Page 1101 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1101
79
Lymphomas
Stefania Pittaluga, Tapan Bhavsar, Elaine S. Jaffe
The classification of malignant lymphomas continues to undergo KEY CONCEPTS
revision based on insights gained through the application of Lymphoma
immunological and molecular techniques and the application of
these discoveries to individualized therapeutic approaches. Early • Classification consists of a list of individual disease entities defined
classifications were based on morphological characteristics of the by morphological, immunophenotypic, genetic, and clinical features.
neoplastic elements; however, with increasing knowledge of the • Neoplastic cells are related to the postulated normal counterpart,
complexity of the immune system, a more functional approach was when possible.
sought. Differentiation schemes provided a useful starting point for • Histological grade should be applied within individual diseases.
understanding lymphomas (Fig. 79.1). High-throughput genomic • Clinical factors for individual patients, as measured by the International
Prognostic Index (IPI) and gene expression profiling, are useful in
studies of both tumor RNA and tumor DNA have been applied to predicting clinical outcome.
lymphomas to define their molecular signatures with the aim of
improving the understanding of oncogenic pathways and their clinical
implications. These studies have led to new prognostic and diagnostic
tools, and as a result, more targeted therapies have emerged. 1
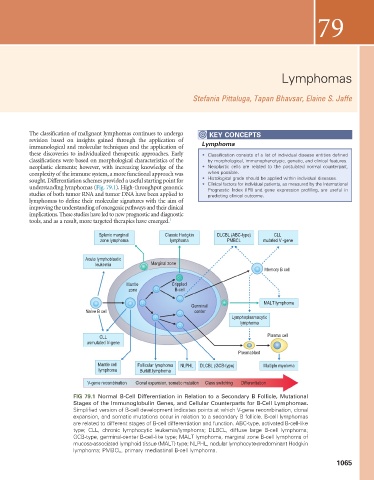
Splenic marginal Classic Hodgkin DLCBL (ABC-type) CLL
zone lymphoma lymphoma PMBCL mutated V -gene
Acute lymphoblastic
leukemia Marginal zone
Memory B cell
Mantle Crippled
zone B-cell
MALT lymphoma
Germinal
NaÏve B cell center
Lymphoplasmacytic
lymphoma
CLL Plasma cell
unmutated V-gene
Plasmablast
Mantle cell Follicular lymphoma NLPHL DLCBL (GCB-type) Multiple myeloma
lymphoma Burkitt lymphoma
V-gene recombination Clonal expansion, somatic mutation Class switching Differentiation
FIG 79.1 Normal B-Cell Differentiation in Relation to a Secondary B Follicle, Mutational
Stages of the Immunoglobulin Genes, and Cellular Counterparts for B-Cell Lymphomas.
Simplified version of B-cell development indicates points at which V-gene recombination, clonal
expansion, and somatic mutations occur in relation to a secondary B follicle. B-cell lymphomas
are related to different stages of B-cell differentiation and function. ABC-type, activated B-cell-like
type; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma;
GCB-type, germinal-center B-cell-like type; MALT lymphoma, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) type; NLPHL, nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin
lymphoma; PMBCL, primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.
1065