Page 465 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 465
440 Part V: Therapeutic Principles Chapter 29: Gene Therapy for Hematologic Diseases 441
Adding prodrug: AP1903
Modified caspase-9 FK506 Dimerization and
Caspase-9 activated
Casepase 3 and 7
activated
The iCasp9 suicide gene system
Apoptosis
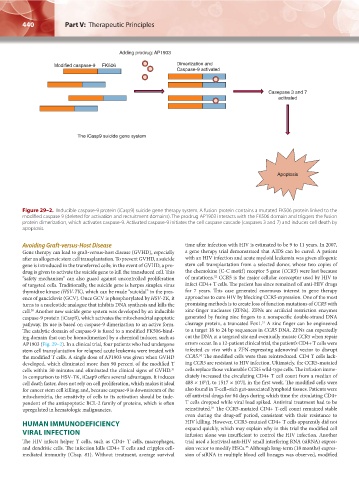
Figure 29–2. Inducible caspase-9 protein (iCasp9) suicide gene therapy system. A fusion protein contains a mutated FK506 protein linked to the
modified caspase 9 (deleted for activation and recruitment domains). The prodrug AP1903 interacts with the FK506 domain and triggers the fusion
protein dimerization, which activates caspase-9. Activated caspase-9 initiates the cell caspase cascade (caspases 3 and 7) and induces cell death by
apoptosis.
Avoiding Graft-versus-Host Disease time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years. In 2007,
Gene therapy can lead to graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), especially a gene therapy trial demonstrated that AIDS can be cured. A patient
after an allogeneic stem cell transplantation. To prevent GVHD, a suicide with an HIV infection and acute myeloid leukemia was given allogenic
gene is introduced in the transferred cells; in the event of GVHD, a pro- stem cell transplantation from a selected donor, whose two copies of
drug is given to activate the suicide gene to kill the transduced cell. This the chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 gene (CCR5) were lost because
32
“safety mechanism” can also guard against uncontrolled proliferation of mutations. CCR5 is the major cellular coreceptor used by HIV to
of targeted cells. Traditionally, the suicide gene is herpes simplex virus infect CD4+ T cells. The patient has since remained off anti-HIV drugs
thymidine kinase (HSV-TK), which can be made “suicidal” in the pres- for 7 years. This case generated enormous interest in gene therapy
ence of ganciclovir (GCV). Once GCV is phosphorylated by HSV-TK, it approaches to cure HIV by blocking CCR5 expression. One of the most
turns to a nucleotide analogue that inhibits DNA synthesis and kills the promising methods is to create loss of function mutations of CCR5 with
cell. Another new suicide gene system was developed by an inducible zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs). ZFNs are artificial restriction enzymes
30
caspase-9 protein (iCasp9), which activates the mitochondrial apoptotic generated by fusing zinc fingers to a nonspecific double-strand DNA
33
pathway. Its use is based on caspase-9 dimerization to an active form. cleavage protein, a truncated Fox1. A zinc finger can be engineered
The catalytic domain of caspase-9 is fused to a modified FK506-bind- to a target 18 to 24 bp sequences in CCR5 DNA. ZFNs can repeatedly
ing domain that can be homodimerized by a chemical inducer, such as cut the DNA at a targeted site and eventually mutate CCR5 when repair
AP1903 (Fig. 29–2). In a clinical trial, four patients who had undergone errors occur. In a 12-patient clinical trial, the patient’s CD4+ T cells were
stem cell transplantation for relapsed acute leukemia were treated with infected ex vivo with a ZFN-expressing adenoviral vector to disrupt
34
the modified T cells. A single dose of AP1903 was given when GVHD CCR5. The modified cells were then reintroduced. CD4 T cells lack-
developed, which eliminated more than 90 percent of the modified T ing CCR5 are resistant to HIV infection. Ultimately, the CCR5-mutated
cells within 30 minutes and eliminated the clinical signs of GVHD. cells replace those vulnerable CCR5 wild-type cells. The infusion imme-
31
In comparison to HSV-TK, iCasp9 offers several advantages. It induces diately increased the circulating CD4+ T cell count from a median of
9
9
cell death faster, does not rely on cell proliferation, which makes it ideal 488 × 10 /L to 1517 × 10 /L in the first week. The modified cells were
for cancer stem cell killing; and, because caspase-9 is downstream of the also found in T-cell–rich gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Patients were
mitochondria, the sensitivity of cells to its activation should be inde- off antiviral drugs for 84 days during which time the circulating CD4+
pendent of the antiapoptotic BCL-2 family of proteins, which is often T cells dropped while viral load spiked. Antiviral treatment had to be
34
upregulated in hematologic malignancies. reinstituted. The CCR5-mutated CD4+ T-cell count remained stable
even during the drug-off period, consistent with their resistance to
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY HIV killing. However, CCR5-mutated CD4+ T cells apparently did not
VIRAL INFECTION expand quickly, which may explain why in this trial the modified cell
infusion alone was insufficient to control the HIV infection. Another
The HIV infects helper T cells, such as CD4+ T cells, macrophages, trial used a lentiviral anti-HIV small interfering RNA (siRNA) expres-
and dendritic cells. The infection kills CD4+ T cells and cripples cell- sion vector to modify HSCs. Although long-term (18 months) expres-
35
mediated immunity (Chap. 81). Without treatment, average survival sion of siRNA in multiple blood cell lineages was observed, modified
Kaushansky_chapter 29_p0437-0446.indd 440 9/19/15 12:22 AM