Page 736 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 736
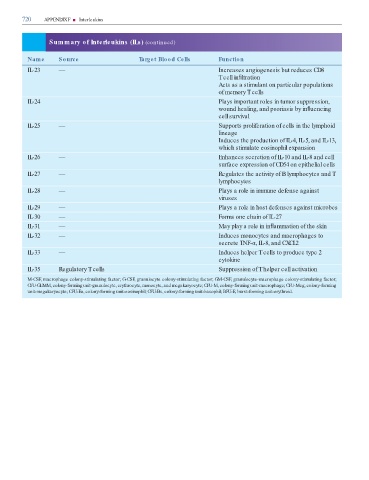
720 APPENDIX F ■ Interleukins
Summary of Interleukins (ILs) (continued)
Name Source Target Blood Cells Function
IL-23 — Increases angiogenesis but reduces CD8
T cell in ltration
Acts as a stimulant on particular populations
of memory T cells
IL-24 — Plays important roles in tumor suppression,
wound healing, and psoriasis by in uencing
cell survival
IL-25 — Supports proliferation of cells in the lymphoid
lineage
Induces the production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13,
which stimulate eosinophil expansion
IL-26 — Enhances secretion of IL-10 and IL-8 and cell
surface expression of CD54 on epithelial cells
IL-27 — Regulates the activity of B lymphocytes and T
lymphocytes
IL-28 — Plays a role in immune defense against
viruses
IL-29 — Plays a role in host defenses against microbes
IL-30 — Forms one chain of IL-27
IL-31 — May play a role in in ammation of the skin
IL-32 — Induces monocytes and macrophages to
secrete TNF-α, IL-8, and CXCL2
IL-33 — Induces helper T cells to produce type 2
cytokine
IL-35 Regulatory T cells Suppression of T helper cell activation
M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor;
CFU-GEMM, colony-forming unit-granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, and megakaryocyte; CFU-M, colony-forming unit-macrophage; CFU-Meg, colony-forming
unit-megakaryocyte; CFU-Eo, colony-forming unit-eosinophil; CFU-Bs, colony-forming unit-basophil; BFU-E, burst-forming unit-erythroid.