Page 242 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 242
216 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 217
the caspase-processed p46 isoform is generated from the larger p110 malignancy. RB controls the activity of several other cell-cycle regula-
99
isoform and it promotes apoptosis when it is ectopically expressed in tory elements such as Skp2. The Skp2 regulation follows an autocrine
93
human cells. Cdk11 also stabilizes the microtubule assembly of cells ; loop where Skp2 triggers degradation of the cdk inhibitor p27 kip1 , fol-
cdk11 is therefore mandatory for the maintenance of sister chromatid lowed by cyclin E/cdk2 activation, consecutive cdk2-induced RB-phos-
100
cohesion and its disruption can contribute to the development of phorylation, and further E2F-dependent Skp2 expression. Causes of
94
cancer. 95 reduced RB activity include changes in the structural gene, the seques-
tration and inactivation of the protein by viral oncogene products, and
SUBSTRATES AND INHIBITORS hyperphosphorylation of RB as a result of increased cdk4 and cyclin
inhibitor of cdk4.
INK4A
D activity or deletion of the gene for the p16
OF CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASES Deletions, mutations, and translocations of RB are common in various
Many cyclin–cdk substrates have been identified by immunoprecipita- malignancies, while homozygous deletions of the p16 INK4A gene are even
tion or two-hybrid assays, but only a few of them are thought to exert more frequent. Many different transforming viruses (papillomavirus,
a direct function in cell-cycle control. The regulation of the cell cycle simian virus 40) produce proteins that interact with RB. Both cyclin
has been studied extensively during the last decade and a consensus D –cdk4 and cyclin D (D , D )–cdk6 complexes are able to phosphory-
3
1
2
1
paradigm of cell-cycle regulation has been suggested. 50,96 According to late RB. 101,102 The time point of RB phosphorylation correlates strongly
103
this paradigm, the important switch of the cell cycle is the RB family with the appearance of the cyclin D –cdk4 complex. The link between
1
of proteins (Fig. 16–2). In its hypophosphorylated state, RB binds to RB and cyclin D is supported by the observation that loss of RB function
104
and inhibits a class of transcription factors, of which the best character- leads to a decrease in the cellular cyclin D level. However, cyclin D is
ized is the E2F transcription factor. Hyperphosphorylation causes RB not the only cyclin that is involved in the RB regulatory pathway. 99,102
to detach from its binding site, permitting transcriptional activation of Ectopic expression of both cyclin A and cyclin E restores RB hyperphos-
genes necessary for DNA synthesis and cell division. This phosphory- phorylation and causes cell-cycle arrest in cancer cell lines. Perhaps the
lation of RB is regulated in a cell-cycle–dependent manner. A widely cdk2–cyclin A complex contributes to additional phosphorylation of
97
accepted model suggests that RB is phosphorylated by different regula- RB, whereas the cdk2–cyclin E complex prolongs the phosphorylation
tors such as cyclin E/cdk2 at the so-called “R” point, a time point during time. 105
G when cell cycle progression becomes independent of exogenous stim- The key regulatory element for the G -to-S transition is the RB–E2F
1
1
uli. Interference with RB function impairs G checkpoint regulation complex. After RB is phosphorylated by cdk4 and/or cdk6 complexes
98
1
and fosters unrestrained cell growth, a nearly universal characteristic of during G phase and cdk2 at G /S interphase, E2F proteins are released
1
1
and promote the transcription of genes essential for the transition to
S phase. 99,106 As mentioned above, the p16 INK4A /cyclin D /cdk4/RB/E2F
1
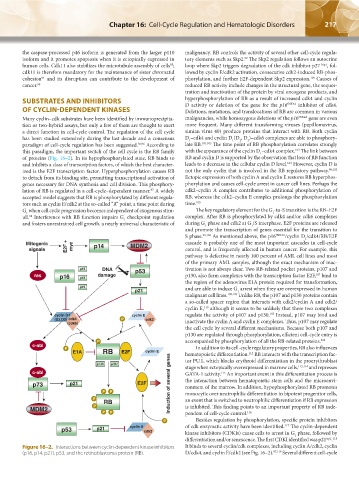
Mitogenic p14 MDM2 cascade is probably one of the most important cascades in cell-cycle
signals E2F + myc control, and is frequently affected in human cancer. For example, this
pathway is defective in nearly 100 percent of AML cell lines and most
of the primary AML samples, although the exact mechanism of inac-
p15 DNA p53 tivation is not always clear. Two RB-related pocket proteins, p107 and
107
ras p16 p18 damage p130, also form complexes with the transcription factor E2F, bind to
the region of the adenovirus E1A protein required for transformation,
p19 and are able to induce G arrest when they are overexpressed in human
p21 1
malignant cell lines. 108,109 Unlike RB, the p107 and p130 proteins contain
a so-called spacer region that interacts with cdk2/cyclin A and cdk2/
cyclin E, although it seems to be unlikely that these two complexes
110
105
cyclin D1 cyclin E regulate the activity of p107 and p130. Instead, p107 may bind and
(D2,D3) cdk4 P cdk2 inactivate the cyclin A and cyclin E complexes. Thus, p107 may regulate
(cdk6)
the cell cycle by several different mechanisms. Because both p107 and
p130 are regulated through phosphorylation, efficient cell-cycle entry is
P accompanied by phosphorylation of all the RB-related proteins. 111
c-abl
P In addition to its cell-cycle regulatory properties, RB also influences
E1A RB E2F cyclin E hematopoietic differentiation. RB interacts with the transcription fac-
112
p130 p107 tor PU.1, which blocks erythroid differentiation in the proerythroblast
stage when ectopically overexpressed in marrow cells,
113,114
and represses
c-abl GATA-1 activity. An important event in this differentiation process is
115
p73 p21 E2F Induction of several genes the interaction between hematopoietic stem cells and the microenvi-
ronment of the marrow. In addition, hypophosphorylated RB promotes
P P monocytic over neutrophilic differentiation in bipotent progenitor cells,
P an event that is switched to neutrophilic differentiation if RB expression
RB
MDM2 P P P is inhibited. This finding points to an important property of RB inde-
116
pendent of cell-cycle control.
P Besides regulation by phosphorylation, specific protein inhibitors
117
p53 p21 cyclin A cdk2 of cdk enzymatic activity have been identified. The cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitors (CDKIs) cause cells to arrest in G phase, followed by
1
differentiation and/or senescence. The first CDKI identified was p21 .
cip1 118
Figure 16–2. Interactions between cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors It binds to several cyclin/cdk complexes, including cyclin A/cdk2, cyclin
(p16, p14, p21), p53, and the retinoblastoma protein (RB). D/cdk4, and cyclin E/cdk2 (see Fig. 16–2). 97,119 Several different cell-cycle
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 217 9/18/15 11:57 PM