Page 1171 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1171
CHAPTER 83 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Malignant Diseases 1135
product and the quantities and functions of other blood cells Influence of graft, donor, and host factors on allogeneic HSC engraftment
comprising most of the cellular content of the HSC product that
may influence the immunological outcomes of transplantation. Greater Lesser
PBSCs have virtually replaced bone marrow as the HSC source for HSC dose
auto-HSCT and are widely used for allo-HSCT. Transplantation
of PBSCs achieves more rapid hematological recovery in both the
auto- and allo-HSCT settings, resulting in lower complication T-cell dose
rates and lower costs of treatment. PBSCs appear to improve
overall survival and disease-free survival of patients with advanced
hematological malignancies who undergo allo-HSCT, although Engraftment HLA-compatibility Rejection
30
at the cost of an increased risk of extensive cGvHD. Use of
PBSCs results in a decreased CD4 T-helper cell-1 (Th1)/Th2 ratio, Pretransplant
which may adversely affect the ability to counteract infections conditioning
and may favor cGvHD development. It is also interesting to note Posttransplant
that PBSC products tend to contain about 10 times more T cells immunosuppression
than bone marrow products, yet those T cells are less functional,
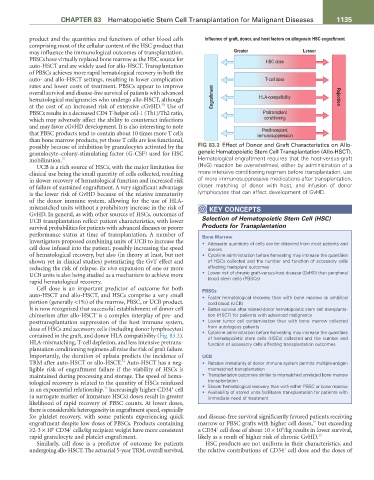
possibly because of inhibition by granulocytes activated by the FIG 83.3 Effect of Donor and Graft Characteristics on Allo-
granulocyte–colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) used for HSC geneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Allo-HSCT).
mobilization. 31 Hematological engraftment requires that the host-versus-graft
UCB is a rich source of HSCs, with the major limitation for (HvG) reaction be overwhelmed, either by administration of a
clinical use being the small quantity of cells collected, resulting more intensive conditioning regimen before transplantation, use
in slower recovery of hematological function and increased risk of more immunosuppressive medications after transplantation,
of failure of sustained engraftment. A very significant advantage closer matching of donor with host, and infusion of donor
is the lower risk of GvHD because of the relative immaturity lymphocytes that can affect development of GvHD.
of the donor immune system, allowing for the use of HLA-
mismatched units without a prohibitory increase in the risk of KEY CONCEPTS
GvHD. In general, as with other sources of HSCs, outcomes of
UCB transplantation reflect patient characteristics, with lower Selection of Hematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC)
survival probabilities for patients with advanced diseases or poorer Products for Transplantation
performance status at time of transplantation. A number of Bone Marrow
investigators proposed combining units of UCB to increase the • Adequate quantities of cells can be obtained from most patients and
cell dose infused into the patient, possibly increasing the speed donors
of hematological recovery, but also (in theory at least, but not • Cytokine administration before harvesting may increase the quantities
shown yet in clinical studies) potentiating the GvT effect and of HSCs collected and the number and function of accessory cells
reducing the risk of relapse. Ex vivo expansion of one or more affecting transplant outcomes
UCB units is also being studied as a mechanism to achieve more • Lower risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) than peripheral
rapid hematological recovery. blood stem cells (PBSCs)
Cell dose is an important predictor of outcome for both PBSCs
auto-HSCT and allo-HSCT, and HSCs comprise a very small • Faster hematological recovery than with bone marrow or umbilical
portion (generally <1%) of the marrow, PBSC, or UCB product. cord blood (UCB)
It is now recognized that successful establishment of donor cell • Better survival after related-donor hematopoietic stem cell transplanta-
chimerism after allo-HSCT is a complex interplay of pre- and tion (HSCT) for patients with advanced malignancy
posttransplantation suppression of the host immune system, • Lower tumor cell contamination than with bone marrow collected
dose of HSCs and accessory cells (including donor lymphocytes) from autologous patients
contained in the graft, and donor HLA compatibility (Fig. 83.3). • Cytokine administration before harvesting may increase the quantities
of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) collected and the number and
HLA-mismatching, T-cell depletion, and less intensive pretrans- function of accessory cells affecting transplantation outcomes
plantation conditioning regimens all raise the risk of graft failure.
Importantly, the duration of aplasia predicts the incidence of UCB
32
TRM after auto-HSCT or allo-HSCT. Auto-HSCT has a neg- • Relative immaturity of donor immune system permits multiple-antigen
ligible risk of engraftment failure if the viability of HSCs is mismatched transplantation
maintained during processing and storage. The speed of hema- • Transplantation outcomes similar to mismatched unrelated bone marrow
tological recovery is related to the quantity of HSCs reinfused transplantation
+
33
in an exponential relationship. Increasingly higher CD34 cell • Slower hematological recovery than with either PBSC or bone marrow
• Availability of stored units facilitates transplantation for patients with
(a surrogate marker of immature HSCs) doses result in greater immediate need of treatment
likelihood of rapid recovery of PBSC counts. At lower doses,
there is considerable heterogeneity in engraftment speed, especially
for platelet recovery, with some patients experiencing quick and disease-free survival significantly favored patients receiving
34
engraftment despite low doses of PBSCs. Products containing marrow or PBSC grafts with higher cell doses, but exceeding
+
+
6
6
≥2-3 × 10 CD34 cells/kg recipient weight have more consistent a CD34 cell dose of about 10 × 10 /kg results in lower survival,
rapid granulocyte and platelet engraftment. likely as a result of higher risk of chronic GvHD. 35
Similarly, cell dose is a predictor of outcome for patients HSC products are not uniform in their characteristics, and
+
undergoing allo-HSCT. The actuarial 5-year TRM, overall survival, the relative contributions of CD34 cell dose and the doses of