Page 345 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 345
320 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 22: Pharmacology and Toxicity of Antineoplastic Drugs 321
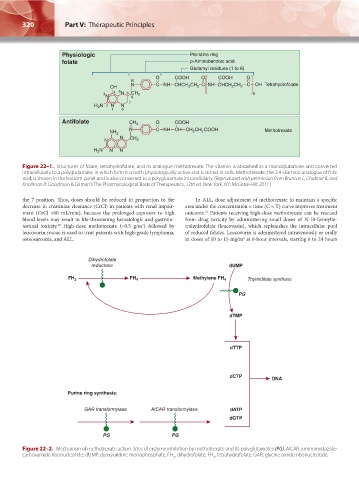
Physiologic Pteridine ring
folate p-Aminobenzoic acid
Glutamyl residues (1 to 6)
O COOH O COOH O
10
OH N C NH CHCH 2 CH 2 C NH CHCH 2 CH 2 C OH Tetrahydrofolate
4 5
3 N 6 CH 2 n
N 9
7
H N 2 N N
2
1 88
Antifolate CH 3 O COOH
N C NH CH CH CH COOH Methotrexate
NH 2 2 2
N CH
N 2
H N N N
2
Figure 22–1. Structures of folate, tetrahydrofolate, and its analogue methotrexate. The vitamin is absorbed as a monoglutamate and converted
intracellularly to a polyglutamate, in which form it is both physiologically active and is stored in cells. Methotrexate, the 2,4-diamino analogue of folic
acid, is shown in the bottom panel and is also converted to a polyglutamate intracellularly. (Reproduced with permission from Brunton L, Chabner B, and
Knollman B: Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011.)
the 7 position. Thus, doses should be reduced in proportion to the In ALL, dose adjustment of methotrexate to maintain a specific
decrease in creatinine clearance (CrCl) in patients with renal impair- area under the concentration × time (C × T) curve improves treatment
31
ment (CrCl <60 mL/min), because the prolonged exposure to high outcome. Patients receiving high-dose methotrexate can be rescued
blood levels may result in life-threatening hematologic and gastroin- from drug toxicity by administering small doses of N-10-formylte-
testinal toxicity. High-dose methotrexate (>0.5 g/m ) followed by trahydrofolate (leucovorin), which replenishes the intracellular pool
30
2
leucovorin rescue is used to treat patients with high-grade lymphoma, of reduced folates. Leucovorin is administered intravenously or orally
2
osteosarcoma, and ALL. in doses of 10 to 15 mg/m at 6-hour intervals, starting 6 to 24 hours
Dihydrofolate
reductase dUMP
FH 2 FH 4 Methylene FH 4 Thymidilate synthase
PG
dTMP
dTTP
dCTP
DNA
Purine ring synthesis:
GAR transformylase AICAR transformylase dATP
dGTP
PG PG
Figure 22–2. Mechanism of methotrexate action. Sites of enzyme inhibition by methotrexate and its polyglutamates (PG). AICAR, aminoimidazole-
carboxamide ribonucleotide; dUMP, deoxyuridine monophosphate; FH , dihydrofolate; FH , tetrahydrofolate; GAR, glycine amide ribonucleotide.
2 4
Kaushansky_chapter 22_p0313-0352.indd 320 9/18/15 10:24 PM