Page 307 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 307
288 ParT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
TABLE 20.1 Major T-Cell Subpopulations
associated with Murine Peyer Patches
Percentage of
T-Cell Phenotype Total T Cells
CD3 αβ T-cell receptor (TCR) + 95–97
+
CD3 γδ TCR + 3–5
+
+
+
CD3 , CD4 (precursors of T-helper [Th] cells) 65–70
CD3 , CD8 (precursors of cytotoxic T 30–35
+
+
lymphocytes [CTLs])
Hi
Naïve (CD45RB ) 50–60
Memory (CD45RB , CD45RO ) 40–50
Lo
Hi
Blasts (in cell cycle) 30–35
have mesenteric and cervical lymph nodes but lack peripheral
lymph nodes and PPs. Tumor necrosis factor–receptor I
−/−
(TNF-RI) mice lack or display abnormal PP structures, whereas
−/−
TNF-α mice exhibit normal patches.
Nasal-Associated Lymphoid Tissues
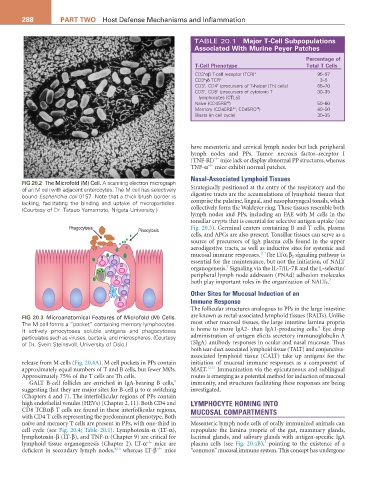
FIG 20.2 The Microfold (M) Cell. A scanning electron micrograph
of an M cell with adjacent enterocytes. The M cell has selectively Strategically positioned at the entry of the respiratory and the
bound Escherichia coli 0157. Note that a thick brush border is digestive tracts are the accumulations of lymphoid tissues that
lacking, facilitating the binding and uptake of microparticles. comprise the palatine, lingual, and nasopharyngeal tonsils, which
(Courtesy of Dr. Tatsuo Yamamoto, Niigata University.) collectively form the Waldeyer ring. These tissues resemble both
lymph nodes and PPs, including an FAE with M cells in the
tonsillar crypts that is essential for selective antigen uptake (see
Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Fig. 20.3). Germinal centers containing B and T cells, plasma
cells, and APCs are also present. Tonsillar tissues can serve as a
source of precursors of IgA plasma cells found in the upper
aerodigestive tracts, as well as inductive sites for systemic and
11
B T mucosal immune responses. The LTα 1 β 2 signaling pathway is
essential for the maintenance, but not the initiation, of NALT
B 7
T organogenesis. Signaling via the IL-7/IL-7R and the L-selectin/
B T peripheral lymph node addressin (PNAd) adhesion molecules
both play important roles in the organization of NALTs. 7
T
Other Sites for Mucosal Induction of an
B Immune Response
The follicular structures analogous to PPs in the large intestine
FIG 20.3 Microanatomical Features of Microfold (M) Cells. are known as rectal-associated lymphoid tissues (RALTs). Unlike
The M cell forms a “pocket” containing memory lymphocytes. most other mucosal tissues, the large intestine lamina propria
8
It actively pinocytoses soluble antigens and phagocytoses is home to more IgA2- than IgA1-producing cells. Eye drop
particulates such as viruses, bacteria, and microspheres. (Courtesy administration of antigen elicits secretory immunoglobulin A
of Dr. Svein Steinsvoll, University of Oslo.) (SIgA) antibody responses in ocular and nasal mucosae. Thus
both tear-duct associated lymphoid tissue (TALT) and conjunctiva-
associated lymphoid tissue (CALT) take up antigens for the
release from M cells (Fig. 20.4A). M cell pockets in PPs contain initiation of mucosal immune responses as a component of
approximately equal numbers of T and B cells, but fewer MØs. MALT. 12,13 Immunization via the epicutaneous and sublingual
Approximately 75% of the T cells are Th cells. routes is emerging as a potential method for induction of mucosal
8
GALT B-cell follicles are enriched in IgA-bearing B cells, immunity, and structures facilitating these responses are being
suggesting that they are major sites for B-cell µ to α switching investigated.
(Chapters 4 and 7). The interfollicular regions of PPs contain
high endothelial venules (HEVs) (Chapter 2, 11). Both CD4 and LYMPHOCYTE HOMING INTO
CD8 TCRαβ T cells are found in these interfollicular regions, MUCOSAL COMPARTMENTS
with CD4 T cells representing the predominant phenotype. Both
naïve and memory T cells are present in PPs, with one-third in Mesenteric lymph node cells of orally immunized animals can
cell cycle (see Fig. 20.4; Table 20.1). Lymphotoxin-α (LT-α), repopulate the lamina propria of the gut, mammary glands,
lymphotoxin-β (LT-β), and TNF-α (Chapter 9) are critical for lacrimal glands, and salivary glands with antigen-specific IgA
−/−
1
lymphoid tissue organogenesis (Chapter 2). LT-α mice are plasma cells (see Fig. 20.4B), pointing to the existence of a
−/−
deficient in secondary lymph nodes, 9,10 whereas LT-β mice “common” mucosal immune system. This concept has undergone