Page 311 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 311
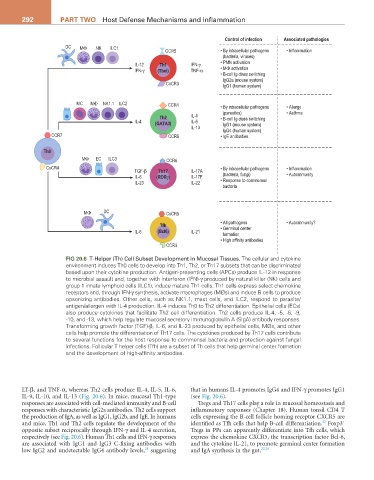
292 ParT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
Control of infection Associated pathologies
DC MΦ NK ILC1
CCR5 • By intracellular pathogens • Inflammation
(bacteria, viruses)
IL-12 Th1 IFN-γ • PMN activation
IFN-γ (Tbet) TNF-α • MΦ activation
• B-cell Ig class switching
IgG2a (mouse system)
CxCR3 IgG1 (human system)
MC MΦ NK1.1 ILC2 CCR4 • By intracellular pathogens • Allergy
(parasites) • Asthma
Th2 IL-4 • B-cell Ig class switching
IL-4 (GATA3) IL-5
IL-13 IgG1 (mouse system)
IgG4 (human system)
CCR7 CCR8 • IgE antibodies
Th0
MΦ EC ILC3 CCR6
CxCR4 • By intracellular pathogens • Inflammation
TGF-β Th17 IL-17A
IL-6 (RORγ) IL-17F (bacteria, fungi) • Autoimmunity
IL-23 IL-22 • Response to commensal
bacteria
MΦ DC CxCR5
• All pathogens • Autoimmunity?
Tfh
IL-6 (Bcl6) IL-21 • Germinal center
formation
• High affinity antibodies
CCR3
FIG 20.6 T-Helper (Th) Cell Subset Development in Mucosal Tissues. The cellular and cytokine
environment induces Th0 cells to develop into Th1, Th2, or Th17 subsets that can be discriminated
based upon their cytokine production. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) produce IL-12 in response
to microbial assault and, together with interferon (IFN)-γ produced by natural killer (NK) cells and
group 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1), induce mature Th1 cells. Th1 cells express select chemokine
receptors and, through IFN-γ synthesis, activate macrophages (MØs) and induce B cells to produce
opsonizing antibodies. Other cells, such as NK1.1, mast cells, and ILC2, respond to parasite/
antigen/allergen with IL-4 production. IL-4 induces Th0 to Th2 differentiation. Epithelial cells (ECs)
also produce cytokines that facilitate Th2 cell differentiation. Th2 cells produce IL-4, -5, -6, -9,
-10, and -13, which help regulate mucosal secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA) antibody responses.
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, IL-6, and IL-23 produced by epithelial cells, MØs, and other
cells help promote the differentiation of Th17 cells. The cytokines produced by Th17 cells contribute
to several functions for the host response to commensal bacteria and protection against fungal
infections. Follicular T helper cells (Tfh) are a subset of Th cells that help germinal center formation
and the development of high-affinity antibodies.
LT-β, and TNF-α, whereas Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, that in humans IL-4 promotes IgG4 and IFN-γ promotes IgG1
IL-9, IL-10, and IL-13 (Fig. 20.6). In mice, mucosal Th1-type (see Fig. 20.6).
responses are associated with cell-mediated immunity and B-cell Tregs and Th17 cells play a role in mucosal homeostasis and
responses with characteristic IgG2a antibodies. Th2 cells support inflammatory responses (Chapter 18). Human tonsil CD4 T
the production of IgA, as well as IgG1, IgG2b, and IgE. In humans cells expressing the B-cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5 are
+
22
and mice, Th1 and Th2 cells regulate the development of the identified as Tfh cells that help B-cell differentiation. Foxp3
opposite subset reciprocally through IFN-γ and IL-4 secretion, Tregs in PPs can apparently differentiate into Tfh cells, which
respectively (see Fig. 20.6). Human Th1 cells and IFN-γ responses express the chemokine CXCR5, the transcription factor Bcl-6,
are associated with IgG1 and IgG3 C-fixing antibodies with and the cytokine IL-21, to promote germinal center formation
21
low IgG2 and undetectable IgG4 antibody levels, suggesting and IgA synthesis in the gut. 23,24