Page 669 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 669
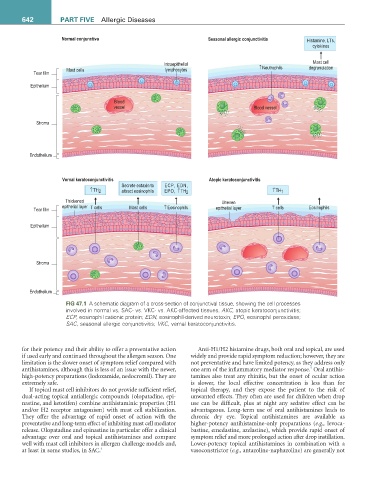
642 ParT fivE Allergic Diseases
Normal conjunctiva Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis Histamine, LTs,
cytokines
Intraepithelial Mast cell
Mast cells lymphocytes ↑Neutrophils degranulation
Tear film
Epithelium
Blood
vessel Blood vessel
Stroma
Endothelium
Vernal keratoconjunctivitis Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
Secrete eotaxin to ECP, EDN,
↑TH 2 attract eosinophils EPO, ↑ TH 2 ↑TH 1
Thickened Uneven
epithelial layer T cells Mast cells ↑Eosinophils T cells Eosinophils
Tear film epithelial layer
Epithelium
Stroma
Endothelium
fiG 47.1 A schematic diagram of a cross-section of conjunctival tissue, showing the cell processes
involved in normal vs. SAC- vs. VKC- vs. AKC-affected tissues. AKC, atopic keratoconjunctivitis;
ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; EPO, eosinophil peroxidase;
SAC, seasonal allergic conjunctivitis; VKC, vernal keratoconjunctivitis.
for their potency and their ability to offer a preventative action Anti-H1/H2 histamine drugs, both oral and topical, are used
if used early and continued throughout the allergen season. One widely and provide rapid symptom reduction; however, they are
limitation is the slower onset of symptom relief compared with not preventative and have limited potency, as they address only
5
antihistamines, although this is less of an issue with the newer, one arm of the inflammatory mediator response. Oral antihis-
high-potency preparations (lodoxamide, nedocromil). They are tamines also treat any rhinitis, but the onset of ocular action
extremely safe. is slower, the local effective concentration is less than for
If topical mast cell inhibitors do not provide sufficient relief, topical therapy, and they expose the patient to the risk of
dual-acting topical antiallergic compounds (olopatadine, epi- unwanted effects. They often are used for children when drop
nastine, and ketotifen) combine antihistaminic properties (H1 use can be difficult, plus at night any sedative effect can be
and/or H2 receptor antagonism) with mast cell stabilization. advantageous. Long-term use of oral antihistamines leads to
They offer the advantage of rapid onset of action with the chronic dry eye. Topical antihistamines are available as
preventative and long-term effect of inhibiting mast cell mediator higher-potency antihistamine-only preparations (e.g., levoca-
release. Olopatadine and epinastine in particular offer a clinical bastine, emedastine, azelastine), which provide rapid onset of
advantage over oral and topical antihistamines and compare symptom relief and more prolonged action after drop instillation.
well with mast cell inhibitors in allergen challenge models and, Lower-potency topical antihistamines in combination with a
at least in some studies, in SAC. 4 vasoconstrictor (e.g., antazoline-naphazoline) are generally not