant activity of IAPs appears to be their noncanonical E3 ligase
pathway nullifies the caspase pathway, negating apoptosis, in addition activity, as well as a protein scaffold role where they serve as platforms
62
to accounting for the untoward inflammatory actions of this cytokine. for assembling multiprotein complexes. Additional roles for IAP family
Several antiapoptotic genes are among the direct transcriptional targets members include cell division, where, for example, the Survivin protein
of NF-κB (REL)-family proteins, including the genes encoding c-FLIP, plays a fundamental role in chromosome segregation and cytokinesis.
c-IAP2, Bcl-X , and Bfl-1. Several of the IAPs are opposed by proteins released from mito-
L
In this regard, the c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 proteins were first identi- chondria, SMAC and HtrA2. SMAC and Htra2 bind BIR domains on
fied because of their association with TNF receptor complexes. These IAPs, thus displacing caspases and other associated proteins. In many
IAPs bind the kinase Rip1 via their BIR3 domains, mediating nonca- cases, SMAC binding to IAPs induces their polyubiquitination and pro-
nonical ubiquitination of Rip1 via interactions of atypical UBCs with teasomal degradation. Thus, factors that cause MOMP take the breaks
their RING domains and possibly also indirectly via interactions of the off the caspases by eliminating various IAP family proteins.
E3 ligase TRAF2, which binds their BIR1 domains. The noncanonical
ubiquitination of Rip1 is required for TNFR1-mediated NF-κB acti- SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION AND
vation and suppression of cytokine-induced apoptosis. The c-IAP1
and c-IAP2 proteins also control the “alternative” pathway for NF-κB APOPTOSIS REGULATION
activation via yet another mechanism, which involves classical lysine
48 mediated polyubiquitination of the kinase Nik. Various receptor-mediated signal transduction pathways converge on
Additional members of the IAP family not described here (Sur- the core components of the cell death machinery outlined above, includ-
vivin, Apollon/Bruce, ML-IAP, etc.) also have interesting mechanisms ing receptors for growth factors, lymphokines and cytokines. Some
of interacting with components of cell-death pathways and they also examples illustrating the intimate links between receptor-mediated sig-
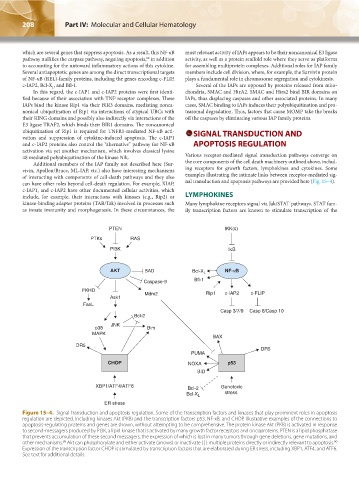
can have other roles beyond cell-death regulation. For example, XIAP, nal transduction and apoptosis pathways are provided here (Fig. 15–4).
c-IAP1, and c-IAP2 have other documented cellular activities, which
include, for example, their interactions with kinases (e.g., Rip2) or LYMPHOKINES
kinase-binding adapter proteins (TAB/Tak) involved in processes such Many lymphokine receptors signal via Jak/STAT pathways. STAT fam-
as innate immunity and morphogenesis. In these circumstances, the ily transcription factors are known to stimulate transcription of the
PTEN IKK(s)
PTKs RAS
PI3K IκB
AKT BAD Bcl-X L NF-κB
Caspase-9 Bfl-1
FKHD Mdm2 Rip1 c-IAP2 c-FLIP
Ask1
FasL
Casp 3/7/9 Casp 8/Casp 10
Bcl-2
JNK
p38 Bim
MAPK
BAX
DR5
DR5
PUMA
CHOP NOXA p53
BID
XBP1/ATF4/ATF6 Bcl-2 Genotoxic
stress
Bcl-X L
ER stress
Figure 15–4. Signal transduction and apoptosis regulation. Some of the transcription factors and kinases that play prominent roles in apoptosis
regulation are depicted, including kinases Akt (PKB) and the transcription factors p53, NF-κB, and CHOP. Illustrative examples of the connections to
apoptosis-regulating proteins and genes are shown, without attempting to be comprehensive. The protein kinase Akt (PKB) is activated in response
to second-messagers produced by PI3K, a lipid kinase that is activated by many growth factor receptors and oncoproteins. PTEN is a lipid phosphatase
that prevents accumulation of these second messagers, the expression of which is lost in many tumors through gene deletions, gene mutations, and
other mechanisms. Akt can phosphorylate and either activate (arrows) or inactivate ( | ) multiple proteins directly or indirectly relevant to apoptosis.
90
89
Expression of the transcription factor CHOP is stimulated by transcription factors that are elaborated during ER stress, including XBP1, ATF4, and ATF6.
See text for additional details.
Kaushansky_chapter 15_p0203-0212.indd 208 17/09/15 6:38 pm