Page 533 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 533
CHAPTER 26 ■ Disorders of Primary Hemostasis and Thrombosis Vasculature and Platelets 517
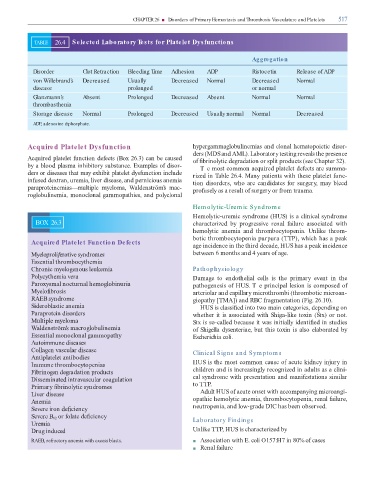
TABLE 26.4 Selected Laboratory Tests for Platelet Dysfunctions
Aggregation
Disorder Clot Retraction Bleeding Time Adhesion ADP Ristocetin Release of ADP
von Willebrand’s Decreased Usually Decreased Normal Decreased Normal
disease prolonged or normal
Glanzmann’s Absent Prolonged Decreased Absent Normal Normal
thrombasthenia
Storage disease Normal Prolonged Decreased Usually normal Normal Decreased
ADP, adenosine diphosphate.
Acquired Platelet Dysfunction hy erga ag obu ine ias an c ona he ato oietic isor-
ers (MDS an AML). Laboratory testing revea s the resence
Acquire ate et unction e ects (Box 26.3) can be cause o brino ytic egra ation or s it ro ucts (see Cha ter 32).
by a b oo as a inhibitory substance. Exa es o isor- T e ost co on acquire ate et e ects are su a-
ers or iseases that ay exhibit ate et ys unction inc u e rize in ab e 26.4. Many atients with these ate et unc-
in use extran, ure ia, iver isease, an ernicious ane ia tion isor ers, who are can i ates or surgery, ay b ee
ara roteine ias— u ti e ye o a, Wa enströ ’s ac- ro use y as a resu t o surgery or ro trau a.
rog obu ine ia, onoc ona ga o athies, an o yc ona
Hem olytic-Urem ic Syndrom e
He o ytic-ure ic syn ro e (HUS) is a c inica syn ro e
BOX 26.3 characterize by rogressive rena ai ure associate with
he o ytic ane ia an thro bocyto enia. Un ike thro -
botic thro bocyto enia ur ura ( P), which has a eak
Acquired Platelet Function Defects
age inci ence in the thir eca e, HUS has a eak inci ence
Myeloproli erative syndromes between 6 onths an 4 years o age.
Essentia thro bocythe ia
Chronic ye ogenous euke ia Pathophysiology
Po ycythe ia vera Da age to en othe ia ce s is the ri ary event in the
Paroxys a nocturna he og obinuria athogenesis o HUS. T e rinci a esion is co ose o
Mye o brosis arterio ar an ca i ary icrothro bi (thro botic icroan-
RAEB syn ro e gio athy [ MA]) an RBC rag entation (Fig. 26.10).
Si erob astic ane ia HUS is c assi e into two ain categories, e en ing on
Paraprotein disorders whether it is associate with Shiga- ike toxin (Stx) or not.
Mu ti e ye o a Stx is so-ca e because it was initia y i enti e in stu ies
Wa enströ ’s acrog obu ine ia o Shigella dysenteriae, but this toxin is a so e aborate by
Essentia onoc ona ga o athy Escherichia coli.
Autoimmune diseases
Co agen vascu ar isease Clinical Signs and Sym ptom s
Anti ate et antibo ies
I une thro bocyto enias HUS is the ost co on cause o acute ki ney injury in
Fibrinogen degradation products chi ren an is increasing y recognize in a u ts as a c ini-
Disse inate intravascu ar coagu ation ca syn ro e with resentation an ani estations si i ar
Pri ary brino ytic syn ro es to P.
Liver isease A u t HUS o acute onset with acco anying icroangi-
Anemia o athic he o ytic ane ia, thro bocyto enia, rena ai ure,
Severe iron e ciency neutro enia, an ow-gra e DIC has been observe .
Severe B or o ate e ciency Laboratory Findings
12
Uremia
Drug induced Un ike P, HUS is characterize by
RAEB, re ractory ane ia with excess b asts. ■ Association with E. coli O157:H7 in 80% o cases
■ Rena ai ure