Page 370 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 370
350 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
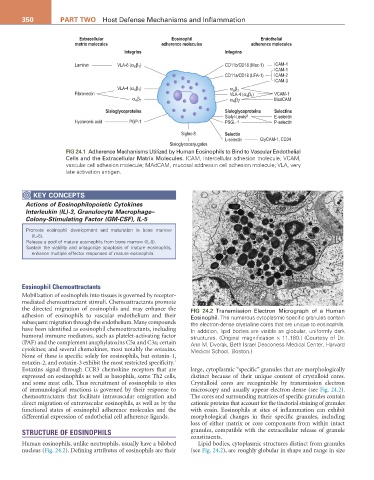
Extracellular Eosinophil Endothelial
matrix molecules adherence molecules adherence molecules
Integrins Integrins
β )
Laminin VLA-6 (α 6 1 CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) ICAM-1
ICAM-1
CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) ICAM-2
ICAM-3
β
VLA-4 (α β ) α d 2
4 1
Fibronectin VLA-4 (α β ) VCAM-1
4 1
β
4 7
α 4 7 α β MadCAM
Sialoglycoproteins Sialoglycoproteins Selectins
Sialyl-Lewis X E-selectin
Hyaluronic acid PGP-1 PSGL-1 P-selectin
Siglec-8 Selectin
L-selectin GlyCAM-1, CD34
Sialoglycoconjugates
FIG 24.1 Adherence Mechanisms Utilized by Human Eosinophils to Bind to Vascular Endothelial
Cells and the Extracellular Matrix Molecules. ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; VCAM,
vascular cell adhesion molecule; MAdCAM, mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule; VLA, very
late activation antigen.
KEY CoNCEPtS
Actions of Eosinophilopoietic Cytokines
Interleukin (IL)-3, Granulocyte Macrophage–
Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF), IL-5
Promote eosinophil development and maturation in bone marrow
(IL-5).
Release a pool of mature eosinophils from bone marrow (IL-5).
Sustain the viability and antagonize apoptosis of mature eosinophils,
enhance multiple effector responses of mature eosinophils.
Eosinophil Chemoattractants
Mobilization of eosinophils into tissues is governed by receptor-
mediated chemoattractant stimuli. Chemoattractants promote
the directed migration of eosinophils and may enhance the FIG 24.2 Transmission Electron Micrograph of a Human
adhesion of eosinophils to vascular endothelium and their Eosinophil. The numerous cytoplasmic specific granules contain
subsequent migration through the endothelium. Many compounds the electron-dense crystalline cores that are unique to eosinophils.
have been identified as eosinophil chemoattractants, including In addition, lipid bodies are visible as globular, uniformly dark
humoral immune mediators, such as platelet-activating factor structures. (Original magnification × 11,180.) (Courtesy of Dr.
(PAF) and the complement anaphylatoxins C5a and C3a; certain Ann M. Dvorak, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard
cytokines; and several chemokines, most notably the eotaxins. Medical School, Boston.)
None of these is specific solely for eosinophils, but eotaxin-1,
1
eotaxin-2, and eotaxin-3 exhibit the most restricted specificity.
Eotaxins signal through CCR3 chemokine receptors that are large, cytoplasmic “specific” granules that are morphologically
expressed on eosinophils as well as basophils, some Th2 cells, distinct because of their unique content of crystalloid cores.
and some mast cells. Thus recruitment of eosinophils to sites Crystalloid cores are recognizable by transmission electron
of immunological reactions is governed by their response to microscopy and usually appear electron dense (see Fig. 24.2).
chemoattractants that facilitate intravascular emigration and The cores and surrounding matrices of specific granules contain
direct migration of extravascular eosinophils, as well as by the cationic proteins that account for the tinctorial staining of granules
functional states of eosinophil adherence molecules and the with eosin. Eosinophils at sites of inflammation can exhibit
differential expression of endothelial cell adherence ligands. morphological changes in their specific granules, including
loss of either matrix or core components from within intact
STRUCTURE OF EOSINOPHILS granules, compatible with the extracellular release of granule
constituents.
Human eosinophils, unlike neutrophils, usually have a bilobed Lipid bodies, cytoplasmic structures distinct from granules
nucleus (Fig. 24.2). Defining attributes of eosinophils are their (see Fig. 24.2), are roughly globular in shape and range in size