Page 161 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 161
CHaPTEr 9 Cytokines and Cytokine Receptors 143
is synthesized as a type II membrane protein and is expressed antibodies against CD40 with possible applications to treat
on activated B cells, T cells, and NK cells. Fas-induced apoptosis transplantation and autoimmune diseases have been developed. 52
can play an essential role in the termination of T-cell responses,
particularly in the peripheral immune system. Fas can also play Other TNF-Family Cytokines
a key role in the induction of cell death by cytotoxic T cells Other members of the TNFR family play various roles in the
(CTLs) and NK cells (Chapter 17), where it functions in conjunc- development and function of the immune system. OX-40, CD27,
tion with perforin. Nonapoptotic functions of FasL include CD30, and 4-1BB can mediate costimulation of T-cell activation.
lymphocyte costimulation and T-cell differentiation into short- The TNF family ligand BAFF (BlyS/TALL1/TNFSF13B) promotes
lived effector memory cells. 49,50 B-cell maturation and antibody secretion and can bind three
distinct receptors, TACI (TNFRSF13B), BADD-R (TNFRSF13C),
CD40 Ligand and CD40 and BCMA (TNFRSF17).
CD40 is expressed by a variety of cell types, including B cells,
DCs, monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. It plays a Signaling
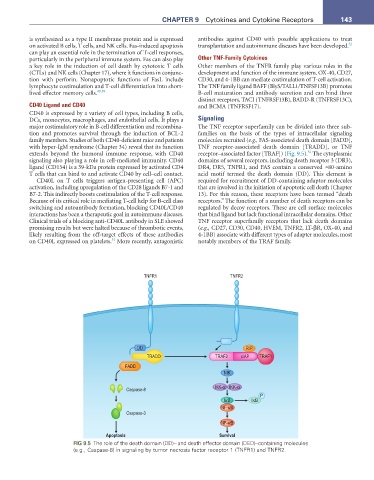
major costimulatory role in B-cell differentiation and recombina- The TNF receptor superfamily can be divided into three sub-
tion and promotes survival through the induction of BCL-2 families on the basis of the types of intracellular signaling
family members. Studies of both CD40-deficient mice and patients molecules recruited (e.g., FAS-associated death domain [FADD],
with hyper-IgM syndrome (Chapter 34) reveal that its function TNF receptor-associated death domain [TRADD], or TNF
53
extends beyond the humoral immune response, with CD40 receptor–associated factor [TRAF]) (Fig. 9.5). The cytoplasmic
signaling also playing a role in cell-mediated immunity. CD40 domains of several receptors, including death receptor 3 (DR3),
ligand (CD154) is a 39-kDa protein expressed by activated CD4 DR4, DR5, TNFR1, and FAS contain a conserved ≈80-amino
T cells that can bind to and activate CD40 by cell–cell contact. acid motif termed the death domain (DD). This element is
CD40L on T cells triggers antigen-presenting cell (APC) required for recruitment of DD-containing adaptor molecules
activation, including upregulation of the CD28 ligands B7-1 and that are involved in the initiation of apoptotic cell death (Chapter
B7-2. This indirectly boosts costimulation of the T-cell response. 13). For this reason, these receptors have been termed “death
Because of its critical role in mediating T-cell help for B-cell class receptors.” The function of a number of death receptors can be
switching and autoantibody formation, blocking CD40L/CD40 regulated by decoy receptors. These are cell surface molecules
interactions has been a therapeutic goal in autoimmune diseases. that bind ligand but lack functional intracellular domains. Other
Clinical trials of a blocking anti-CD40L antibody in SLE showed TNF receptor superfamily receptors that lack death domains
promising results but were halted because of thrombotic events, (e.g., CD27, CD30, CD40, HVEM, TNFR2, LT-βR, OX-40, and
likely resulting from the off-target effects of these antibodies 4-1BB) associate with different types of adapter molecules, most
51
on CD40L expressed on platelets. More recently, antagonistic notably members of the TRAF family.
TNFR1 TNFR2
DD RIP
TRADD TRAF2 cIAP TRAF1
FADD
NIK
IKK-α IKK-α
Caspase-8
P
IκB IκB
NF-κB
Caspase-3
NF-κB
Apoptosis Survival
FIG 9.5 The role of the death domain (DD)– and death effector domain (DED)–containing molecules
(e.g., Caspase-8) in signaling by tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and TNFR2.