Page 355 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 355
330 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 22: Pharmacology and Toxicity of Antineoplastic Drugs 331
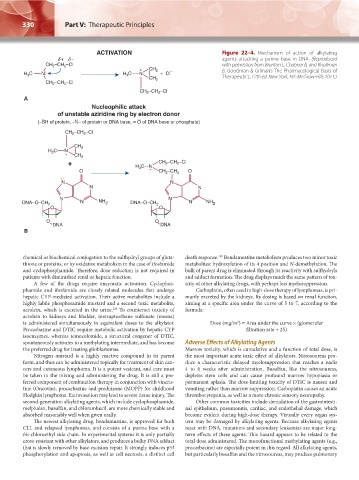
Figure 22–4. Mechanism of action of alkylating
agents attacking a purine base in DNA. (Reproduced
with permission from Brunton L, Chabner B, and Knollman
B: Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of
Therapeutics, 12th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011.)
(–SH of protein, –N– of protein or DNA base, = O of DNA base or phosphate)
chemical or biochemical conjugation to the sulfhydryl groups of gluta- death response. Bendamustine metabolism produces two minor toxic
130
thione or proteins, or by oxidative metabolism in the case of ifosfamide metabolites: hydroxylation of its 4 position and N-demethylation. The
and cyclophosphamide. Therefore, dose reduction is not required in bulk of parent drug is eliminated through its reactivity with sulfhydryls
patients with diminished renal or hepatic function. and adduct formation. The drug displays much the same pattern of tox-
A few of the drugs require enzymatic activation. Cyclophos- icity of other alkylating drugs, with perhaps less myelosuppression.
phamide and ifosfamide are closely related molecules that undergo Carboplatin, often used in high-dose therapy of lymphomas, is pri-
hepatic CYP-mediated activation. Their active metabolites include a marily excreted by the kidneys. Its dosing is based on renal function,
highly labile phosphoramide mustard and a second toxic metabolite, aiming at a specific area under the curve of 5 to 7, according to the
acrolein, which is excreted in the urine. To counteract toxicity of formula:
129
acrolein to kidneys and bladder, mercaptoethane sulfonate (mesna)
is administered simultaneously in equivalent doses to the alkylator. Dose (mg/m ) = Area under the curve × (glomerular
2
Procarbazine and DTIC require metabolic activation by hepatic CYP filtration rate + 25)
isoenzymes, whereas temozolomide, a structural congener of DTIC,
spontaneously activates to a methylating intermediate, and has become Adverse Effects of Alkylating Agents
the preferred drug for treating glioblastomas. Marrow toxicity, which is cumulative and a function of total dose, is
Nitrogen mustard is a highly reactive compound in its parent the most important acute toxic effect of alkylators. Nitrosoureas pro-
form, and thus can be administered topically for treatment of skin can- duce a characteristic delayed myelosuppression that reaches a nadir
cers and cutaneous lymphoma. It is a potent vesicant, and care must 4 to 6 weeks after administration. Busulfan, like the nitrosoureas,
be taken in the mixing and administering the drug. It is still a pre- depletes stem cells and can cause profound marrow hypoplasia or
ferred component of combination therapy in conjunction with vincris- permanent aplasia. The dose-limiting toxicity of DTIC is nausea and
tine (Oncovin), procarbazine and prednisone (MOPP) for childhood vomiting rather than marrow suppression. Carboplatin causes an acute
Hodgkin lymphoma. Extravasation may lead to severe tissue injury. The thrombocytopenia, as well as a more chronic sensory neuropathy.
second-generation alkylating agents, which include cyclophosphamide, Other common toxicities include denudation of the gastrointesti-
melphalan, busulfan, and chlorambucil, are more chemically stable and nal epithelium, pneumonitis, cardiac, and endothelial damage, which
absorbed reasonably well when given orally. become evident during high-dose therapy. Virtually every organ sys-
The newest alkylating drug, bendamustine, is approved for both tem may be damaged by alkylating agents. Because alkylating agents
CLL and relapsed lymphomas, and consists of a purine base with a react with DNA, mutations and secondary leukemias are major long-
bis-chloroethyl side chain. In experimental systems it is only partially term effects of these agents. This hazard appears to be related to the
cross-resistant with other alkylators, and produces a bulky DNA adduct total dose administered. The monofunctional methylating agents (e.g.,
that is slowly removed by base excision repair. It strongly induces p53 procarbazine) are especially potent in this regard. All alkylating agents,
phosphorylation and apoptosis, as well as cell necrosis, a distinct cell but particularly busulfan and the nitrosoureas, may produce pulmonary
Kaushansky_chapter 22_p0313-0352.indd 330 9/18/15 10:25 PM