Page 1102 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1102
1066 ParT EIGhT Immunology of Neoplasia
The guiding principles of the World Health Organization (GEP) in lymphomas has generated distinct molecular “signatures”
(WHO) classification of neoplasms of the hematopoietic and for a variety of disease entities, in some cases corresponding
lymphoid tissues, published in 2001 and updated in 2008 and more closely to different stages of lymphoid differentiation
2
2016, were based on the Revised European American Classification and in other instances offering insights into mechanisms of
of Lymphoid Neoplasms (REAL), which was published by the neoplastic transformation with delineation of alterations in
International Lymphoma Study group in 1994. The focus was specific pathways. The advent of whole-genome sequencing
on the identification of individual diseases based on an integration contributes additional new insights into pathogenetic mechanisms.
of morphological, immunophenotypic, genetic, and clinical Recently, a revision of the nearly 8-year-old WHO classification
features. The recent application of gene expression profiling of lymphoid neoplasms (Table 79.1) was published clarifying
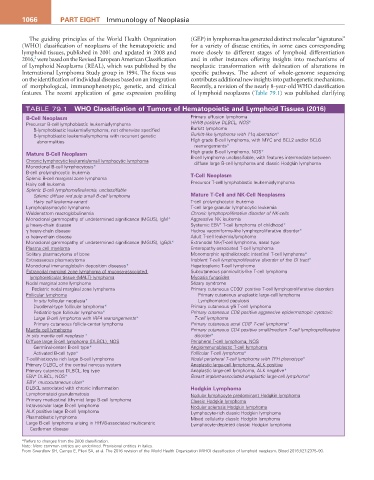
TABLE 79.1 WhO Classification of Tumors of hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (2016)
B-Cell Neoplasm Primary effusion lymphoma
Precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma HHV8 positive DLBCL, NOS*
B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, not otherwise specified Burkitt lymphoma
B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with recurrent genetic Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration*
abnormalities High grade B-cell lymphoma, with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6
rearrangements*
Mature B-Cell Neoplasm High grade B-cell lymphoma, NOS*
B-cell lymphoma unclassifiable, with features intermediate between
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis*
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia T-Cell Neoplasm
Splenic B-cell marginal zone lymphoma
Hairy cell leukemia Precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
Splenic B-cell lymphoma/leukemia, unclassifiable
Splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma Mature T-Cell and NK-Cell Neoplasms
Hairy cell leukemia-variant T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK-cells
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), IgM* Aggressive NK leukemia
+
µ heavy-chain disease Systemic EBV T-cell lymphoma of childhood*
γ heavy-chain disease Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder*
α heavy-chain disease Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), IgG/A* Extranodal NK-/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type
Plasma cell myeloma Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma
Solitary plasmacytoma of bone Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma*
Extraosseous plasmacytoma Indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the GI tract*
Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition diseases* Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
lymphoreticular tissue (MALT) lymphoma Mycosis fungoides
Nodal marginal zone lymphoma Sézary syndrome
+
Pediatric nodal marginal zone lymphoma Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders
Follicular lymphoma Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
In situ follicular neoplasia* Lymphomatoid papulosis
Duodenal-type follicular lymphoma* Primary cutaneous γ/δ T-cell lymphoma
Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma* Primary cutaneous CD8 positive aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic
Large B-cell lymphoma with IRF4 rearrangements* T-cell lymphoma
+
Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma Primary cutaneous acral CD8 T-cell lymphoma*
Mantle cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous CD4 positive small/medium T-cell lymphoproliferative
In situ mantle cell neoplasia * disorder*
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), NOS Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, NOS
Germinal-center B-cell type* Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
Activated B-cell type* Follicular T-cell lymphoma*
T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma Nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with TFH phenotype*
Primary DLBCL of the central nervous system Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, ALK positive
Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, ALK negative*
EBV DLBCL, NOS* Breast implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma*
+
+
EBV mucocutaneous ulcer*
DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation hodgkin Lymphoma
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma
ALK positive large B-cell lymphoma Lymphocyte-rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Plasmablastic lymphoma Mixed cellularity classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Large B-cell lymphoma arising in HHV8-associated multicentric Lymphocyte-depleted classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Castleman disease
*Refers to changes from the 2008 classification.
Note: More common entities are underlined. Provisional entities in italics.
From Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of lymphoid neoplasm. Blood 2016;127:2375–90.