Page 888 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 888
CHaPtEr 63 Bullous Diseases of the Skin and Mucous Membranes 859
and serum from patients with PF contains IgG antibodies, which IgA deposition mainly in the upper epidermis. The IEN subtype
bind to normal stratified squamous epithelium. Although the is characterized by pustules deeper in the epidermis, with intercel-
immunofluorescence patterns of PF and PV are virtually identical, lular IgA deposition throughout the epidermis. Circulating IgA
the antigenic targets of these autoantibodies are different (see antibodies to intraepidermal structures are present in ~50% of
below). cases. Desmocollin 1 (a desmosomal cadherin) has been identified
as a target autoantigen in most cases with the SPD phenotype.
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus In some IEN-type cases, desmoglein-1 (Dsg1) and Dsg3 are
Anhalt described a series of patients with severe oral erosions autoantibody targets, but in most IEN cases the autoantigen
and polymorphic skin lesions suggestive of coexistent PV and remains unknown. Patients of both types commonly present
8
erythema multiforme. All these patients had associated malignan- with flat pustules, often on a slightly erythematous base, which
cies, which were mostly lymphoreticular, including lymphoma, tend to coalesce to form annular patterns. IgA pemphigus mainly
chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and thymoma. The histological affects the trunk, axillae, and groin but not the mucosa. Histology
features of the skin lesions in these patients resembled PV, of lesional skin reveals subcorneal or intraepidermal blisters,
including suprabasilar blister formation, but with additional with acantholytic cells and a neutrophilic infiltrate. 9
keratinocyte cell necrosis as found in erythema multiforme. Skin
biopsies from these patients revealed IgG bound to keratinocyte Pathogenesis
cell surfaces, and granular–linear deposits of IgG and C3 at the The antigenic targets in pemphigus have been identified as
basement membrane. Serum contained circulating IgG antibodies, components of desmosomes, key structures involved in kerati-
which bound to normal keratinocyte cell surfaces of squamous nocyte adhesion (Table 63.1). IgG from patients with PF binds
epithelium. Although initial reports suggested that these antibodies to a 160-kilodalton (kDa) glycoprotein, Dsg1. IgG from patients
bound to stratified and nonstratified squamous epithelium, this with PV with only mucosal lesions binds predominantly to Dsg3,
is not always the case. The antigenic targets of these antibodies an epithelial cadherin with significant homology to Dsg1. Patients
were also distinct from both PV and PF (see below). with PV who have both skin and mucosal diseases have IgG
10
antibodies directed against both Dsg1 and Dsg3. In paraneo-
IgA Pemphigus plastic pemphigus, IgG antibodies bind to members of the plakin
IgA pemphigus presents as an annular, vesiculopustular eruption family of desmosomal/hemidesmosomal proteins (desmoplakin
characterized by intraepidermal blisters with numerous neutro- I, desmoplakin II, envoplakin, periplakin, plectin, and BPAG1)
phils. Intercellular deposits of IgA are present. This entity is also as well as to Dsg1 and Dsg3. 8
known as intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis, intercellular It has been clearly shown that these autoantibodies are
IgA vesiculopustular dermatosis, and intercellular IgA dermatosis. 9 pathogenic. Neonatal mice injected with IgG from patients with
IgA pemphigus is a distinct clinical entity with two subtypes PV, PF, or paraneoplastic pemphigus develop cutaneous blisters,
that differ in histology and epidermal IgA deposition patterns: histological changes, and immunofluorescence findings consistent
subcorneal pustular dermatosis (SPD) and intraepidermal with pemphigus. 8,11
neutrophilic IgA dermatosis (IEN). Biopsy specimens from SPD The causes of the autoimmune response remain unknown.
show subcorneal acantholysis and pustules, with intercellular An increased frequency of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR4
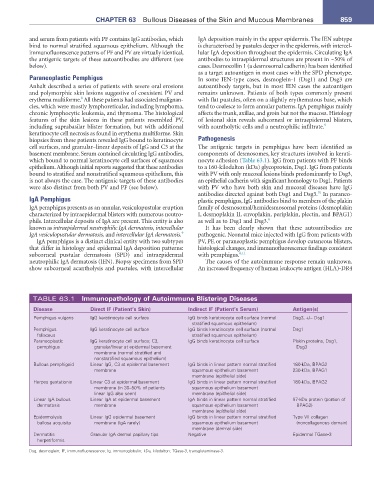
TABLE 63.1 Immunopathology of autoimmune Blistering Diseases
Disease Direct IF (Patient’s Skin) Indirect IF (Patient’s Serum) antigen(s)
Pemphigus vulgaris IgG keratinocyte cell surface IgG binds keratinocyte cell surface (normal Dsg3, +/− Dsg1
stratified squamous epithelium)
Pemphigus IgG keratinocyte cell surface IgG binds keratinocyte cell surface (normal Dsg1
foliaceus stratified squamous epithelium)
Paraneoplastic IgG keratinocyte cell surface; C3, IgG binds keratinocyte cell surface Plakin proteins, Dsg1,
pemphigus granular/linear at epidermal basement Dsg3
membrane (normal stratified and
nonstratified squamous epithelium)
Bullous pemphigoid Linear IgG, C3 at epidermal basement IgG binds in linear pattern normal stratified 180-kDa, BPAG2
membrane squamous epithelium basement 230-kDa, BPAG1
membrane (epithelial side)
Herpes gestationis Linear C3 at epidermal basement IgG binds in linear pattern normal stratified 180-kDa, BPAG2
membrane (in 30–50% of patients squamous epithelium basement
linear IgG also seen) membrane (epithelial side)
Linear IgA bullous Linear IgA at epidermal basement IgA binds in linear pattern normal stratified 97-kDa protein (portion of
dermatosis membrane squamous epithelium basement BPAG2)
membrane (epithelial side)
Epidermolysis Linear IgG epidermal basement IgG binds in linear pattern normal stratified Type VII collagen
bullosa acquisita membrane (IgA rarely) squamous epithelium basement (noncollagenous domain)
membrane (dermal side)
Dermatitis Granular IgA dermal papillary tips Negative Epidermal TGase-3
herpetiformis
Dsg, desmoglein; IF, immunofluorescence; Ig, immunoglobulin; kDa, kilodalton; TGase-3, transglutaminase-3.