Page 405 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 405
386 PARt tHREE Host Defenses to Infectious Agents
Unconventional T cells γδ IL-10
TGF-β
IL-1β
Phospholigand IL-6 IL-6
T P T reg IL-23 IL-17
IL-21
P IL-22
IL-27
T h17
Lipid TGF-β
Metabolite CD1, MR RA
CD8 Cytosol TGF-β IFN-γ
Conventional T cells Peptide MHC I Golgi 1 2 IL-21 (human) T h1 LT/TNF-α
IL-6 (mouse)
IL-2
GM-CSF
IL-12
IL-18
3 IFN-γ IL-4
IL-4
CD4 MHC II IL-25
Phagosome IL-33 T
h2
IL-4
IL-5
IL-13
IL-25
MHC B7.1
ICOS-L (B7.h) B7.2
B7.1 PD-L
B7.2
ICOS CD28 TCR PD-1 CTLA-4
T cell
Activation Inhibition
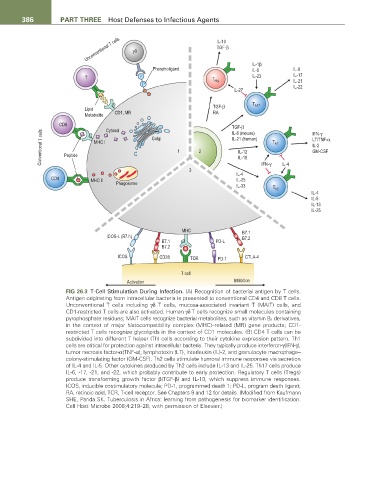
FIG 26.3 T-Cell Stimulation During Infection. (A) Recognition of bacterial antigen by T cells.
Antigen originating from intracellular bacteria is presented to conventional CD4 and CD8 T cells.
Unconventional T cells including γδ T cells, mucosa-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, and
CD1-restricted T cells are also activated. Human γδ T cells recognize small molecules containing
pyrophosphate residues; MAIT cells recognize bacterial metabolites, such as vitamin B 2 derivatives,
in the context of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)–related (MR) gene products; CD1-
restricted T cells recognize glycolipids in the context of CD1 molecules. (B) CD4 T cells can be
subdivided into different T helper (Th) cells according to their cytokine expression pattern. Th1
cells are critical for protection against intracellular bacteria. They typically produce interferon-γ(IFN-γ),
tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), lymphotoxin (LT), interleukin (IL)-2, and granulocyte macrophage–
colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Th2 cells stimulate humoral immune responses via secretion
of IL-4 and IL-5. Other cytokines produced by Th2 cells include IL-13 and IL-25. Th17 cells produce
IL-6, -17, -21, and -22, which probably contribute to early protection. Regulatory T cells (Tregs)
produce transforming growth factor β(TGF-β) and IL-10, which suppress immune responses.
ICOS, inducible costimulatory molecule; PD-1, programmed death 1; PD-L, program death ligand;
RA, retinoic acid; TCR, T-cell receptor. See Chapters 9 and 12 for details. (Modified from Kaufmann
SHE, Parida SK. Tuberculosis in Africa: learning from pathogenesis for biomarker identification.
Cell Host Microbe 2008;4:219–28, with permission of Elsevier.)