Page 740 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 740
712 Part SIX Systemic Immune Diseases
Acute Phasic Chronic
Counter-regulatory networks TLR inhibitors IL-4, IL-10, TGFβ, IL-13, L-11, IL-2 IL-1Ra, sTNF-R, IL-10, IL-18bp, OPG, adiponectin
Tissue damage, IL-12, IL-23 IL-2, deficiency
LTβR
TLR ligands IL-15, IL-18 +IL-6
TLR IFNs + TGFβ CD28 null
survival T reg TCRζ dim
factors IL-10
IL-2 BlyS T reg Adipo
IL-1, TNF, IL-6, IL-22, TCR April
PGE , bFGF, PDGF, EGF, CXCL5/8/9/10/12/13, TGFβ T eff
2
VEGF, TGFβ COX, LOX CCL2/3/5/20/21, CX3CL1 CD28 IL-10
CD40 Mφ Adipokines
T eff B IL-17+
CD40L RANKL Oncostatin M
TNF TNF MMP
Transmigration of monocytes M-CSF IL-1 ADAM
PMN, mast cells, and NK cells OPG PGE 2 ADAM-TS
Early Late IL-6 IL-1, IL-6, TNF
IL-2, IL-4, IFNγ IL-10 IL-15, IL-32
activation of endothelium, IL-13, TGFβ IL-17 chemokines GM-CSF
↑ adhesion molecules IL-15 RANTES AutoAb oncostatin M
GM-CSF TNF M-CSF, VEGF Osteoclasts Chondrocyte
LTα/β Chemokines
IL-10 adipokines features of inflammation and repair
HMGB1 tissue response
IL-10
Initiation Antigen Mode Inflammation Mode
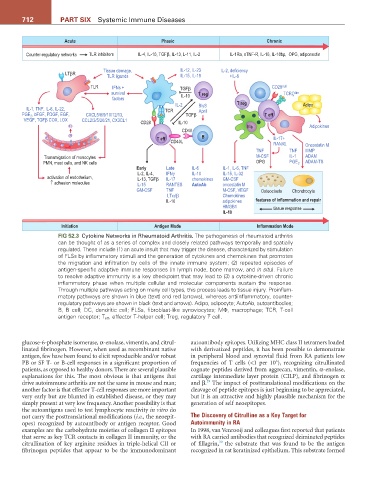
FIG 52.3 Cytokine Networks in Rheumatoid Arthritis. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
can be thought of as a series of complex and closely related pathways temporally and spatially
regulated. These include (1) an acute insult that may trigger the disease, characterized by stimulation
of FLSs by inflammatory stimuli and the generation of cytokines and chemokines that promotes
the migration and infiltration by cells of the innate immune system; (2) repeated episodes of
antigen-specific adaptive immune responses (in lymph node, bone marrow, and in situ). Failure
to resolve adaptive immunity is a key checkpoint that may lead to (3) a cytokine-driven chronic
inflammatory phase when multiple cellular and molecular components sustain the response.
Through multiple pathways acting on many cell types, this process leads to tissue injury. Proinflam-
matory pathways are shown in blue (text) and red (arrows), whereas antiinflammatory, counter-
regulatory pathways are shown in black (text and arrows). Adipo, adipocyte; AutoAb, autoantibodies;
B, B cell; DC, dendritic cell; FLSs, fibroblast-like synoviocytes; MΦ, macrophage; TCR, T-cell
antigen receptor; T eff , effector T-helper cell; Treg, regulatory T cell.
glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, α-enolase, vimentin, and citrul- autoantibody epitopes. Utilizing MHC class II tetramers loaded
linated fibrinogen. However, when used as recombinant native with derivatized peptides, it has been possible to demonstrate
antigen, few have been found to elicit reproducible and/or robust in peripheral blood and synovial fluid from RA patients low
6
PB or SF T- or B-cell responses in a significant proportion of frequencies of T cells (<1 per 10 ), recognizing citrullinated
patients, as opposed to healthy donors. There are several plausible cognate peptides derived from aggrecan, vimentin, α-enolase,
explanations for this. The most obvious is that antigens that cartilage intermediate layer protein (CILP), and fibrinogen α
29
drive autoimmune arthritis are not the same in mouse and man; and β. The impact of posttranslational modifications on the
another factor is that effector T-cell responses are more important cleavage of peptide epitopes is just beginning to be appreciated,
very early but are blunted in established disease, or they may but it is an attractive and highly plausible mechanism for the
simply present at very low frequency. Another possibility is that generation of self neoepitopes.
the autoantigens used to test lymphocyte reactivity in vitro do
not carry the posttranslational modifications (i.e., the neoepit- The Discovery of Citrulline as a Key Target for
opes) recognized by autoantibody or antigen receptor. Good Autoimmunity in RA
examples are the carbohydrate moieties of collagen II epitopes In 1998, van Venrooij and colleagues first reported that patients
that serve as key TCR contacts in collagen II immunity, or the with RA carried antibodies that recognized deiminated peptides
30
citrullination of key arginine residues in triple-helical CII or of fillagrin, the substrate that was found to be the antigen
fibrinogen peptides that appear to be the immunodominant recognized in rat keratinized epithelium. This substrate formed