Page 908 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 908
882 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 57: Primary and Secondary Erythrocytoses 883
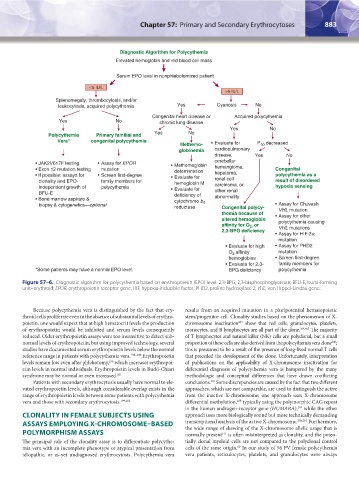
Figure 57–6. Diagnostic algorithm for polycythemia based on erythropoietin (EPO) level. 2,3-BPG, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate; BFU-E, burst-forming
unit–erythroid; EPOR, erythropoietin receptor gene; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; PHD2, proline hydroxylase 2; VHL, von Hippel-Lindau gene.
Because polycythemia vera is distinguished by the fact that ery- results from an acquired mutation in a pluripotential hematopoietic
throid cells proliferate even in the absence of substantial levels of erythro- stem/progenitor cell. Clonality studies based on the phenomenon of X-
poietin, one would expect that at high hematocrit levels the production chromosome inactivation show that red cells, granulocytes, platelets,
203
of erythropoietin would be inhibited and serum levels consequently monocytes, and B lymphocytes are all part of the clone. 204,205 The majority
reduced. Older erythropoietin assays were too insensitive to detect sub- of T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells are polyclonal, but a small
normal levels of erythropoietin, but using improved technology, several proportion of these cells are also derived from the polycythemia vera clone ;
206
studies have documented serum erythropoietin levels below the normal this is presumed to be a result of the presence of long-lived normal T cells
reference range in patients with polycythemia vera. 198–200 Erythropoietin that preceded the development of the clone. Unfortunately, interpretation
levels remain low even after phlebotomy, which increases erythropoi- of publications on the applicability of X-chromosome inactivation for
198
etin levels in normal individuals. Erythropoietin levels in Budd-Chiari differential diagnosis of polycythemia vera is hampered by the many
syndrome may be normal or even increased. 201 methodologic and conceptual differences that have drawn conflicting
Patients with secondary erythrocytosis usually have normal to ele- conclusions. Some discrepancies are caused by the fact that two different
207
vated erythropoietin levels, although considerable overlap exists in the approaches, which are not comparable, are used to distinguish the active
range of erythropoietin levels between some patients with polycythemia from the inactive X-chromosome; one approach uses X-chromosome
vera and those with secondary erythrocytosis. 199,202 differential methylation, typically using the polymorphic CAG repeat
208
in the human androgen-receptor gene (HUMARA), while the other
209
CLONALITY IN FEMALE SUBJECTS USING approach uses more biologically sound but more technically demanding
ASSAYS EMPLOYING X-CHROMOSOME–BASED transcriptional analysis of the active X-chromosome. 208,210 Furthermore,
the wide range of skewing of the X-chromosome allelic usage that is
POLYMORPHISM ASSAYS normally present is often misinterpreted as clonality, and the poten-
211
The principal role of the clonality assay is to differentiate polycythe- tially clonal myeloid cells are not compared to the polyclonal control
mia vera with an incomplete phenotype or atypical presentation from cells of the same origin. In our study of 56 PV female polycythemia
50
idiopathic, or as-yet undiagnosed erythrocytosis. Polycythemia vera vera patients, reticulocytes, platelets, and granulocytes were always
Kaushansky_chapter 57_p0871-0888.indd 883 9/18/15 9:37 AM