Page 1206 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1206
1170 ParT TEN Prevention and Therapy of Immunological Diseases
21
CH OH CH OH CH 2 OH
2
2
20
18 CO CO CO
12 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
O OH O OH HO OH
19 11 13 17 16 CH 3
CH 3 9 C D CH 3 CH 3
2 14 15
A B 8 F
3
O 5 7 O O
4 6
Cortisone Prednisone Dexamethasone
CH OH CH OH CH OH
2
2
2
CO CO CO
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
HO OH HO OH HO OH
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
O O O
CH 3
Hydrocortisone (cortisol) Prednisolone Methylprednisolone
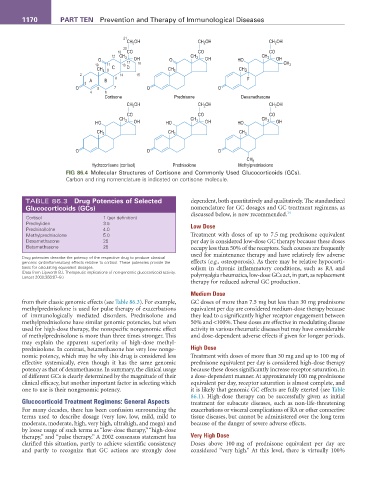
FIG 86.4 Molecular Structures of Cortisone and Commonly Used Glucocorticoids (GCs).
Carbon and ring nomenclature is indicated on cortisone molecule.
TABLE 86.3 Drug Potencies of Selected dependent, both quantitatively and qualitatively. The standardized
Glucocorticoids (GCs) nomenclature for GC dosages and GC treatment regimens, as
discussed below, is now recommended. 14
Cortisol 1 (per definition)
Prednyliden 3.5 Low Dose
Predniso(lo)ne 4.0
Methylprednisolone 5.0 Treatment with doses of up to 7.5 mg prednisone equivalent
Dexamethasone 25 per day is considered low-dose GC therapy because these doses
Betamethasone 25 occupy less than 50% of the receptors. Such courses are frequently
used for maintenance therapy and have relatively few adverse
Drug potencies describe the potency of the respective drug to produce classical
genomic (antiinflammatory) effects relative to cortisol. These potencies provide the effects (e.g., osteoporosis). As there may be relative hypocorti-
basis for calculating equivalent dosages. solism in chronic inflammatory conditions, such as RA and
(Data from Lipworth BJ. Therapeutic implications of non-genomic glucocorticoid activity.
Lancet 2000;356:87–9.) polymyalgia rheumatica, low-dose GCs act, in part, as replacement
therapy for reduced adrenal GC production.
Medium Dose
from their classic genomic effects (see Table 86.3). For example, GC doses of more than 7.5 mg but less than 30 mg prednisone
methylprednisolone is used for pulse therapy of exacerbations equivalent per day are considered medium-dose therapy because
of immunologically mediated disorders. Prednisolone and they lead to a significantly higher receptor engagement between
methylprednisolone have similar genomic potencies, but when 50% and <100%. These doses are effective in modulating disease
used for high-dose therapy, the nonspecific nongenomic effect activity in various rheumatic diseases but may have considerable
of methylprednisolone is more than three times stronger. This and dose-dependent adverse effects if given for longer periods.
may explain the apparent superiority of high-dose methyl-
prednisolone. In contrast, betamethasone has very low nonge- High Dose
nomic potency, which may be why this drug is considered less Treatment with doses of more than 30 mg and up to 100 mg of
effective systemically, even though it has the same genomic prednisone equivalent per day is considered high-dose therapy
potency as that of dexamethasone. In summary, the clinical usage because these doses significantly increase receptor saturation, in
of different GCs is clearly determined by the magnitude of their a dose-dependent manner. At approximately 100 mg prednisone
clinical efficacy, but another important factor in selecting which equivalent per day, receptor saturation is almost complete, and
one to use is their nongenomic potency. it is likely that genomic GC effects are fully exerted (see Table
86.1). High-dose therapy can be successfully given as initial
Glucocorticoid Treatment Regimens: General Aspects treatment for subacute diseases, such as non-life-threatening
For many decades, there has been confusion surrounding the exacerbations or visceral complications of RA or other connective
terms used to describe dosage (very low, low, mild, mild to tissue diseases, but cannot be administered over the long term
moderate, moderate, high, very high, ultrahigh, and mega) and because of the danger of severe adverse effects.
by loose usage of such terms as “low-dose therapy,” “high-dose
therapy,” and “pulse therapy.” A 2002 consensus statement has Very High Dose
clarified this situation, partly to achieve scientific consistency Doses above 100 mg of prednisone equivalent per day are
and partly to recognize that GC actions are strongly dose considered “very high.” At this level, there is virtually 100%