Page 148 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 148
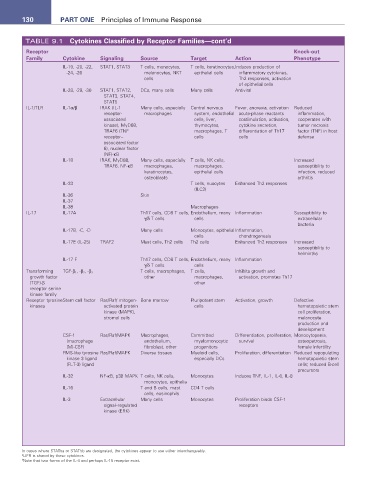
130 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
TABLE 9.1 Cytokines Classified by receptor Families—cont’d
receptor Knock-out
Family Cytokine Signaling Source Target action Phenotype
IL-19, -20, -22, STAT1, STAT3 T cells, monocytes, T cells, keratinocytes, Induces production of
-24, -26 melanocytes, NKT epithelial cells inflammatory cytokines,
cells Th2 responses, activation
of epithelial cells
IL-28, -29, -30 STAT1, STAT2, DCs, many cells Many cells Antiviral
STAT3, STAT4,
STAT5
IL-1/TLR IL-1α/β IRAK (IL-1 Many cells, especially Central nervous Fever, anorexia, activation Reduced
receptor- macrophages system, endothelial acute-phase reactants inflammation,
associated cells, liver, costimulation, activation, cooperates with
kinase), MyD88, thymocytes, cytokine secretion, tumor necrosis
TRAF6 (TNF macrophages, T differentiation of Th17 factor (TNF) in host
receptor– cells cells defense
associated factor
6), nuclear factor
(NF)-κB
IL-18 IRAK, MyD88, Many cells, especially T cells, NK cells, Increased
TRAF6, NF-κB macrophages, macrophages, susceptibility to
keratinocytes, epithelial cells infection, reduced
osteoblasts arthritis
IL-33 T cells, nuocytes Enhanced Th2 responses
(ILC2)
IL-36 Skin
IL-37
IL-38 Macrophages
IL-17 IL-17A Th17 cells, CD8 T cells, Endothelium, many Inflammation Susceptibility to
γ/δ T cells cells extracellular
bacteria
IL-17B, -C, -D Many cells Monocytes, epithelial Inflammation,
cells chondrogenesis
IL-17E (IL-25) TRAF2 Mast cells, Th2 cells Th2 cells Enhanced Th2 responses Increased
susceptibility to
helminths
IL-17 F Th17 cells, CD8 T cells, Endothelium, many Inflammation
γ/δ T cells cells
Transforming TGF-β 1 , -β 2 , -β 3 T cells, macrophages, T cells, Inhibits growth and
growth factor other macrophages, activation, promotes Th17
(TGF)-β other
receptor serine
kinase family
Receptor tyrosine Stem cell factor Ras/Raf/ mitogen- Bone marrow Pluripotent stem Activation, growth Defective
kinases activated protein cells hematopoietic stem
kinase (MAPK), cell proliferation,
stromal cells melanocyte
production and
development
CSF-1 Ras/Raf/MAPK Macrophages, Committed Differentiation, proliferation, Monocytopenia,
(macrophage endothelium, myelomonocytic survival osteopetrosis,
(M)-CSF) fibroblast, other progenitors female infertility
FMS-like tyrosine Ras/Raf/MAPK Diverse tissues Myeloid cells, Proliferation, differentiation Reduced repopulating
kinase 3 ligand especially DCs hematopoietic stem
(FLT-3) ligand cells; reduced B-cell
precursors
IL-32 NF-κB, p38 MAPK T cells, NK cells, Monocytes Induces TNF, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8
monocytes, epithelia
IL-16 T and B cells, mast CD4 T cells
cells, eosinophils
IL-3 Extracellular Many cells Monocytes Proliferation binds CSF-1
signal–regulated receptors
kinase (ERK)
In cases where STAT5a or STAT5b are designated, the cytokines appear to use either interchangeably.
a LIFR is shared by these cytokines.
b Note that two forms of the IL-4 and perhaps IL-15 receptor exist.