Page 344 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 344
318 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 22: Pharmacology and Toxicity of Antineoplastic Drugs 319
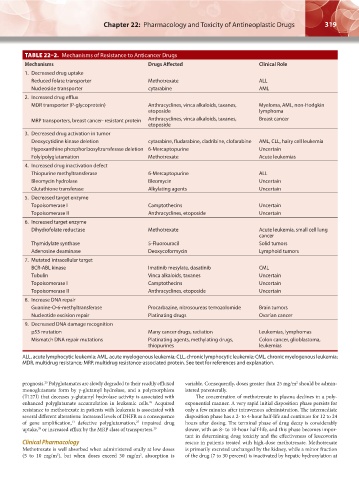
TABLE 22–2. Mechanisms of Resistance to Anticancer Drugs
Mechanisms Drugs Affected Clinical Role
1. Decreased drug uptake
Reduced folate transporter Methotrexate ALL
Nucleoside transporter cytarabine AML
2. Increased drug efflux
MDR transporter (P-glycoprotein) Anthracyclines, vinca alkaloids, taxanes, Myeloma, AML, non-Hodgkin
etoposide lymphoma
MRP transporters, breast cancer- resistant protein Anthracyclines, vinca alkaloids, taxanes, Breast cancer
etoposide
3. Decreased drug activation in tumor
Deoxycytidine kinase deletion cytarabine, fludarabine, cladribine, clofarabine AML, CLL, hairy cell leukemia
Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase deletion 6-Mercaptopurine Uncertain
Folylpolyglutamation Methotrexate Acute leukemias
4. Increased drug inactivation defect
Thiopurine methyltransferase 6-Mercaptopurine ALL
Bleomycin hydrolase Bleomycin Uncertain
Glutathione transferase Alkylating agents Uncertain
5. Decreased target enzyme
Topoisomerase I Camptothecins Uncertain
Topoisomerase II Anthracyclines, etoposide Uncertain
6. Increased target enzyme
Dihydrofolate reductase Methotrexate Acute leukemia, small cell lung
cancer
Thymidylate synthase 5-Fluorouracil Solid tumors
Adenosine deaminase Deoxycoformycin Lymphoid tumors
7. Mutated intracellular target
BCR-ABL kinase Imatinib mesylate, dasatinib CML
Tubulin Vinca alkaloids, taxanes Uncertain
Topoisomerase I Camptothecins Uncertain
Topoisomerase II Anthracyclines, etoposide Uncertain
8. Increase DNA repair
Guanine-O-6-methyltransferase Procarbazine, nitrosoureas temozolomide Brain tumors
Nucleotide excision repair Platinating drugs Ovarian cancer
9. Decreased DNA damage recognition
p53 mutation Many cancer drugs, radiation Leukemias, lymphomas
Mismatch DNA repair mutations Platinating agents, methylating drugs, Colon cancer, glioblastoma,
thiopurines leukemias
ALL, acute lymphocytic leukemia; AML, acute myelogenous leukemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia;
MDR, multidrug resistance; MRP, multidrug resistance-associated protein. See text for references and explanation.
25
2
prognosis. Polyglutamates are slowly degraded to their readily effluxed variable. Consequently, doses greater than 25 mg/m should be admin-
monoglutamate form by γ-glutamyl hydrolase, and a polymorphism istered parenterally.
(T127I) that deceases γ-glutamyl hydrolase activity is associated with The concentration of methotrexate in plasma declines in a poly-
enhanced polyglutamate accumulation in leukemic cells. Acquired exponential manner. A very rapid initial disposition phase persists for
26
resistance to methotrexate in patients with leukemia is associated with only a few minutes after intravenous administration. The intermediate
several different alterations: increased levels of DHFR as a consequence disposition phase has a 2- to 4-hour half-life and continues for 12 to 24
13
27
of gene amplification, defective polyglutamation, impaired drug hours after dosing. The terminal phase of drug decay is considerably
28
uptake, or increased efflux by the MRP class of transporters. 29 slower, with an 8- to 10-hour half-life, and this phase becomes impor-
tant in determining drug toxicity and the effectiveness of leucovorin
Clinical Pharmacology rescue in patients treated with high-dose methotrexate. Methotrexate
Methotrexate is well absorbed when administered orally at low doses is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidney, while a minor fraction
(5 to 10 mg/m ), but when doses exceed 30 mg/m , absorption is of the drug (7 to 30 percent) is inactivated by hepatic hydroxylation at
2
2
Kaushansky_chapter 22_p0313-0352.indd 319 9/18/15 10:24 PM