Page 239 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 239
214 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 215
M
cdk1
Cyclin B
p21 p15 p16 p18
P
cdc25B P
Cyclin B Cyclin
cdk1 D1, D2, D3 cdk4, 6
P P
G 2 Cyclin B P p107 P P G 1
Cyclin B
cdk1 cdk1 P Rb E2F p107 Rb P Cyclin E PCNA
cdk2
P E2F
Cyclin A P
Cyclin A cdk1 Rb Rb
P E2F Transcription G 0
P factors
(e.g., E2F)
cdc25 Activation of p53 and p21 p21
p73 by DNA damage
p73
p53 Cyclin A Cyclin H
P
cdk2 cdk7
p21 P
cdk2
Cyclin A
MDM2 P Cyclin E
cdk2
p14
cdc25
S
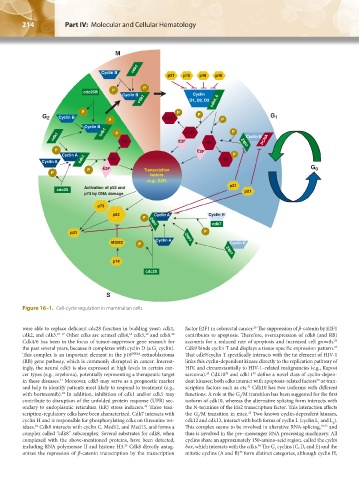
Figure 16–1. Cell-cycle regulation in mammalian cells.
were able to replace deficient cdc28 function in budding yeast: cdk1, factor E2F1 in colorectal cancer. The suppression of β-catenin by E2F1
26
cdk2, and cdk3. 15–17 Other cdks are termed cdk4, cdk5, and cdk6. contributes to apoptosis. Therefore, overexpression of cdk8 (and RB)
20
19
18
Cdk4/6 has been in the focus of tumor-suppressor gene research for accounts for a reduced rate of apoptosis and increased cell growth.
26
the past several years, because it complexes with cyclin D (a G cyclin). Cdk9 binds cyclin T and displays a tissue-specific expression pattern.
27
1
This complex is an important element in the p16 INK4A -retinoblastoma That cdk9/cyclin T specifically interacts with the tat element of HIV-1
(RB) gene pathway, which is commonly disrupted in cancer. Interest- links this cyclin-dependent kinase directly to the replication pathway of
ingly, the neural cdk5 is also expressed at high levels in certain can- HIV, and circumstantially to HIV-1–related malignancies (e.g., Kaposi
cer types (e.g., myeloma), potentially representing a therapeutic target sarcoma). Cdk10 and cdk11 define a novel class of cyclin-depen-
29
30
28
in these diseases. Moreover, cdk5 may serve as a prognostic marker dent kinases; both cdks interact with apoptosis-related factors or tran-
21
30
and help to identify patients most likely to respond to treatment (e.g., scription factors such as ets. Cdk10 has two isoforms with different
31
with bortezomib). In addition, inhibition of cdk1 and/or cdk5 may functions. A role at the G /M transition has been suggested for the first
22
2
contribute to disruption of the unfolded protein response (UPR) sec- isoform of cdk10, whereas the alternative splicing form interacts with
ondary to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducers. Three tran- the N-terminus of the Ets2 transcription factor. This interaction affects
23
scription-regulatory cdks have been characterized. Cdk7 interacts with the G /M transition in mice. Two known cyclin-dependent kinases,
32
2
cyclin H and is responsible for phosphorylating cdks on threonine res- cdk12 and cdk13, interact with both forms of cyclin L (cyclin L and L ).
2
1
idues. Cdk8 interacts with cyclin C, Med12, and Med13, and forms a This complex seems to be involved in alterative RNA-splicing, 10,33 and
24
complex called “cdk8” subcomplex. Several substrates for cdk8, when thus is involved in the pre–messenger RNA processing machinery. All
complexed with the above-mentioned proteins, have been detected, cyclins share an approximately 150-amino-acid region, called the cyclin
including RNA polymerase II and histone H3. Cdk8 directly antag- box, which interacts with the cdks. The G cyclins (C, D, and E) and the
25
34
1
onizes the repression of β-catenin transcription by the transcription mitotic cyclins (A and B) form distinct categories, although cyclin H,
35
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 214 9/18/15 11:56 PM