Page 365 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 365
340 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 22: Pharmacology and Toxicity of Antineoplastic Drugs 341
CH 2
N
CH 3
H
N N
N
N
HN
CH SO H
2
2
N O
Imatinib
HO
N Cl
H O
N N S
N H O
2
N N N H
H C CI CI
3
CH 3
Dasatinib
O NH
N O
H 3 C
N
N O N
N N
Bosutinib
2
O HCL, H O
H
N N
N CF 3
H H
N N
H C N
2
N O N
N
F F N
N
F
Nilotinib Ponatinib
A B
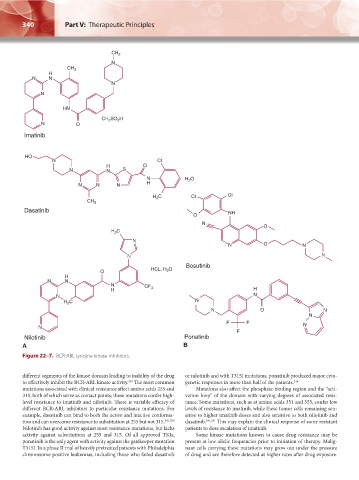
Figure 22–7. BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
different segments of the kinase domain leading to inability of the drug or nilotinib and with T315I mutations, ponatinib produced major cyto-
to effectively inhibit the BCR-ABL kinase activity. The most common genetic responses in more than half of the patients. 246
249
mutations associated with clinical resistance affect amino acids 255 and Mutations also affect the phosphate-binding region and the “acti-
315, both of which serve as contact points; these mutations confer high- vation loop” of the domain with varying degrees of associated resis-
level resistance to imatinib and nilotinib. There is variable efficacy of tance. Some mutations, such as at amino acids 351 and 355, confer low
different BCR-ABL inhibitors to particular resistance mutations. For levels of resistance to imatinib, while these tumor cells remaining sen-
example, dasatinib can bind to both the active and inactive conforma- sitive to higher imatinib doses and also sensitive to both nilotinib and
tion and can overcome resistance to substitution at 255 but not 315. 241,250 dasatinib. 241,251 This may explain the clinical response of some resistant
Nilotinib has good activity against most resistance mutations, but lacks patients to dose escalation of imatinib.
activity against substitutions at 255 and 315. Of all approved TKIs, Some kinase mutations known to cause drug resistance may be
ponatinib is the only agent with activity against the gatekeeper mutation present at low allelic frequencies prior to initiation of therapy. Malig-
T315I. In a phase II trial of heavily pretreated patients with Philadelphia nant cells carrying these mutations may grow out under the pressure
chromosome positive leukemias, including those who failed dasatinib of drug and are therefore detected at higher rates after drug exposure.
Kaushansky_chapter 22_p0313-0352.indd 340 9/18/15 10:26 PM